Concentration cells are commonly used to calculate the value of equilibrium constants for various reactions. For example,
Question:
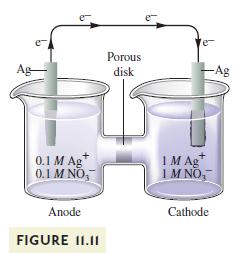
Concentration cells are commonly used to calculate the value of equilibrium constants for various reactions. For example, the silver concentration cell illustrated in Fig. 11.11 can be used to determine the \(K_{\text {sp }}\) value for \(\mathrm{AgCl}(s)\). To do so, \(\mathrm{NaCl}\) is added to the anode compartment until no more precipitate forms. The \(\left[\mathrm{Cl}^{-}ight]\)in solution is then determined somehow. What happens to \(\mathscr{E}_{\text {cell }}\) when \(\mathrm{NaCl}\) is added to the anode compartment? To calculate the \(K_{\mathrm{sp}}\) value, \(\left[\mathrm{Ag}^{+}ight]\)must be calculated. Given the value of \(\mathscr{E}_{\text {cell }}\), how is \(\left[\mathrm{Ag}^{+}ight]\)determined at the anode?
Step by Step Answer:






