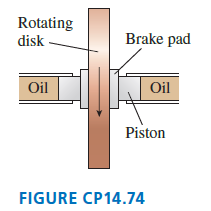
Disk brakes, such as those in your car, operate by using pressurized oil to push outward on
Question:
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Physics for Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics
ISBN: 978-0133942651
4th edition
Authors: Randall D. Knight
Question Posted:





