A stripping column with a partial reboiler is processing (100.0 mathrm{kmol} / mathrm{h}) of a saturated liquid
Question:
A stripping column with a partial reboiler is processing \(100.0 \mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\) of a saturated liquid feed at \(300.0 \mathrm{kPa}\). The feed is \(25.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-butane, 35.0 \(\mathrm{mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-pentane, and \(40.0 \mathrm{~mol} \% \mathrm{n}\)-hexane. The column is at \(300.0 \mathrm{kPa}\), and CMO is valid. Bottoms flow rate is \(20.0 \mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\). The fractional recovery of \(\mathrm{n}-\) pentane in distillate is \(95.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\). Assume all \(\mathrm{n}\)-butane is in distillate, and calculate the distillate flow rate and distillate and bottoms compositions. Determine the temperature, vapor mole fractions, and liquid mole fractions leaving each stage. Manually increment the stage location (see this chapter's appendix). Determine the total number of stages required. Use Eq. (2-28) for equilibrium data. Do NOT converge on a better guess for n-butane distribution. Note: The spreadsheet in Figure 5-A1 and Table 5-A2 can be used if preliminary calculations are changed,
Equation (2-28)
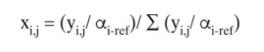
Figure 5-A1
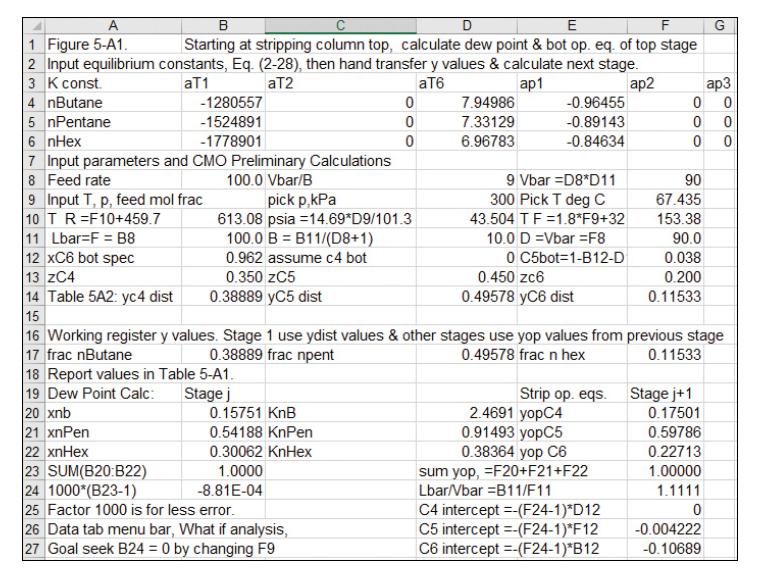
Table 5-A2
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





