Question: As we have seen, a potential drawback of SSDs is that the underlying flash memory can wear out. For example, for the SSD in Figure
As we have seen, a potential drawback of SSDs is that the underlying flash memory can wear out. For example, for the SSD in Figure 6.14, Intel guarantees about 128 petabytes (128 × 1015 bytes) of writes before the drive wears out. Given this assumption, estimate the lifetime (in years) of this SSD for the following workloads:
A. Worst case for sequential writes: The SSD is written to continuously at a rate of 470 MB/s (the average sequential write throughput of the device).
B. Worst case for random writes: The SSD is written to continuously at a rate of 303 MB/s (the average random write throughput of the device).
C. Average case: The SSD is written to at a rate of 20 GB/day (the average daily write rate assumed by some computer manufacturers in their mobile computer workload simulations).
Figure 6.14
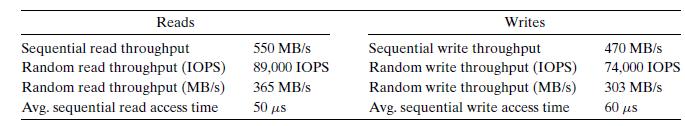
Reads Sequential read throughput Random read throughput (IOPS) Random read throughput (MB/s) Avg. sequential read access time 550 MB/s 89,000 IOPS 365 MB/s 50 s Writes Sequential write throughput Random write throughput (IOPS) Random write throughput (MB/s) Avg. sequential write access time 470 MB/s 74,000 IOPS 303 MB/s 60 s
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (144 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
This is a simple problem that will give you some interesti... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


