The equations for an armature-controlled dc motor follow. The motors current is i and its rotational velocity
Question:
The equations for an armature-controlled dc motor follow. The motor’s current is i and its rotational velocity is ω.
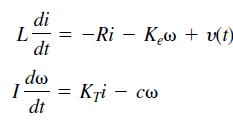
where L, R, and I are the motor’s inductance, resistance, and inertia; KT and Ke are the torque constant and back-emf constant; c is a viscous damping constant; and υ(t) is the applied voltage.
Use the values R = 0.8 1, L = 0.003 H, KT = 0.05 N ∙ m/A, Ke = 0.05
V ∙ s/rad, c = 0, and I = 8 , 10-5 kg · m2.
Suppose the applied voltage is 20 V. Use MuPAD to obtain the motor’s speed and current versus time for zero initial conditions. Choose a final time large enough to show the motor’s speed becoming constant.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:




