If 1 mole of a gas in a constant-volume system is heated, and both the heat flow
Question:
If 1 mole of a gas in a constant-volume system is heated, and both the heat flow and the gas temperature are measured as a function of time, the constant volume heat capacity can be computed from
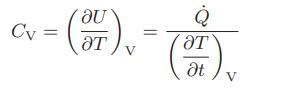
This equation can also be used to calculate the effective heat capacity CV,eff of a gas that is undergoing a chemical reaction, such as nitrogen tetroxide dissociating to form nitrogen dioxide,
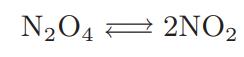
In such cases CV,eff can be much larger than the heat capacity of the nonreacting gas.
a. Develop an expression for CV,eff for dissociating nitrogen tetroxide, and comment on the dependence of CV,eff on the internal energy change on chemical reaction.
b. Compute the molar effective heat capacity CV,eff as a function of temperature for nitrogen tetroxide over the temperature range of 300 to 600 K, if pure N2O4 is loaded into a constant-volume reactor at 300 K at a pressure of 1.013 bar.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Biochemical And Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780470504796
5th Edition
Authors: Stanley I. Sandler