A mixture of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen is fed to a perfectly mixed GP system with
Question:
A mixture of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen is fed to a perfectly mixed GP system with a natural rubber membrane. Membrane properties are given in Geankoplis data in Table 19-2. Membrane active layer thickness is \(1.0 \mu \mathrm{m}\). Feed pressure is \(17.0 \mathrm{bar}=\) retentate pressure and feed temperature is \(22^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). Permeate pressure is \(1.1 \mathrm{bar}\). Feed is \(15.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) carbon dioxide, \(75.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) methane, and \(10.0 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) nitrogen. For \(\theta=\) 0.40 , find retentate mole fractions, permeate mole fractions, and membrane area (in \(\mathrm{m}^{2}\) ) needed for \(1.0 \mathrm{~m}^{3} / \mathrm{s}\) of feed gas at 17.0 bar and \(22^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
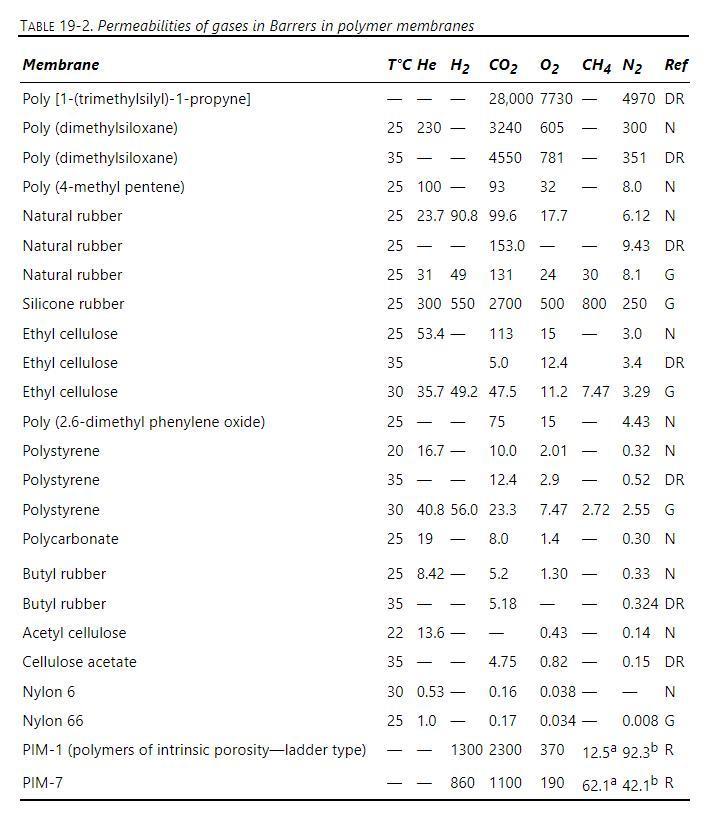
Suggestion: Set up on a spreadsheet or other computer solution method and converge \(\Sigma \mathrm{y}-\Sigma \mathrm{x}=0\) using Goal Seek or Solver to determine A.
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





