Coupled Reactions in Biological Systems. The Gibbs energy available from the complete combustion of 1 mol of
Question:
Coupled Reactions in Biological Systems. The Gibbs energy available from the complete combustion of 1 mol of glucose to carbon dioxide and water is
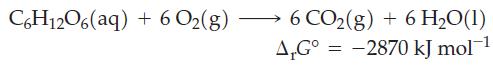
(a) Under biological standard conditions, compute the maximum number of moles of ATP that could form from ADP and phosphate if all the energy of combustion of 1 mol of glucose could be utilized.
(b) The actual number of moles of ATP formed by a cell under aerobic conditions (that is, in the presence of oxygen) is about 38. Calculate the efficiency of energy conversion of the cell.
(c) Consider these typical physiological conditions.
![Pco = 0.050 bar; Po = 0.132 bar; [glucose] = 1.0 mg/mL; pH = 7.0; [ATP] = [ADP] = [P] = 0.00010 M.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/2/2/3/180655758cc99c891700223180209.jpg)
Calculate ΔrG° for the conversion of 1 mol ADP to ATP and ΔrG° for the oxidation of 1 mol glucose under these conditions.
(d) Calculate the efficiency of energy conversion for the cell under the conditions given in part (c).
Compare this efficiency with that of a diesel engine that attains 78% of the theoretical efficiency operating with Th = 1923 K and T1 = 873 K. Suggest a reason for your result.
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





