Question: 1. Consider the following Bayesian network where C is the event of a person having a cold and S is the event of the person
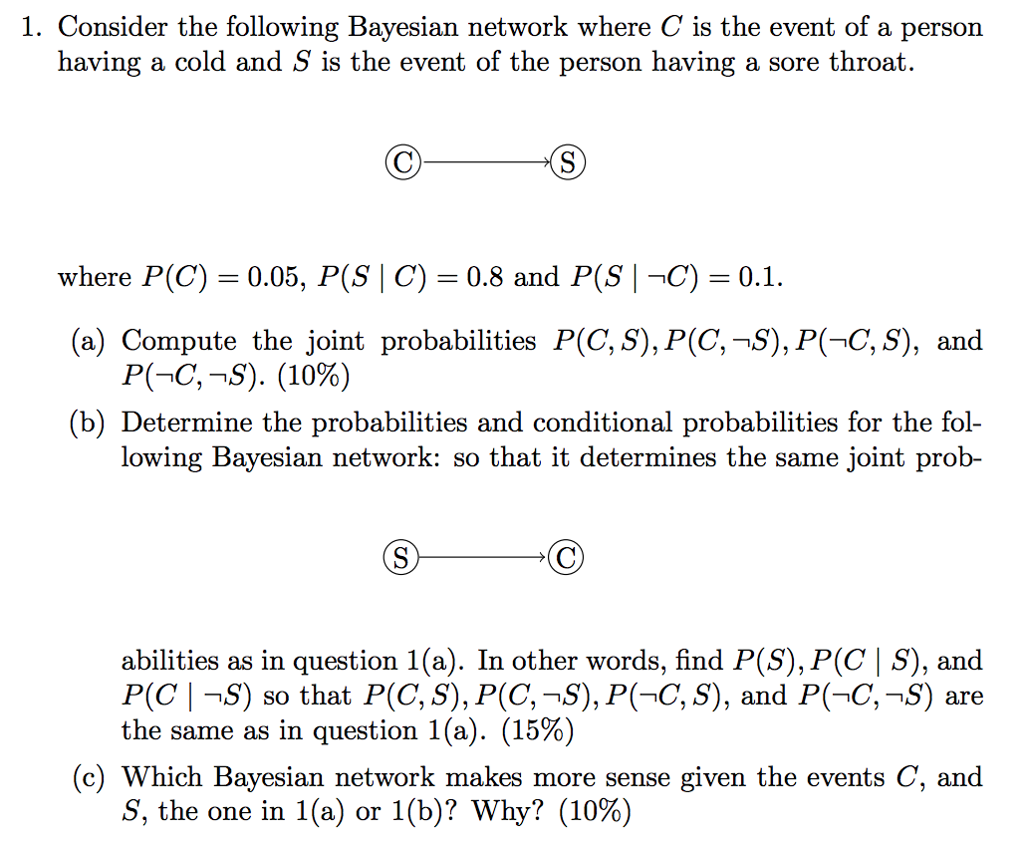
1. Consider the following Bayesian network where C is the event of a person having a cold and S is the event of the person having a sore throat. where P(C) 0.05, P(S C) 0.8 and P(S-C) 0.1. (a) Compute the joint probabilities PC, s),P(C,-S), P(7C,S), and PGC,-S). (1096) (b) Determine the probabilities and conditional probabilities for the fol- lowing Bayesian network: so that it determines the same joint prob- abilities as in question 1(a). In other words, find P(S), P(C S), and P(C |-S) so that P(C, S), P(C,-S), P(C, S), and P(-C,-S) are the same as in question 1 (a), (15%) (c) Which Bayesian network makes more sense given the events C, and S, the one in 1(a) or 1(b)? Why? (10%) 1. Consider the following Bayesian network where C is the event of a person having a cold and S is the event of the person having a sore throat. where P(C) 0.05, P(S C) 0.8 and P(S-C) 0.1. (a) Compute the joint probabilities PC, s),P(C,-S), P(7C,S), and PGC,-S). (1096) (b) Determine the probabilities and conditional probabilities for the fol- lowing Bayesian network: so that it determines the same joint prob- abilities as in question 1(a). In other words, find P(S), P(C S), and P(C |-S) so that P(C, S), P(C,-S), P(C, S), and P(-C,-S) are the same as in question 1 (a), (15%) (c) Which Bayesian network makes more sense given the events C, and S, the one in 1(a) or 1(b)? Why? (10%)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


