The kinetic energy KE of an object of mass m moving with velocity v is defined as
Question:
The kinetic energy KE of an object of mass m moving with velocity v is defined as KE = 1/2 mv2. If a force f(x) acts on the object, moving it along the x-axis from x1 to x2, the Work-Energy Theorem states that the net work done is equal to the change in kinetic energy: 1/2 mv22 – 1/2 mv21, where ν1 is the velocity at x1 and ν2 is the velocity at x2.
Suppose that when launching an 800-kg roller coaster car an electromagnetic propulsion system exerts a force of (5.7x2 + 1.5x) newtons on the car at a distance x meters along the track. Use Exercise 31 to find the speed of the car when it has traveled 60 meters.
Data From Exercise 31:
Let x = s(t) be the position function of the object at time t and ν(t), a(t) the velocity and acceleration functions. Prove the Work-Energy Theorem by first using the Substitution Rule for Definite Integrals to show that
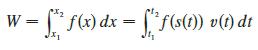
Then use Newton’s Second Law of Motion (force − mass 3 acceleration) and the substitution u = ν(t) to evaluate the integral.
Step by Step Answer:

Calculus Early Transcendentals
ISBN: 9781337613927
9th Edition
Authors: James Stewart, Daniel K. Clegg, Saleem Watson, Lothar Redlin





