The overall reaction in the lead storage battery is a. Calculate (mathscr{E}) at (25^{circ} mathrm{C}) for this
Question:
The overall reaction in the lead storage battery is
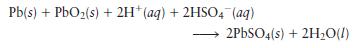
a. Calculate \(\mathscr{E}\) at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) for this battery when \(\left[\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}ight]=4.5 \mathrm{M}\); that is, \(\left[\mathrm{H}^{+}ight]=\left[\mathrm{HSO}_{4}{ }^{-}ight]=4.5 \mathrm{M}\). At \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}, \mathscr{E}^{\circ}=2.04 \mathrm{~V}\) for the lead storage battery.
b. For the cell reaction \(\Delta H^{\circ}=-315.9 \mathrm{~kJ}\) and \(\Delta S^{\circ}=\) \(263.5 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{K}\). Calculate \(\mathscr{C}^{\circ}\) at \(-20 .^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
c. Calculate \(\mathscr{E}\) at \(-20 .{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) when \(\left[\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}ight]=4.5 \mathrm{M}\).
d. Based on your previous answers, why does it seem that batteries fail more often on cold days than on warm days?
Step by Step Answer:






