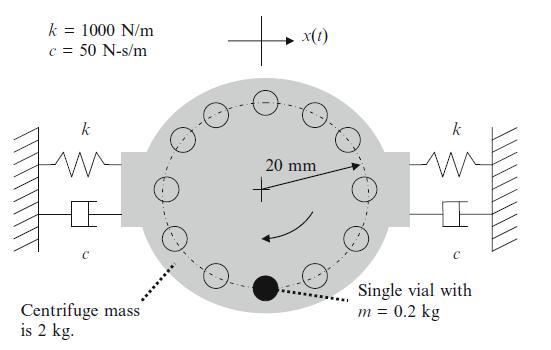
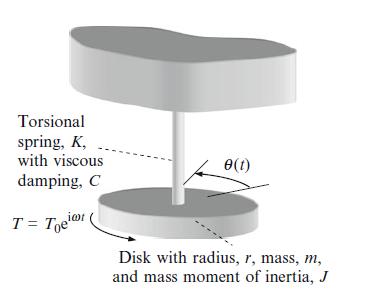
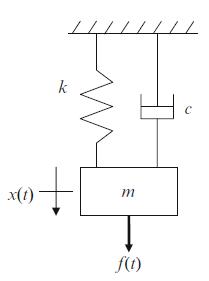
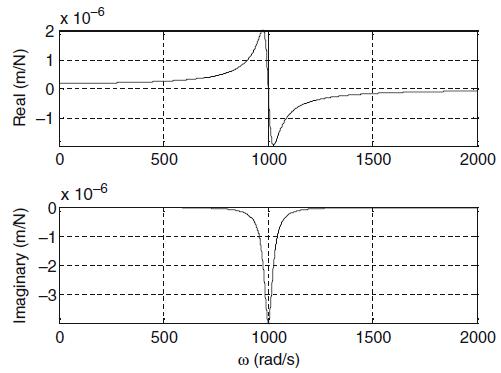
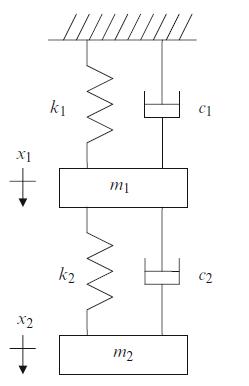
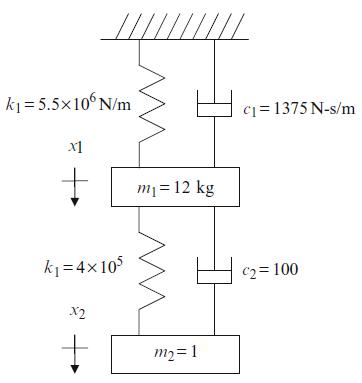
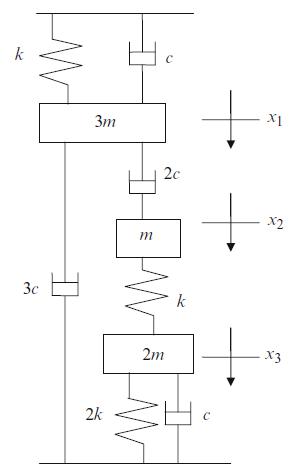
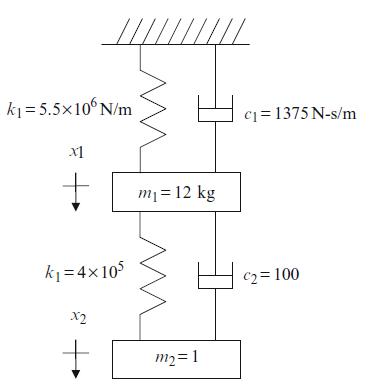
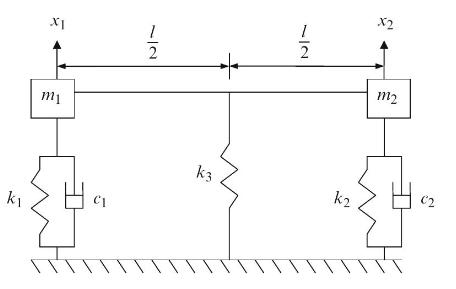
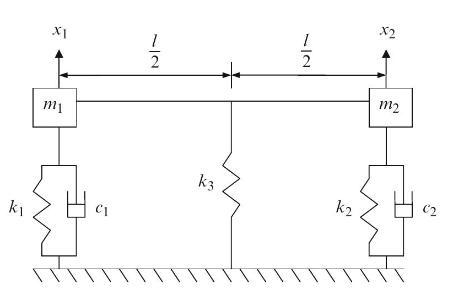
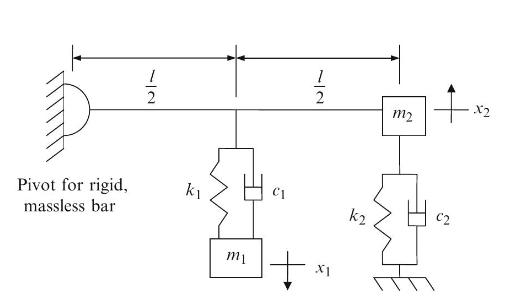
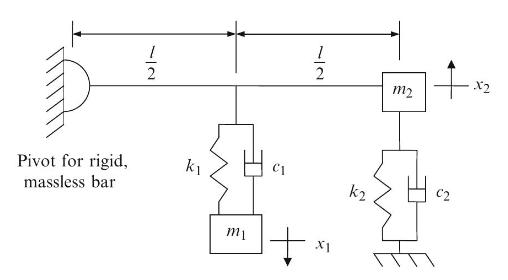
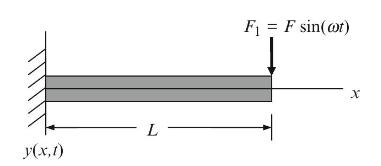
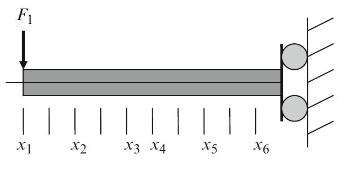
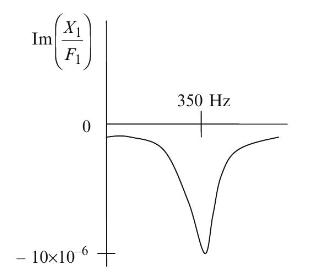
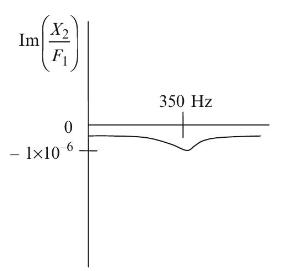
Principles Of Mechanical Engineering 1st Edition Sadhu Singh - Solutions
Unlock the potential of your studies with the "Principles of Mechanical Engineering 1st Edition" by Sadhu Singh. Discover an extensive range of resources including an online answers key and comprehensive solutions manual, all available in convenient solutions PDF format. Dive into solved problems, detailed questions and answers, and a robust test bank to enhance your learning experience. Each chapter offers step-by-step answers and chapter solutions, guided by an instructor manual to ensure thorough understanding. This textbook is your gateway to mastering mechanical engineering concepts, and best of all, it's available for free download to support your academic journey.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()