Question:
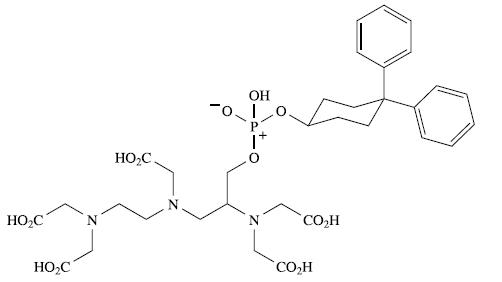
Vasovist® is the tradename of a Gd(III) complex which was the first intravascular contrast agent (see Box 4.3) approved in the EU for use in magnetic resonance angiography. Interactions between the lipophilic domain of the contrast agent and human serum albumin allow Vasovist® to bind reversibly to the protein. Vasovist® has the formula Na3[GdL(OH2)] where the ligand Ln− is derived from HnL shown in Fig. 27.12.
(a) What is the value of n in Ln− and HnL?
(b) Explain why one part of the ligand is described as being lipophilic.
(c) In Na3[GdL(OH2)], the Gd3+ ion is 9-coordinate. Suggest a possible coordination environment for the metal ion, and indicate how Ln− is likely to coordinate to Gd3+.
(d) Why is HnL chiral?
(e) Starting from (R)-HnL, four diastereoisomers of [GdL(OH2)]3− are possible: ΔR, R, ΔR,S, ∧R,R, ∧R,S. How do these arise?
(f) The FAB mass spectrum of Na3[GdL(OH2)] shows peak envelopes at m/z 981, 959, 937 and 915. Suggest assignments for these peaks.
Box 4.3.
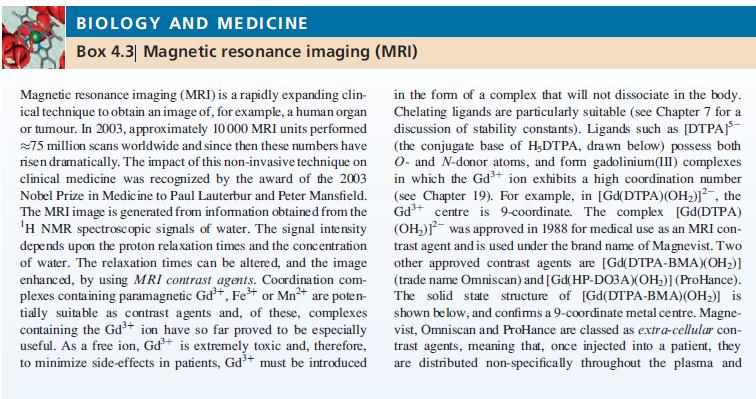
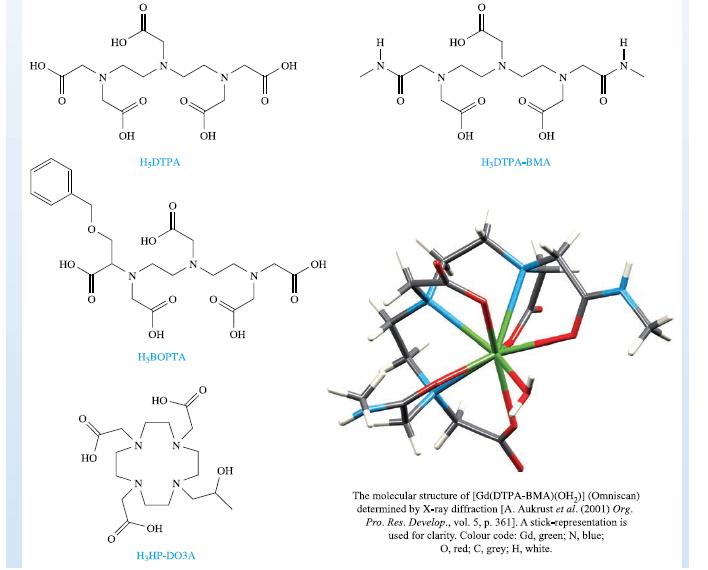
Figure 27.12.
Transcribed Image Text:
BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE
Box 4.3 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a rapidly expanding clin-
ical technique to obtain an image of, for example, a human organ
or tumour. In 2003, approximately 10 000 MRI units performed
75 million scans worldwide and since then these numbers have
risen dramatically. The impact of this non-invasive technique on
clinical medicine was recognized by the award of the 2003
Nobel Prize in Medicine to Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield.
The MRI image is generated from information obtained from the
¹H NMR spectroscopic signals of water. The signal intensity
depends upon the proton relaxation times and the concentration
of water. The relaxation times can be altered, and the image
enhanced, by using MRI contrast agents. Coordination com-
plexes containing paramagnetic Gd³+, Fe³+ or Mn²+ are poten-
tially suitable as contrast agents and, of these, complexes
containing the Gd³+ ion have so far proved to be especially
useful. As a free ion, Gd³+ is extremely toxic and, therefore,
to minimize side-effects in patients, Gd³+ must be introduced
in the form of a complex that will not dissociate in the body.
Chelating ligands are particularly suitable (see Chapter 7 for a
discussion of stability constants). Ligands such as [DTPA-
(the conjugate base of H,DTPA, drawn below) possess both
O- and N-donor atoms, and form gadolinium(III) complexes
in which the Gd³+ ion exhibits a high coordination number
(see Chapter 19). For example, in [Gd(DTPA)(OH₂)], the
Gd³+ centre is 9-coordinate. The complex [Gd(DTPA)
(OH₂)]² was approved in 1988 for medical use as an MRI con-
trast agent and is used under the brand name of Magnevist. Two
other approved contrast agents are [Gd(DTPA-BMA)(OH₂)]
(trade name Omniscan) and [Gd(HP-DO3A)(OH₂)] (ProHance).
The solid state structure of [Gd(DTPA-BMA)(OH₂)] is
shown below, and confirms a 9-coordinate metal centre. Magne-
vist, Omniscan and ProHance are classed as extra-cellular con-
trast agents, meaning that, once injected into a patient, they
are distributed non-specifically throughout the plasma and









