With the exception of helium, the noble gases condense to form solids when they are cooled sufficiently.
Question:
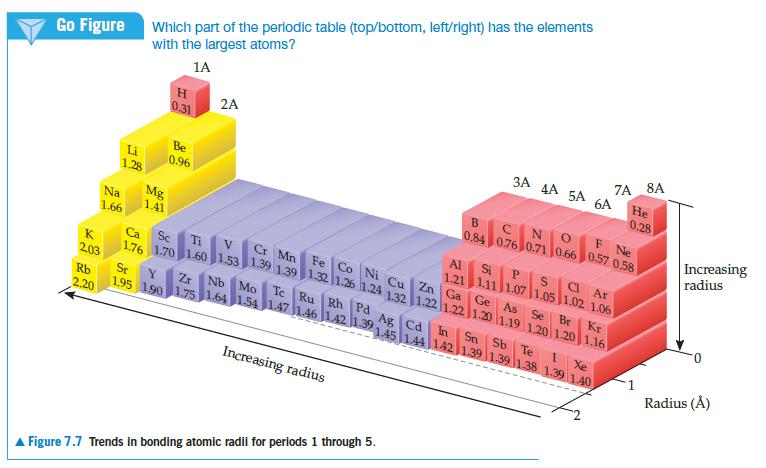
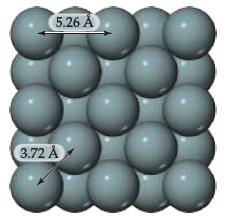
With the exception of helium, the noble gases condense to form solids when they are cooled sufficiently. At temperatures below 83 K, argon forms a close-packed solid whose structure is shown below.
(a) What is the apparent radius of an argon atom in solid argon, assuming the atoms touch as shown in this figure?
(b) Is this value larger or smaller than the bonding atomic radius estimated for argon in Figure 7.7?
(c) Based on this comparison would you say that the atoms are held together by chemical bonds in solid argon?
Figure 7.7
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Chemistry The Central Science
ISBN: 978-0134414232
14th Edition
Authors: Theodore Brown, H. LeMay, Bruce Bursten, Catherine Murphy, Patrick Woodward, Matthew Stoltzfus
Question Posted:





