Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two-dimensional velocity field of Prob. 417. Since the flow
Question:
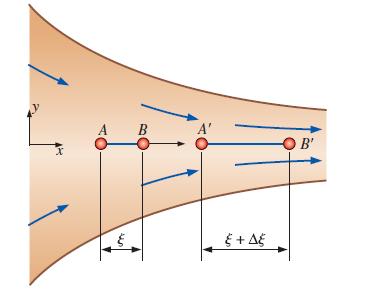
Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two-dimensional velocity field of Prob. 4–17. Since the flow is symmetric about the x-axis, line segment AB along the x-axis remains on the axis, but stretches from length ξ to length + 1 Δξ as it flows along the channel centerline (Fig. P4–52). Generate an analytical expression for the change in length of the line segment, Δξ.
Data from Problem 4-17.
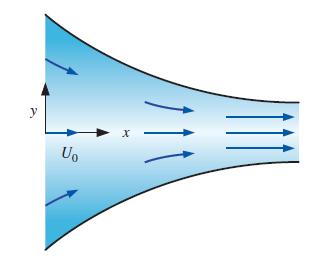
Consider steady, incompressible, two-dimensional flow through a converging duct (Fig. P4–17). A simple approximate velocity field for this flow is
![]()
where U0 is the horizontal speed at x = 0. Note that this equation ignores viscous effects along the walls but is a reasonable approximation throughout the majority of the flow field. Calculate the material acceleration for fluid particles passing through this duct. Give your answer in two ways:
(1) As acceleration components ax and ay
(2) As acceleration vector a(vector)
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala





