Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Methane and oxygen react in the presence of a catalyst to form formaldehyde. In a parallel reaction, methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide and
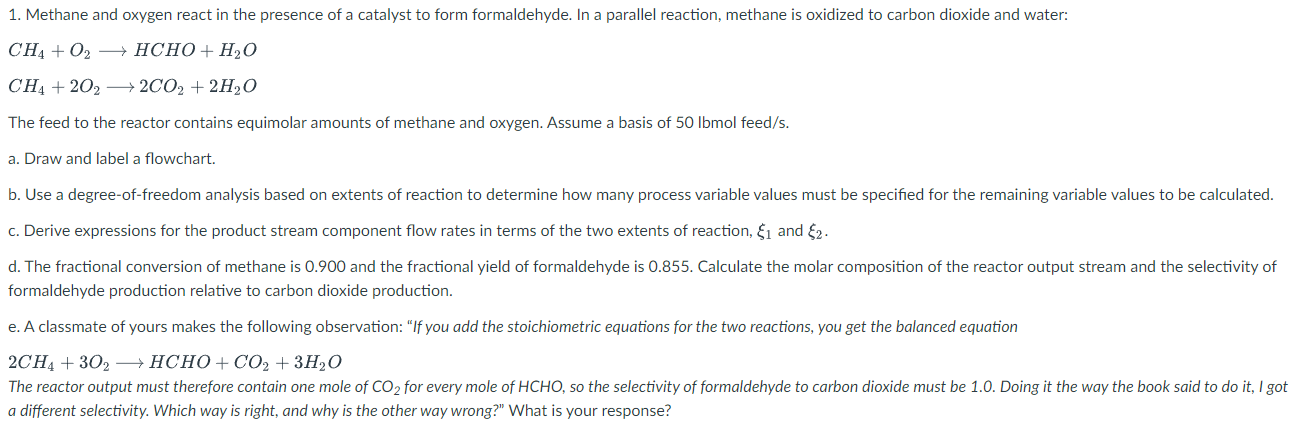 1. Methane and oxygen react in the presence of a catalyst to form formaldehyde. In a parallel reaction, methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water: CH4+O2HCHO+H2OCH4+2O22CO2+2H2O The feed to the reactor contains equimolar amounts of methane and oxygen. Assume a basis of 50lbmolfeed/s. a. Draw and label a flowchart. b. Use a degree-of-freedom analysis based on extents of reaction to determine how many process variable values must be specified for the remaining variable values to be calculated. c. Derive expressions for the product stream component flow rates in terms of the two extents of reaction, 1 and 2. d. The fractional conversion of methane is 0.900 and the fractional yield of formaldehyde is 0.855 . Calculate the molar composition of the reactor output stream and the selectivity of formaldehyde production relative to carbon dioxide production. e. A classmate of yours makes the following observation: "If you add the stoichiometric equations for the two reactions, you get the balanced equation 2CH4+3O2HCHO+CO2+3H2O The reactor output must therefore contain one mole of CO2 for every mole of HCHO, so the selectivity of formaldehyde to carbon dioxide must be 1.0 . Doing it the way the book said to do it, I got a different selectivity. Which way is right, and why is the other way wrong?" What is your response
1. Methane and oxygen react in the presence of a catalyst to form formaldehyde. In a parallel reaction, methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water: CH4+O2HCHO+H2OCH4+2O22CO2+2H2O The feed to the reactor contains equimolar amounts of methane and oxygen. Assume a basis of 50lbmolfeed/s. a. Draw and label a flowchart. b. Use a degree-of-freedom analysis based on extents of reaction to determine how many process variable values must be specified for the remaining variable values to be calculated. c. Derive expressions for the product stream component flow rates in terms of the two extents of reaction, 1 and 2. d. The fractional conversion of methane is 0.900 and the fractional yield of formaldehyde is 0.855 . Calculate the molar composition of the reactor output stream and the selectivity of formaldehyde production relative to carbon dioxide production. e. A classmate of yours makes the following observation: "If you add the stoichiometric equations for the two reactions, you get the balanced equation 2CH4+3O2HCHO+CO2+3H2O The reactor output must therefore contain one mole of CO2 for every mole of HCHO, so the selectivity of formaldehyde to carbon dioxide must be 1.0 . Doing it the way the book said to do it, I got a different selectivity. Which way is right, and why is the other way wrong?" What is your response Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


