4. In early 2001, US equity marketplaces started trading all listed shares in minimal increments (ticks) of
Question:
4. In early 2001, US equity marketplaces started trading all listed shares in minimal increments (ticks) of $0.01 (decimalization). After decimalization, bid–ask spreads of stocks traded on the NASDAQ tended to decline. In response, spreads of NASDAQ stocks cross-listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSE) tended to decline as well.
Researchers Oppenheimer and Sabherwal (2003) hypothesized that the percentage decline in TSE spreads of cross-listed stocks was related to company size, the predecimalization ratio of spreads on NASDAQ to those on the TSE, and the percentage decline in NASDAQ spreads. The following table gives the regression coefficient estimates from estimating that relationship for a sample of 74 companies.
Company size is measured by the natural logarithm of the book value of company’s assets in thousands of Canadian dollars.
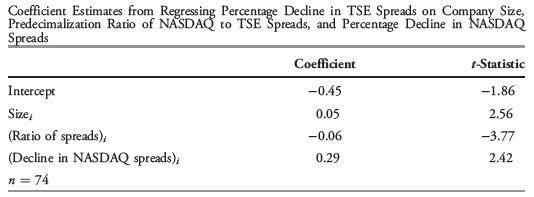
The average company in the sample has a book value of assets of C$900 million and a predecimalization ratio of spreads equal to 1.3. Based on the above model, what is the predicted decline in spread on the TSE for a company with these average characteristics, given a 1 percentage point decline in NASDAQ spreads?
Step by Step Answer:







