A heat exchanger is a device in which heat flows between two fluid streams brought into thermal
Question:
A heat exchanger is a device in which heat flows between two fluid streams brought into thermal contact through a barrier, such as a pipe wall. Heat exchangers can be operated in either the cocurrent (both fluid streams flowing in the same direction) or countercurrent (streams flowing in opposite direction) configuration; schematic diagrams are given here.
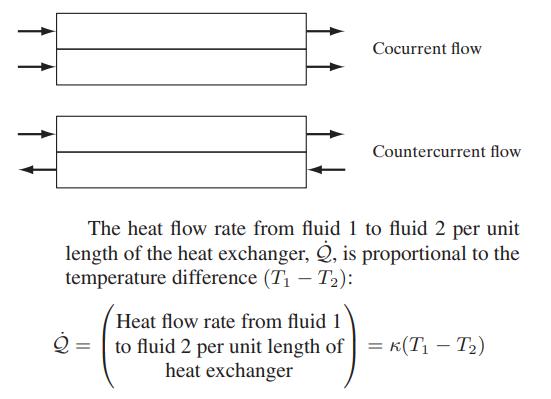
where κ is a constant of proportionality with units of J/(m s K). The fluids in the two streams are the same and their flow rates are equal. The initial and final temperatures of stream 1 will be 35°C and 15°C, respectively, and those for stream 2 will be −15°C and 5°C.
a. Write the balance equations for each fluid stream in a portion of the heat exchanger of length dL and obtain differential equations by letting dL → 0
b. Integrate the energy balance equations over the length of the exchanger to obtain expressions for the temperature of each stream at any point in the exchanger for each flow configuration. Also compute the length of the exchanger, in units of L0 = ṀCP/2κ (where Ṁ is the mass flow rate of either stream), needed to accomplish the desired heat transfer.
c. Write an expression for the change of entropy of stream 1 with distance for any point in the exchanger.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Biochemical And Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780470504796
5th Edition
Authors: Stanley I. Sandler