Question: A nonvolatile pharmaceutical is dissolved in a solution that is (90.0 mathrm{~mol} %) acetone and (10.0 mathrm{~mol} %) ethanol. A constant volume batch distillation is
A nonvolatile pharmaceutical is dissolved in a solution that is \(90.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) acetone and \(10.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) ethanol. A constant volume batch distillation is used to switch the solvent to \(20.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) acetone and \(80.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) ethanol without diluting the concentration of solute. The charge to the still pot is \(\mathrm{W}=1.5 \mathrm{kmol}\). VLE data are in Problem 4.D7. What are the values of the amount (kmol) of pure solvent ethanol added, the kmol of acetone that are evaporated, the \(\mathrm{kmol}\) of ethanol evaporated, and the average mole fraction of acetone in the distillate?
Problem 4.D7.
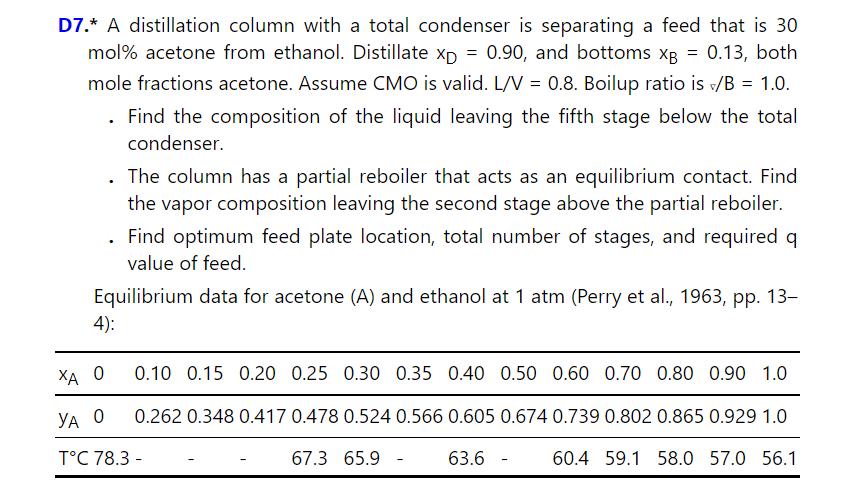
D7.* A distillation column with a total condenser is separating a feed that is 30 mol% acetone from ethanol. Distillate xD = 0.90, and bottoms XB = 0.13, both mole fractions acetone. Assume CMO is valid. L/V = 0.8. Boilup ratio is
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


