Continuous steam distillation is used to recover benzene from (100.0 mathrm{~kg} / mathrm{h}) of a mixture that
Question:
Continuous steam distillation is used to recover benzene from \(100.0 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{h}\) of a mixture that is \(20.0 \mathrm{wt} \%\) benzene, and the remainder consists of nonvolatile organics and solids of unknown composition. The feed is preheated to the still pot temperature, which operates at \(1.0 \mathrm{~atm}\) pressure. There is liquid water in the pot. Recover \(90.0 \%\) of the benzene in the distillate. Because composition of the nonvolatile organics is not known, we do a simple experiment, and boil the feed mixture with no water present. At \(1.0 \mathrm{~atm}\) pressure, the mixture boils at \(93.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
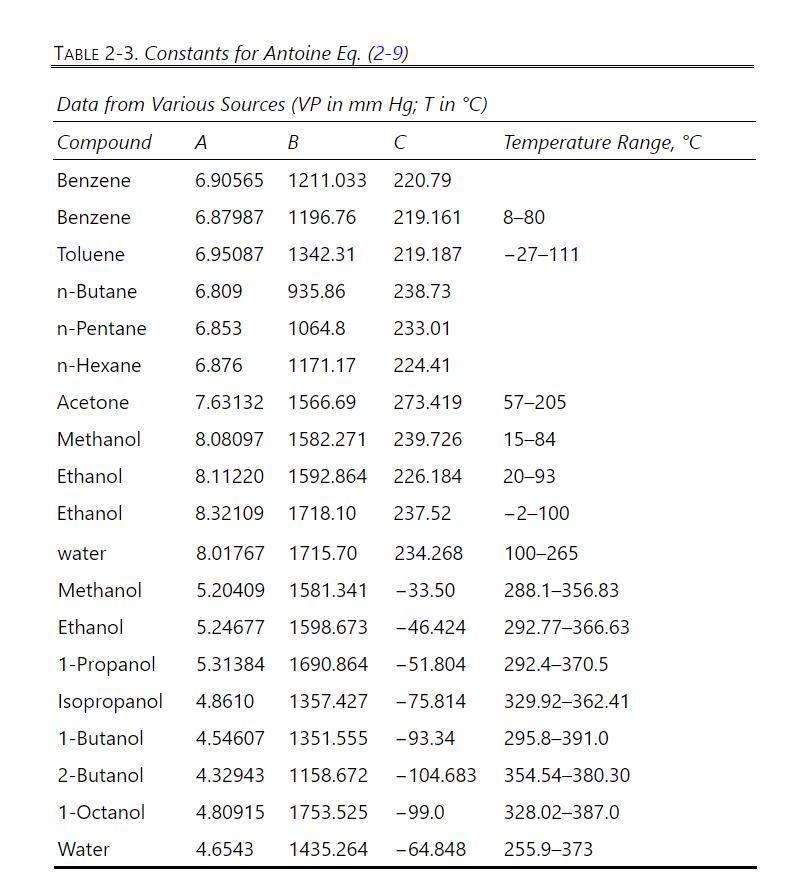
Assumptions and data: Assume that the nonvolatile organics are completely immiscible with water. Although not totally valid (see Example 8-1), assume that benzene and water are completely immiscible. Enthalpy data for benzene and water are available in Tables 2-237 and 2352, respectively, in the seventh edition of Perry's Handbook (Perry and Green, 1997) and in Tables 2-193 and 2-305 in the eighth edition. In the seventh edition, \(H=h_{g}\) and \(h=h_{f}\). In the eighth edition, read the instructions at the bottom of Table 2-193 to find the values you need. Data from these sources are very slightly different. Antoine coefficients to determine vapor pressure for benzene and water are listed in Table 2-3.
Example 8-1
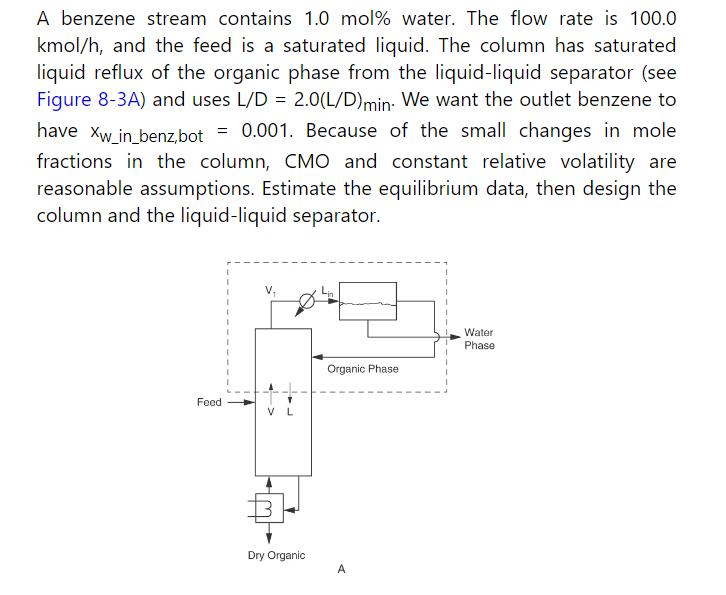
Table 2-3
It is always a good idea to check equations by using known points (e.g., benzene boils at \(80.1^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) when pressure is \(760.0 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\) ).
a. Find the mole fraction of benzene in the feed and the effective average molecular weight of the nonvolatile organics and solids.
b. Find the \(\mathrm{kg} / \mathrm{h}\) and \(\mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\) of benzene in the distillate, the \(\mathrm{kg} / \mathrm{h}\) of total organics in the waste, and the benzene weight fraction and mole fraction in the waste.
c. Find the still pot temperature. A spreadsheet or MATLAB is highly recommended.
d. Find the \(\mathrm{kg} / \mathrm{h}\) and \(\mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\) of water in the distillate.
e. Find the \(\mathrm{kg} / \mathrm{h}\) and \(\mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\) of water in the waste stream.
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





