Question: Use values from Appendix E at the back of the book to calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following gaseous reactions: (a) H 2
Use values from Appendix E at the back of the book to calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following gaseous reactions:
(a) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇄ 2 HCl(g)
(b) CH4(g) + H2O(g) ⇄ CO(g) + 3 H2(g)
(c) SO2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇄ SO2Cl2(g)
(d) 2 HCl(g) + F2(g) ⇄ 2 HF(g) + Cl2(g)
Data from appendix E
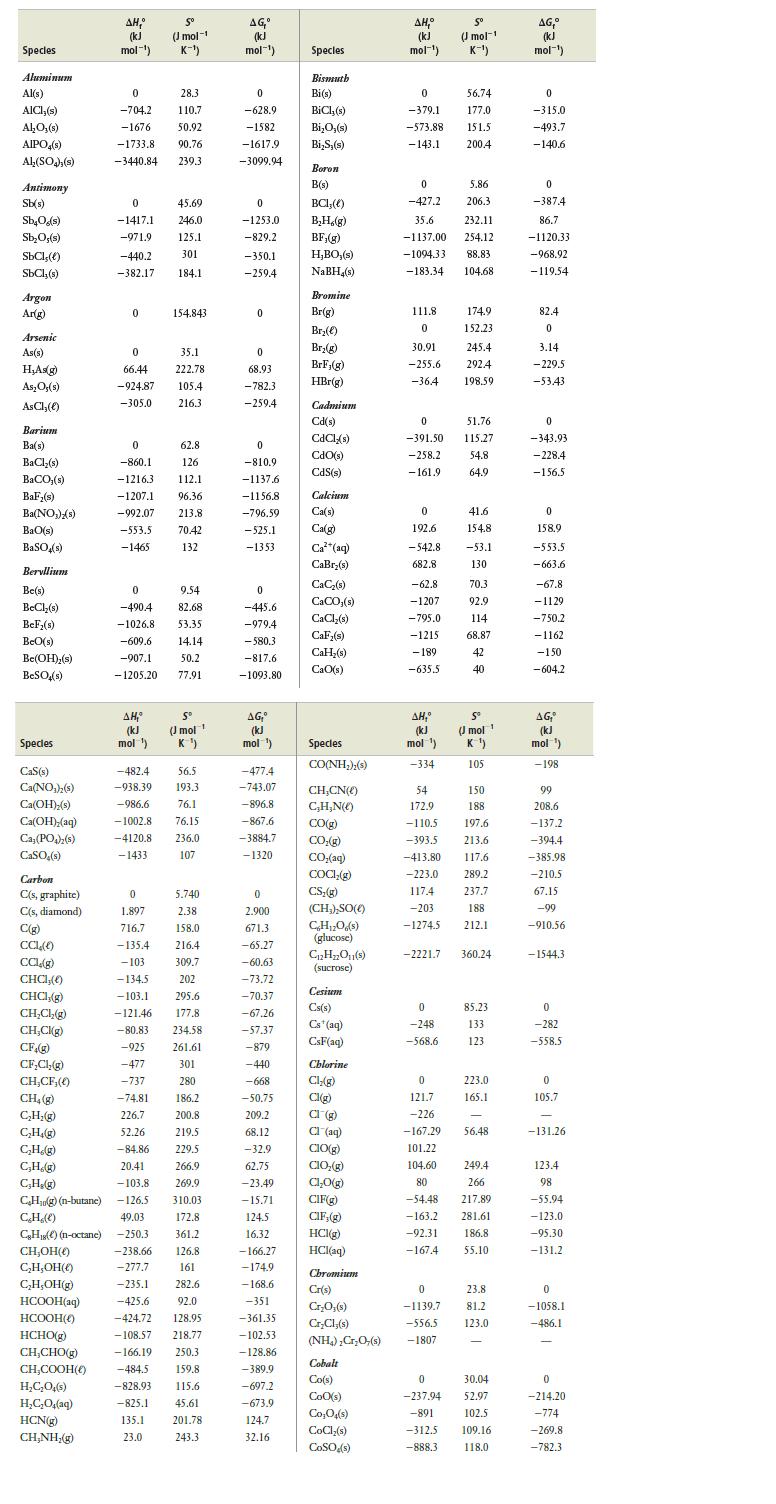
Specles Aluminum Al(s) AICI;(s) AlO (s) AIPO4(s) Al(SO4),(s) Antimony Sb(s) SbO(s) SbO,(s) SbCl,() SbCl,(s) Argon Ar(g) Arsenic As(s) HAs(g) AsOs(s) AsCl(e) Barium Ba(s) BaCl(s) BaCO,(s) BaF,(s) Ba(NO)(s) BaD(s) BaSO4(s) Beryllium Be(s) BeCl(s) BeF(s) BeO(s) Be(OH)(s) BeSO4(s) Species Cas(s) Ca(NO)2(s) Ca(OH)(s) Ca(OH)(aq) Ca,(PO)(s) CaSO4(s) Carbon C(s, graphite) C(s, diamond) C(g) CCL(0) CCL,(g) CHCI,() CHCI,(g) CHCl(g) CH,CI(g) CF.(g) CFCl(g) CH,CF,(0) CH(g) CH(g) CH(g) CH(g) CH(g) CH(g) CH(g) (n-butane) CH(e) CHOH() CHOH() CHOH(g) HCOOH(aq) HCOOH(0) HCHO(g) CH,CHO(g) CHCOOH() HCO4(s) HCO4(aq) AH, (kJ mol-) HCN(g) CH,NH,(g) 0 28.3 -704.2 110.7 -1676 50.92 -1733.8 90.76 -3440.84 239.3 0 -1417.1 -971.9 -440.2 -382.17 184.1 0 0 66.44 -924.87 -305.0 5 (J mol-1 K-) 49.03 C,H(C)(n-octane) -250.3 45.69 246.0 , (kJ mol ) 125.1 301 154.843 0 62.8 -860.1 126 -1216.3 112.1 -1207.1 96.36 -992.07 213.8 -553.5 70.42 -1465 132 35.1 222.78 105.4 216.3 9.54 0 -490.4 82.68 -1026.8 53.35 -609.6 14.14 -907.1 50.2 -1205.20 77.91 S (mol 1 K) -482.4 56.5 -938.39 193.3 -986.6 76.1 -1002.8 76.15 -4120.8 236.0 -1433 107 0 5.740 1.897 2.38 716.7 158.0 -135.4 216.4 -103 309,7 -134.5 202 -103.1 295.6 -121.46 177.8 -80.83 234.58 -925 261.61 -477 301 -737 280 -74.81 186.2 226.7 200.8 52.26 219.5 -84.86 229.5 20.41 266.9 -103.8 269.9 -126.5 310.03 172.8 361.2 -238.66 126.8 -277.7 161 -235.1 282.6 -425.6 92.0 -424.72 128.95 -108.57 218.77 -166.19 250.3 -484.5 159.8 -828.93 115.6 -825.1 45.61 135.1 23.0 201.78 243.3 AG (kJ mol-) 0 -628.9 -1582 -1617.9 -3099.94 0 -1253.0 -829.2 -350.1 -259.4 0 0 68.93 -782.3 -259.4 0 -810.9 -1137.6 -1156.8 -796.59 -525.1 -1353 0 -445.6 -979.4 -580.3 -817.6 -1093.80 AG, (kJ mol ) -477.4 -743.07 -896.8 -867.6 -3884.7 -1320 0 2.900 671.3 -65.27 -60.63 -73.72 -70.37 -67.26 -57.37 -879 -440 -668 -50.75 209.2 68.12 -32.9 62.75 -23.49 -15.71 124.5 16.32 -166.27 -174.9 -168.6 -351 -361.35 -102.53 -128.86 -389.9 -697.2 -673.9 124.7 32.16 Specles Bismuth Bi(s) BiCl(s) BiO,(s) BiS,(s) Boron B(s) BCI,() BH,(g) BF,(g) HBO,(s) NaBH4(s) Bromine Br(g) Br(e) Br(g) BrF, (g) HBr(g) Cadmium Cd(s) CdCl(s) CdO(s) CdS(s) Calcium Ca(s) Ca(g) Ca+ (aq) CaBr(s) CaC(s) CaCO (s) CaCl(s) CaF(s) CaH(s) CaO(s) Specles CO(NH,),(s) CHCN() CH,N() CO(g) CO(g) CO,(aq) COCI,(g) CS(g) (CH) SO() CHO(s) (glucose) CH2O1(s) (sucrose) Cesium Cs(s) Cs (aq) CsF(aq) Chlorine Cl(g) Cl(g) 1 (g) Cl(aq) CIO(g) CIO(g) ClO(g) CIF(g) CIF; (g) HCl(g) HCl(aq) Chromium Cr(s) CrO;(s) CryCl,(s) (NH4)CrO,(s) Cobalt Co(s) Coo(s) CoO (s) CoCl(s) COSO (s) AH, (kJ mol-) 0 -379.1 -573.88 -143.1 0 -427.2 111.8 0 30.91 -255.6 -36.4 35.6 232.11 -1137.00 254.12 -1094.33 88.83 -183.34 104.68 0 192.6 -542.8 682.8 -62.8 -1207 -795.0 -1215 -189 -635.5 5 (mol-1 K-) AH, (kJ mol ) -334 56.74 177.0 151.5 200.4 0 51.76 -391.50 115.27 -258.2 - 161.9 5.86 206.3 0 -248 -568.6 174.9 152.23 245.4 292.4 198,59 54.8 64.9 41.6 154.8 -53.1 130 70.3 92.9 114 68.87 42 40 S (J mol 1 K) 105 54 150 172.9 188 -110.5 197.6 -393.5 213.6 -413.80 117.6 -223.0 289.2 117.4 237.7 -203 188 -1274.5 212.1 -2221.7 360.24 85.23 133 123 0 121.7 -226 -167.29 56.48 101.22 104.60 80 -54.48 -163.2 281.61 -92.31 186.8 -167.4 55.10 223.0 165.1 249.4 266 217.89 0 23.8 -1139,7 81.2 -556.5 123.0 -1807 0 30.04 -237.94 52.97 -891 102.5 -312.5 -888.3 109.16 118.0 AG, (kJ mol-) 0 -315.0 -493.7 -140.6 0 -387.4 86.7 -1120.33 -968.92 -119.54 82.4 0 3.14 -229.5 -53.43 0 -343.93 -228.4 -156.5 0 158.9 -553.5 -663.6 -67.8 -1129 -750.2 -1162 -150 -604.2 AG, (kJ mol ) -198 99 208.6 -137.2 -394.4 -385.98 -210.5 67.15 -99 -910.56 - 1544.3 0 -282 -558.5 0 105.7 -131.26 123.4 98 -55.94 -123.0 -95.30 -131.2 0 -1058.1 -486.1 0 -214.20 -774 -269.8 -782.3
Step by Step Solution
3.29 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer and explanation is attached below hope you like ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


