Calculate the change in pH observed when 1.50 mL of 0.0670 M H 3 O + is
Question:
Calculate the change in pH observed when 1.50 mL of 0.0670 M H3O+ is added to
(a) 100.0 mL of an unbuffered HCl solution of pH 4.74
(b) 100.0 mL of a pH 4.74 buffer that is 0.120 M acetic acid and 0.120 M sodium acetate (the pKa for acetic acid is 4.74 ).
(a) Calculate the change in pH observed when 1.5 mL of 0.0670 M H3O+ is added to 100.0 mL of a pH 4.74 HCl solution.
Strategy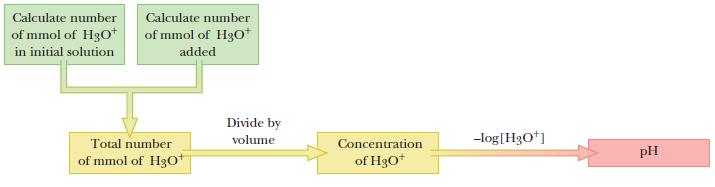
The system is unbuffered and the acid comes from two sources, the initial 100.0 mL of pH 4.74 HCl and the added 1.50 mL of 0.0679 M H3O+. Express amounts in moles, for both sources, add together, and divide by volume to fi nd [H3O+]. Compute the pH from the negative log.
(b) Calculate the change in pH observed when 1.50 mL of 0.0670 M H3O+ is added to 100.0 mL of a pH 4.74 buffer that is 0.120 M acetic acid and 0.120 M sodium acetate (the pKa for acetic acid is 4.74 ).
Strategy
This problem is similar to a titration problem such as those presented in Section 16.2. We are adding H3O+, which will react with the weak base form of the buffer. As a result of this reaction, which goes to completion, the number of moles of the base will decrease and the number of moles of the conjugate acid will increase. The pH will be computed by using the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation.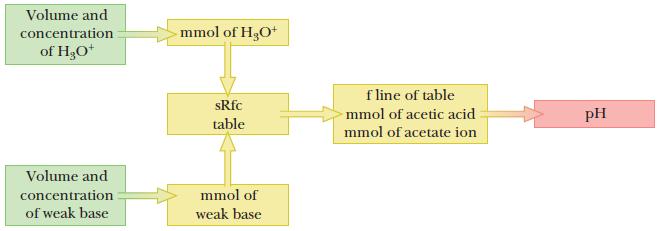
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry Principles And Practice
ISBN: 9780534420123
3rd Edition
Authors: Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball





