Digital Systems Principles And Application 12th Edition Ronald Tocci, Neal Widmer, Gregory Moss - Solutions
Discover the ultimate resource for mastering "Digital Systems Principles And Application 12th Edition" by Ronald Tocci, Neal Widmer, and Gregory Moss. Our platform offers comprehensive solutions, including an online answers key and step-by-step answers to enhance your understanding. Access the complete solutions manual and free download options for solved problems and chapter solutions. Whether you're looking for test bank materials or an instructor manual, our collection of textbook solutions and answers provides invaluable support. Dive into the world of digital systems with ease and confidence through our expertly crafted solutions PDF.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


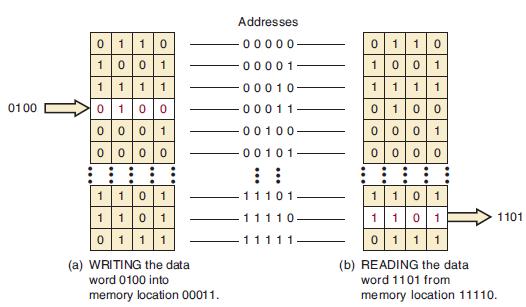
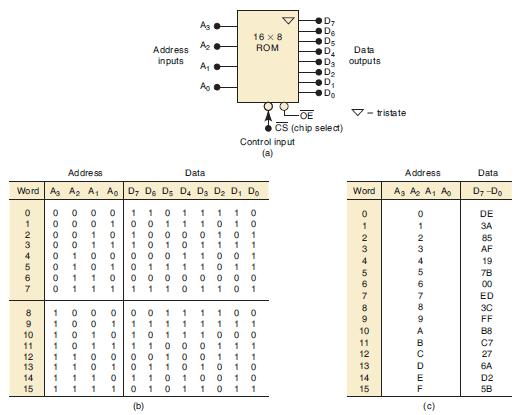
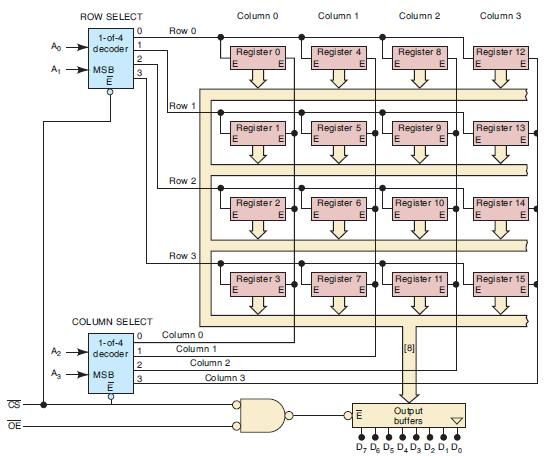
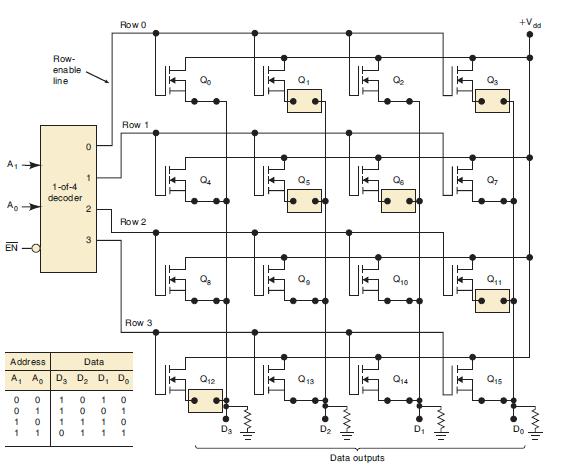
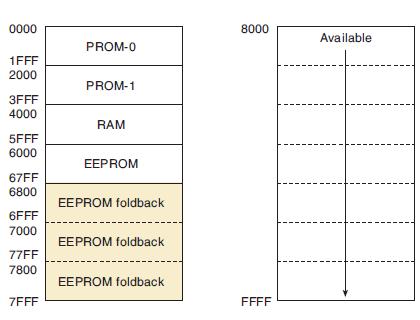
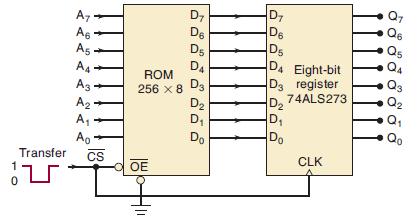
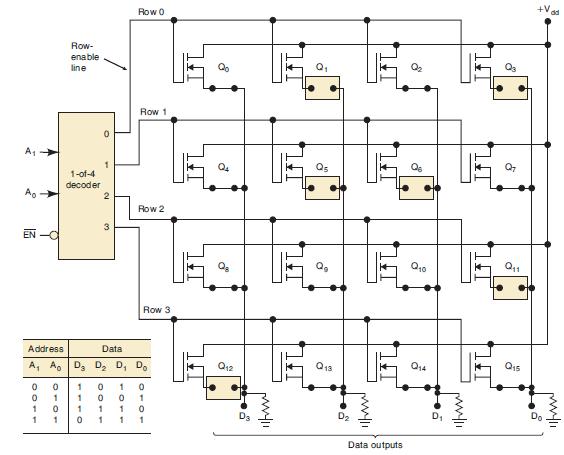
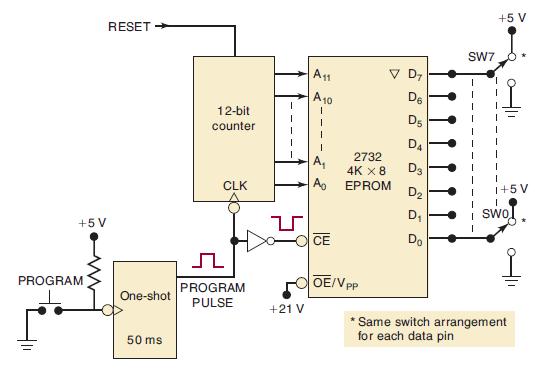
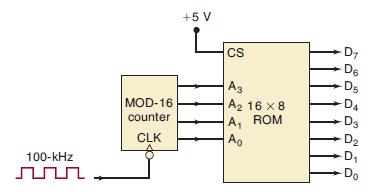
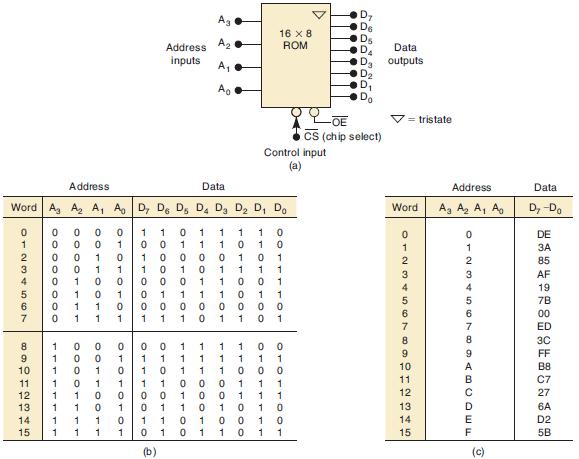
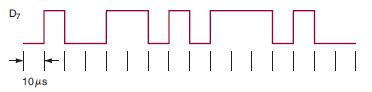
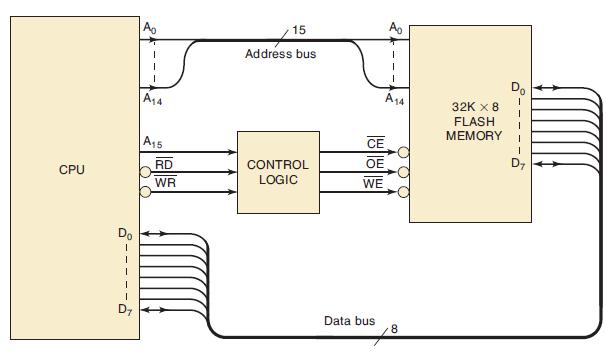
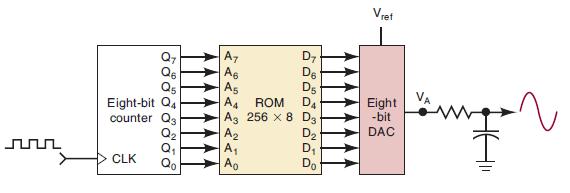
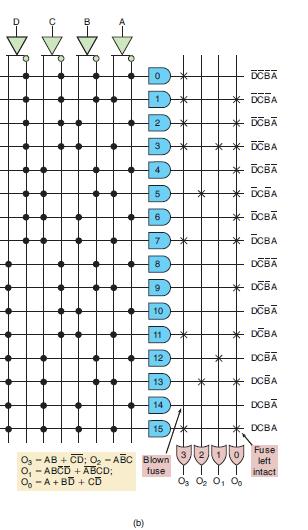
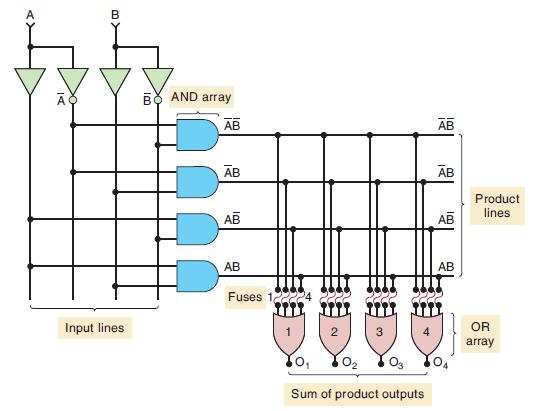
![Phase A Load Phase B Load- Phase Load Eight-bit binary counters asynchronous load tristate outputs CLK [8]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/2/2/7696557573144cbe1700222768824.jpg)