Question: Reimplement the fibonacci method of Fig. 18.5 to calculate Fibonacci numbers using lambdas and streams, rather than recursion. Fig. 18.5 I // Fig. 18.5: FibonacciCalculator.java
Reimplement the fibonacci method of Fig. 18.5 to calculate Fibonacci numbers using lambdas and streams, rather than recursion.
Fig. 18.5
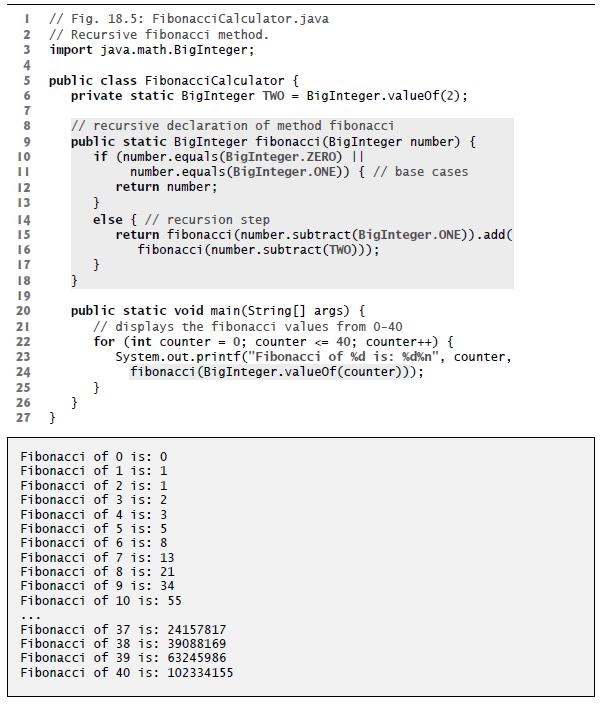
I // Fig. 18.5: FibonacciCalculator.java // Recursive fibonacci method. import java.math.BigInteger; 23456780 5 public class FibonacciCalculator { 9 10 II 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2222 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 } private static BigInteger TWO = BigInteger.value0f (2); ... // recursive declaration of method fibonacci public static Big Integer fibonacci (BigInteger number) { if (number.equals (BigInteger.ZERO) || { // base cases } } } number.equals(BigInteger.ONE)) } else {//recursion step return fibonacci (number.subtract (BigInteger.ONE)) .add( fibonacci (number.subtract (TWO))); return number; public static void main(String[] args) { // displays the fibonacci values from 0-40 } for (int counter = 0; counter
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To reimplement the Fibonacci calculator shown in Fig 185 using lambdas and streams instead of recurs... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


