Your plant has a catalytic system for burning methane in the stoichiometric quantity of air. All of
Question:
Your plant has a catalytic system for burning methane in the stoichiometric quantity of air. All of the methane is converted to carbon dioxide and water vapor. The flue gas is cooled, and the water vapor is condensed out of the gas stream. Assume that air is \(21 \%\) oxygen and \(79 \%\) nitrogen. The gas that will be fed to the permeator consists of carbon dioxide and nitrogen. This gas is sent to a perfectly mixed membrane separator equipped with a silicone rubber membrane with an effective membrane thickness of \(1.0 \mu \mathrm{m}\). The pressure on the permeate side is \(1.02 \mathrm{bar}\), and the membrane unit is operating at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). Choose a basis of \(1.0 \mathrm{kmol}\) methane burned/minute. Data are in Table 19-2. Assume ideal gas.
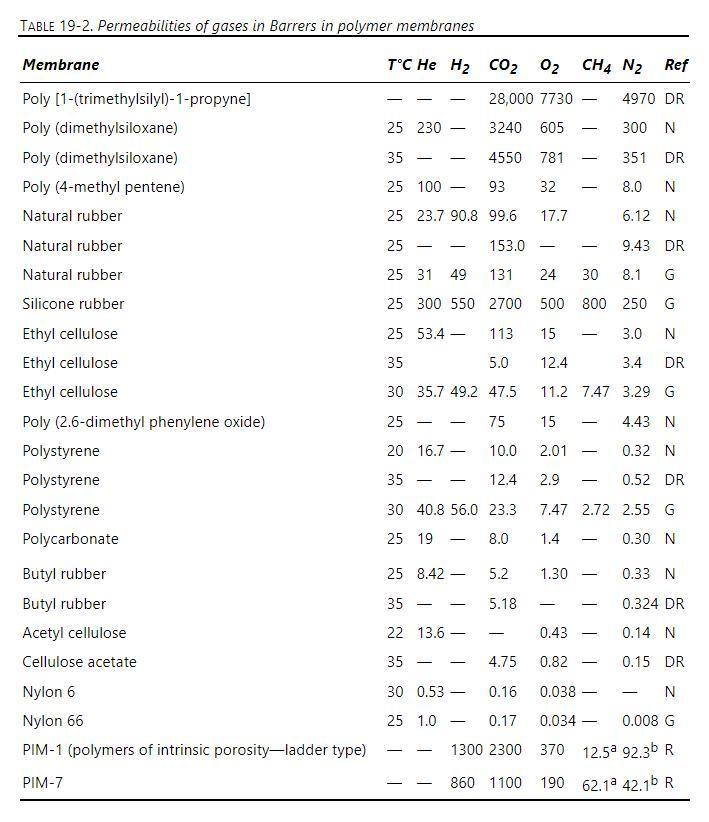
a. What is the flow rate and the concentration of the gas that is fed to the permeators?
b. If the cut \(\theta=0.20\), what value of retentate pressure is needed to obtain a permeate product that is 30 \(\mathrm{mol} \%\) carbon dioxide? What is corresponding retentate concentration?
c. With \(\theta=0.20\), what is the highest value of \(\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}}\) that can be obtained by increasing \(\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{r}}\) ?
d. What membrane area in \(\mathrm{m}^{2}\) is required for a basis of burning \(1.0 \mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{min}\) methane for part \(\mathrm{b}\) ?
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





