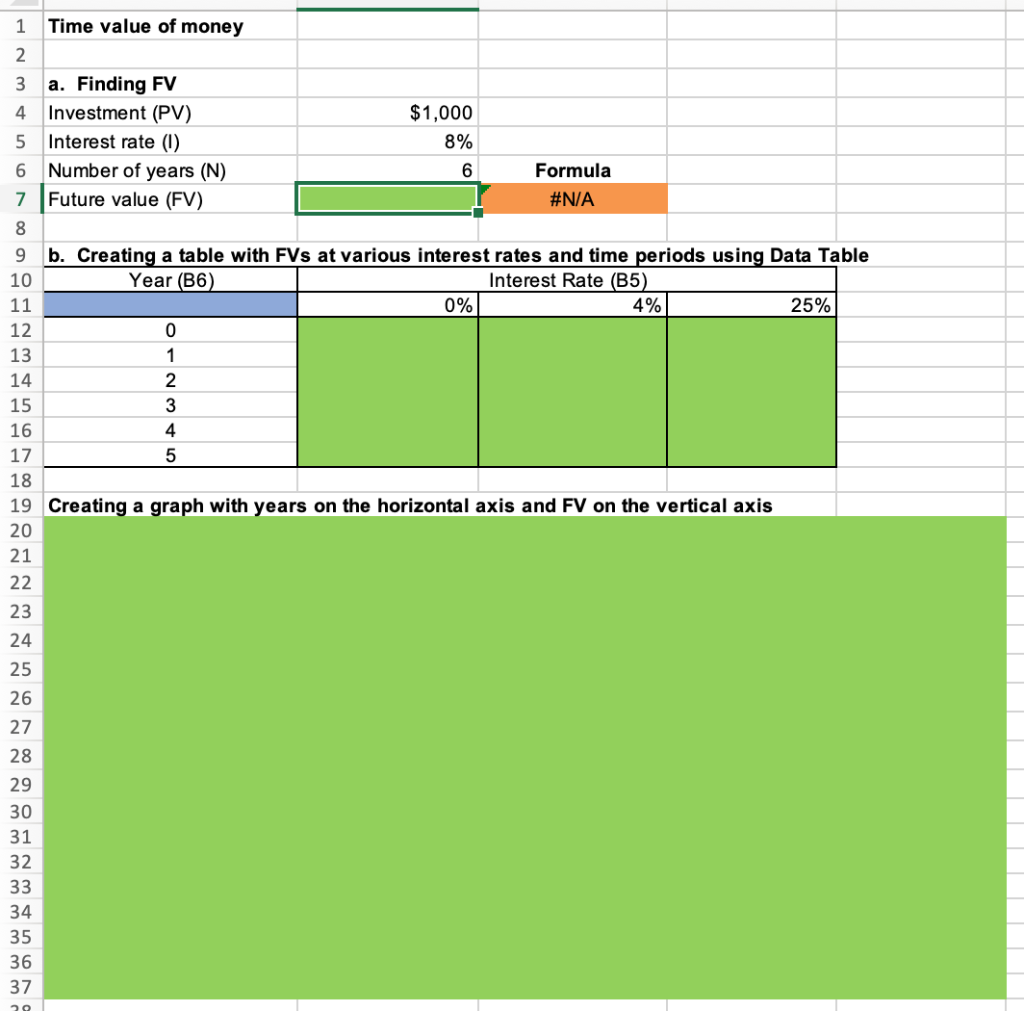
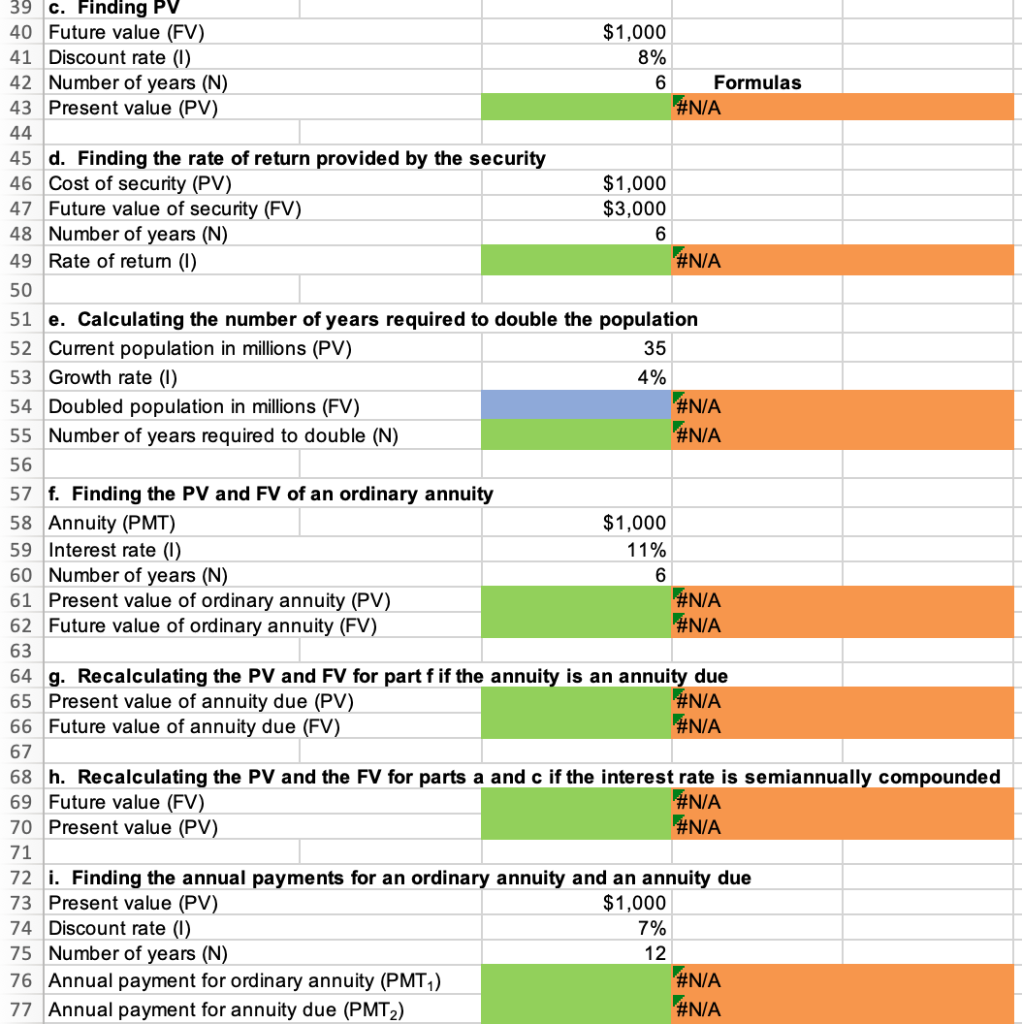
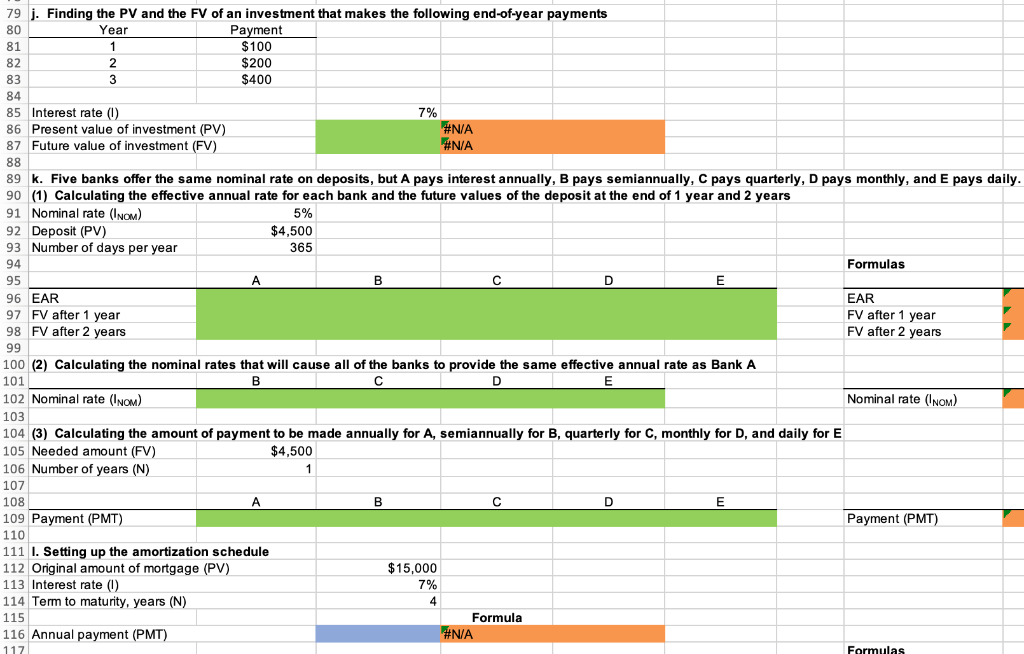
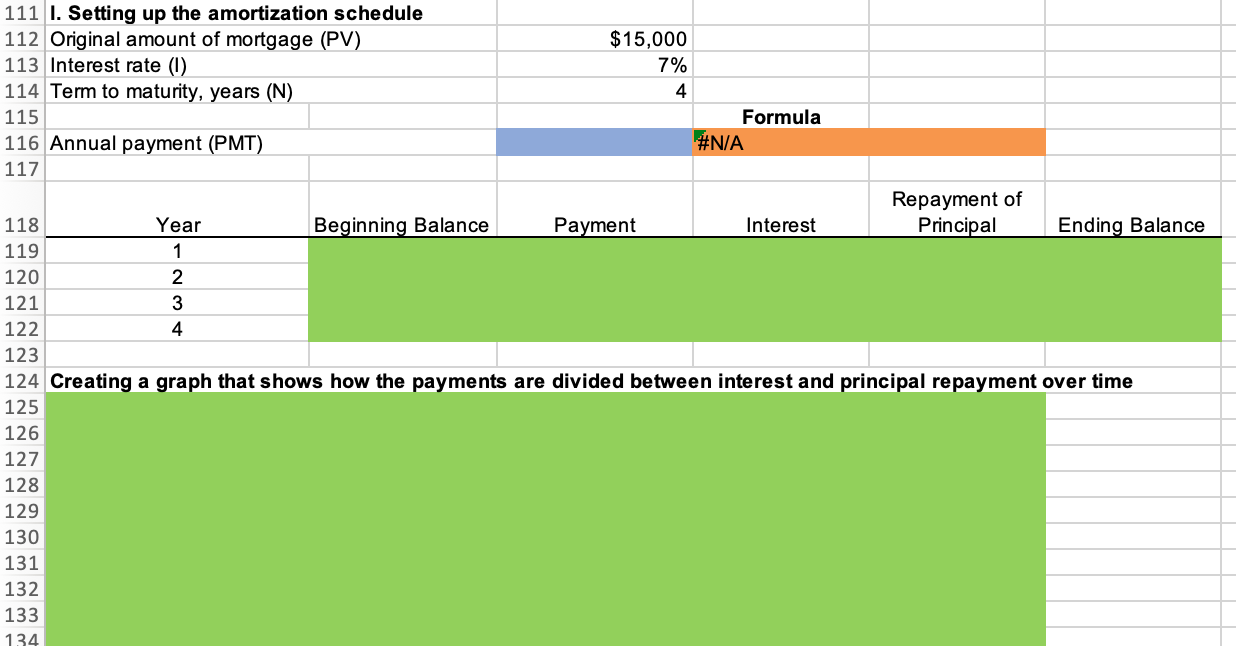
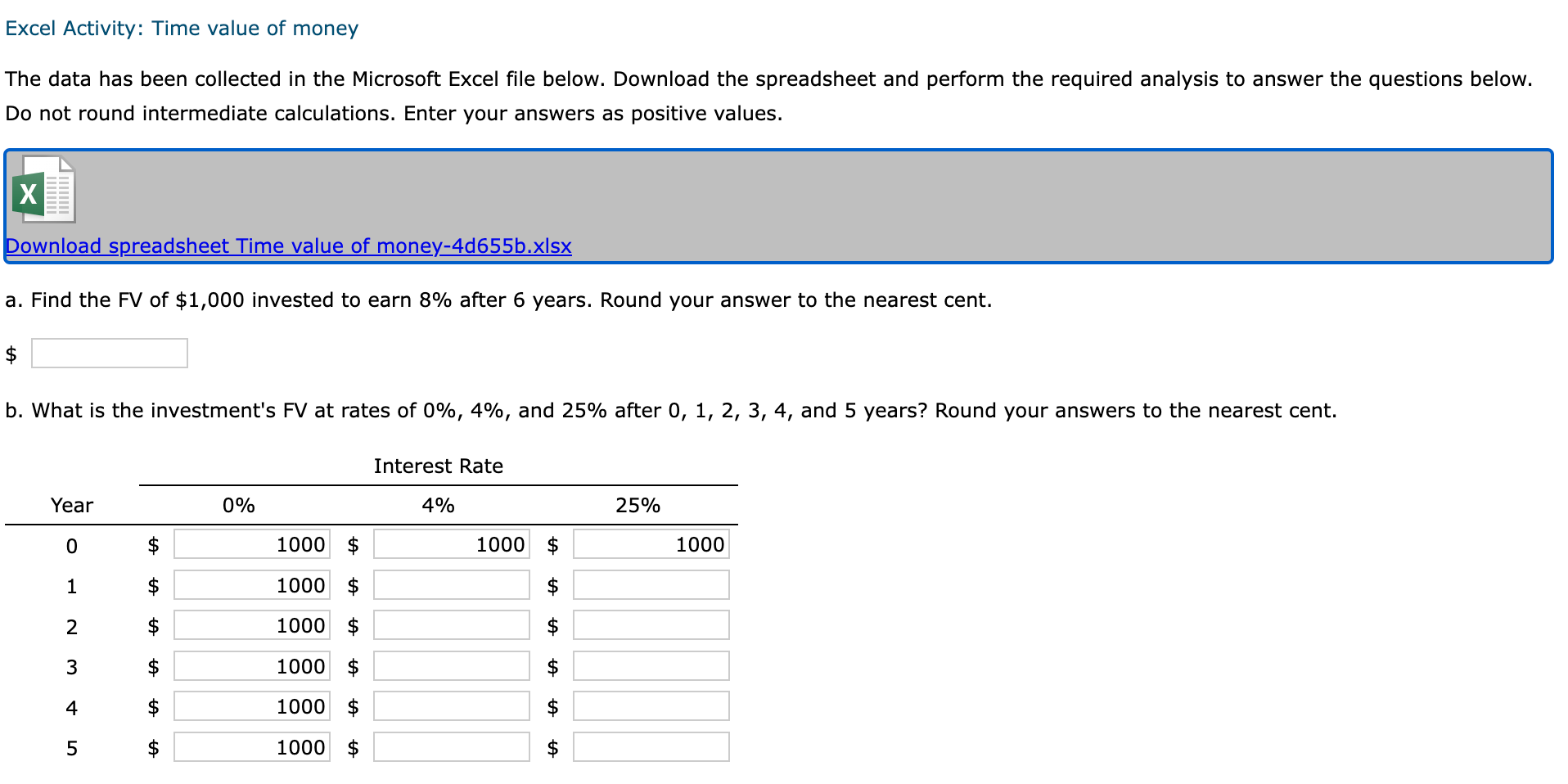
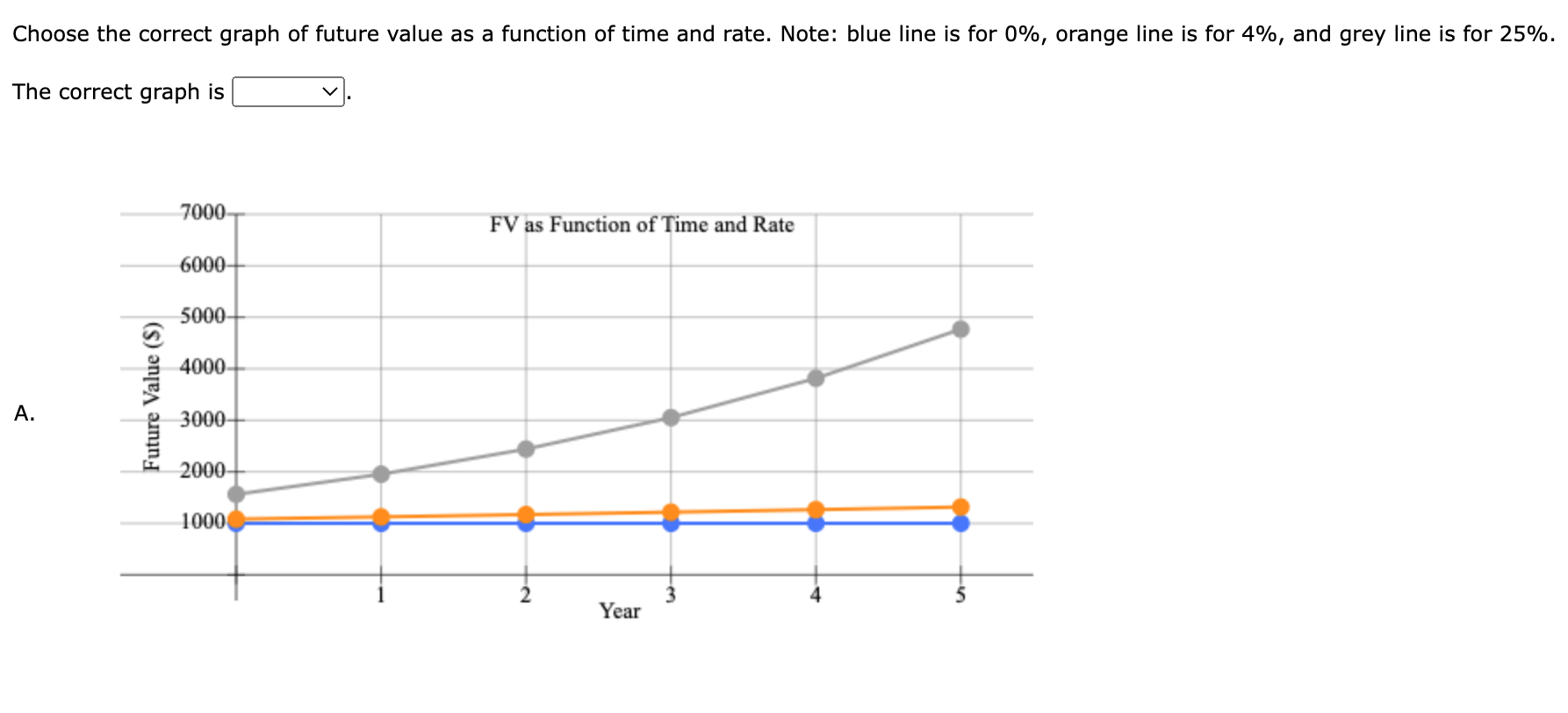
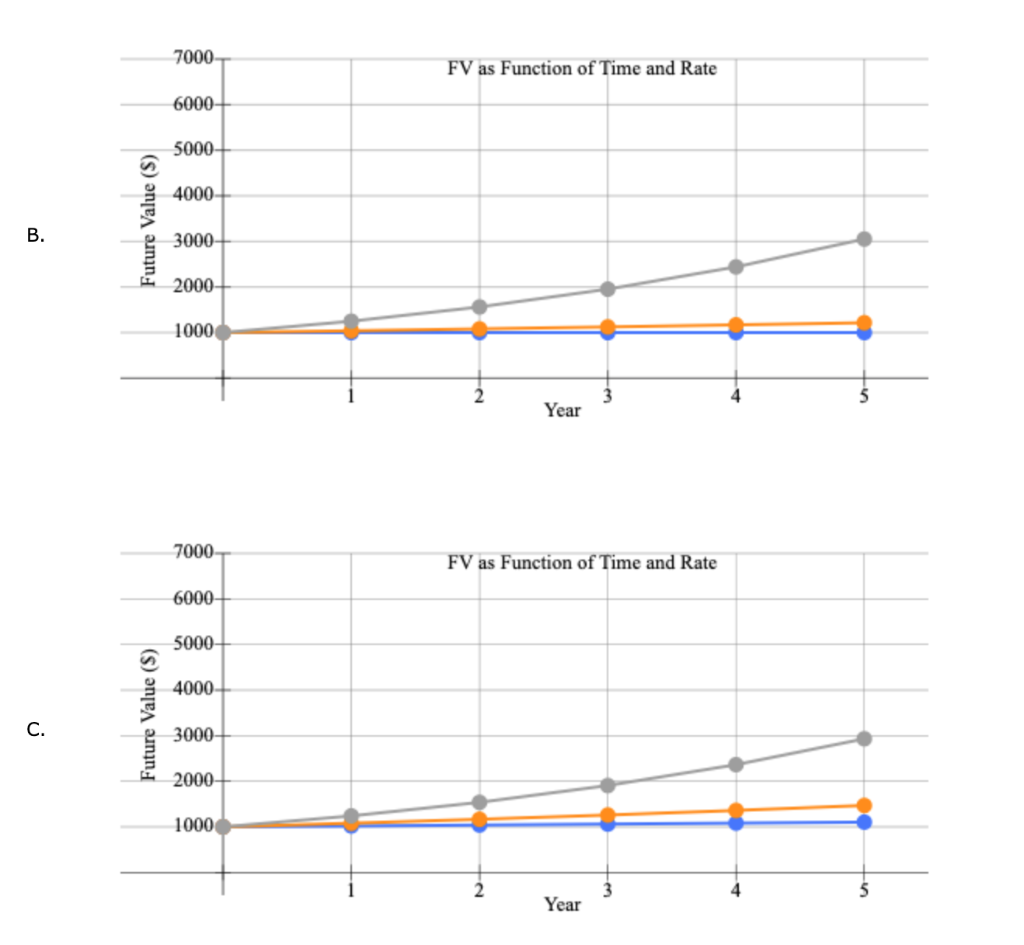
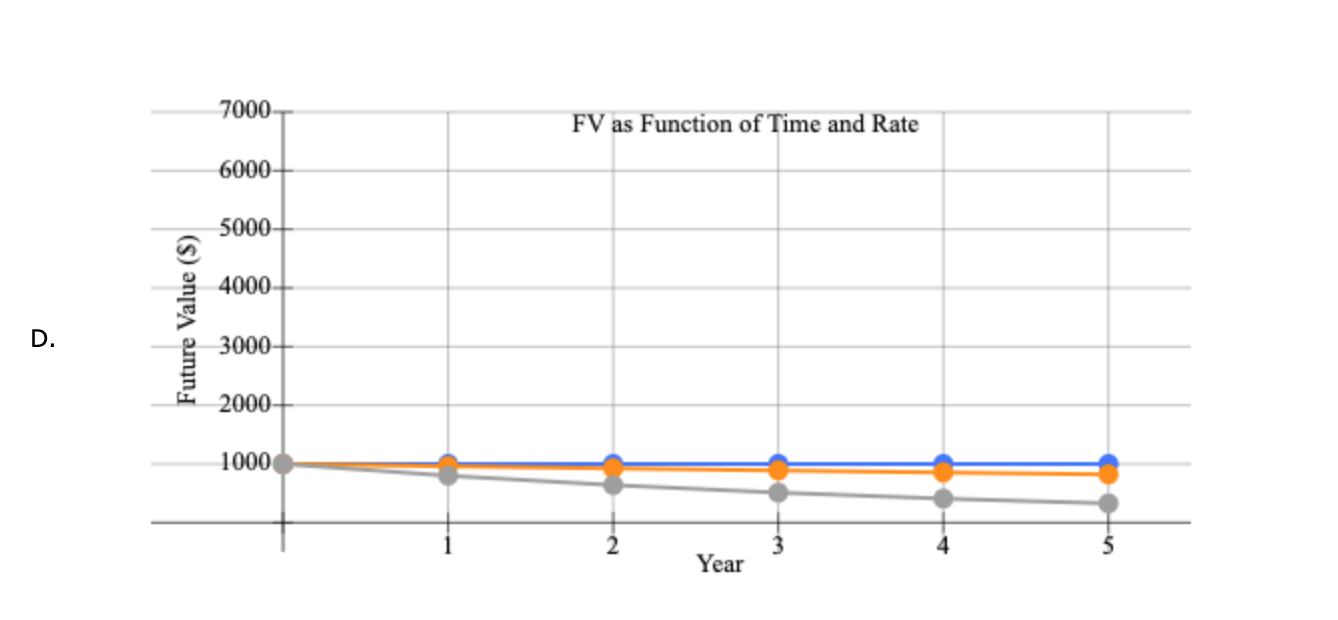
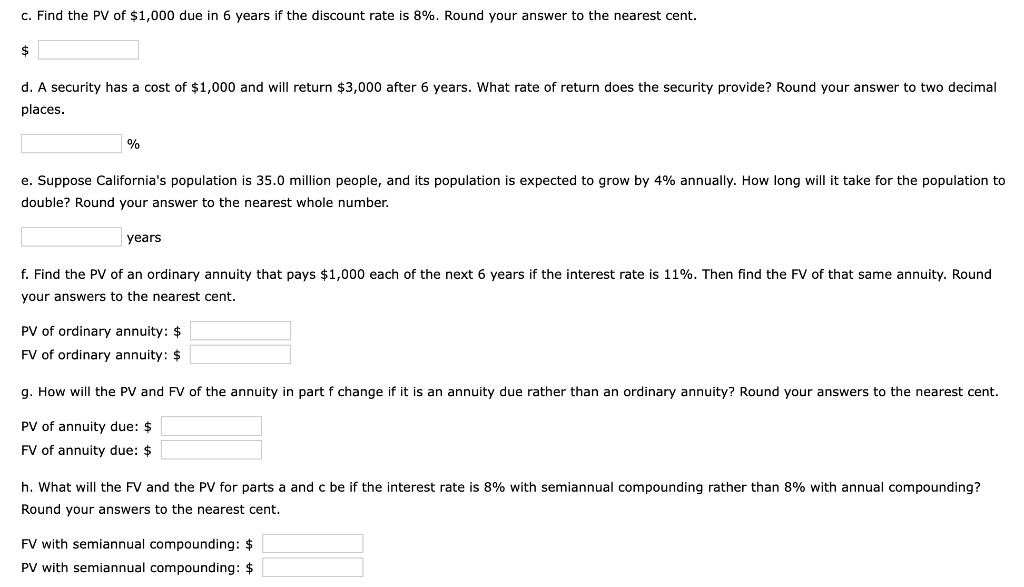
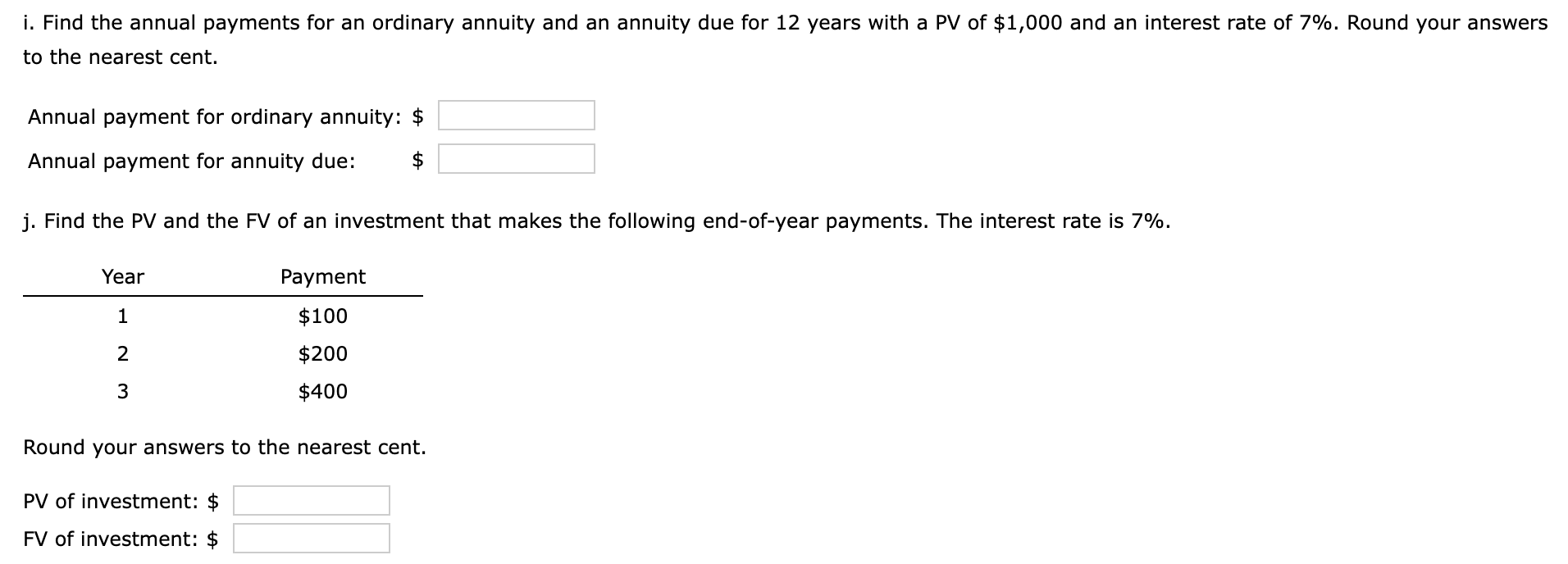
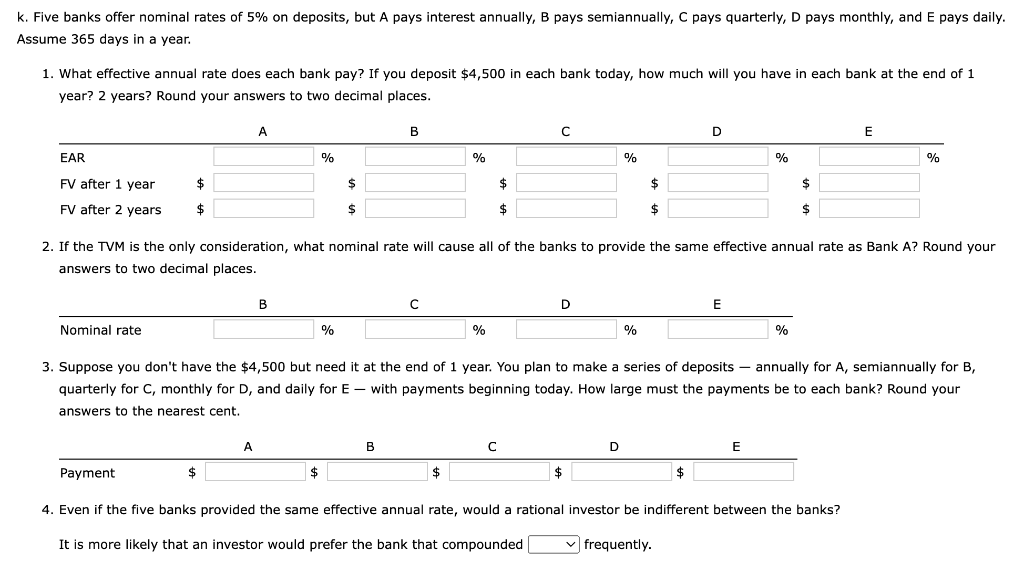
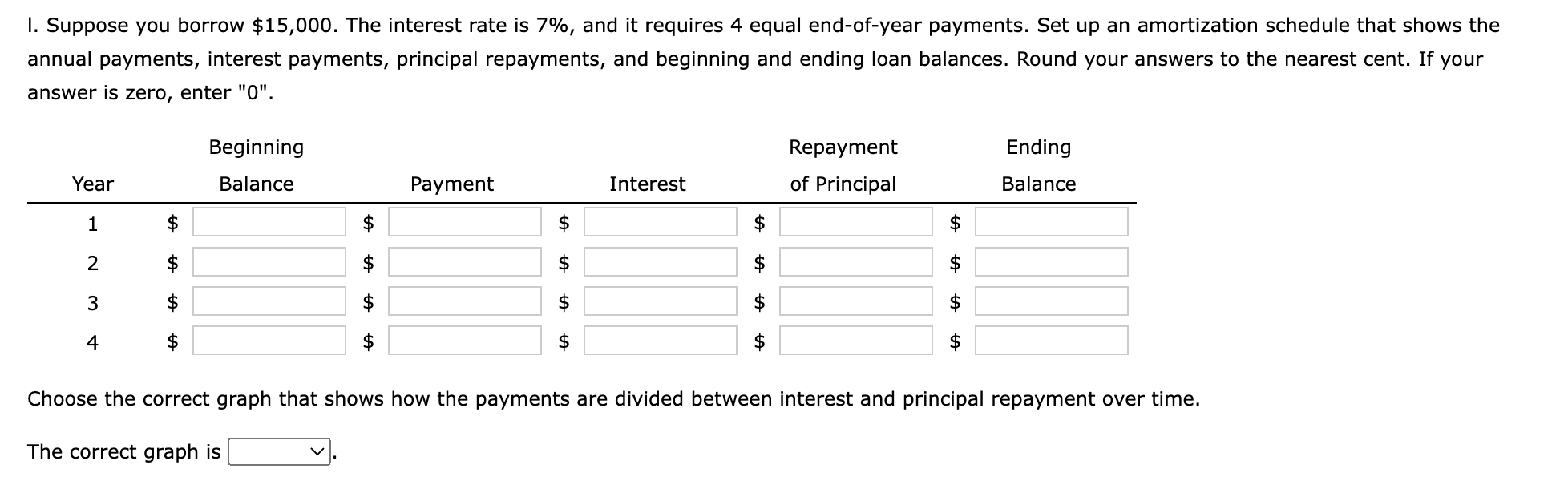
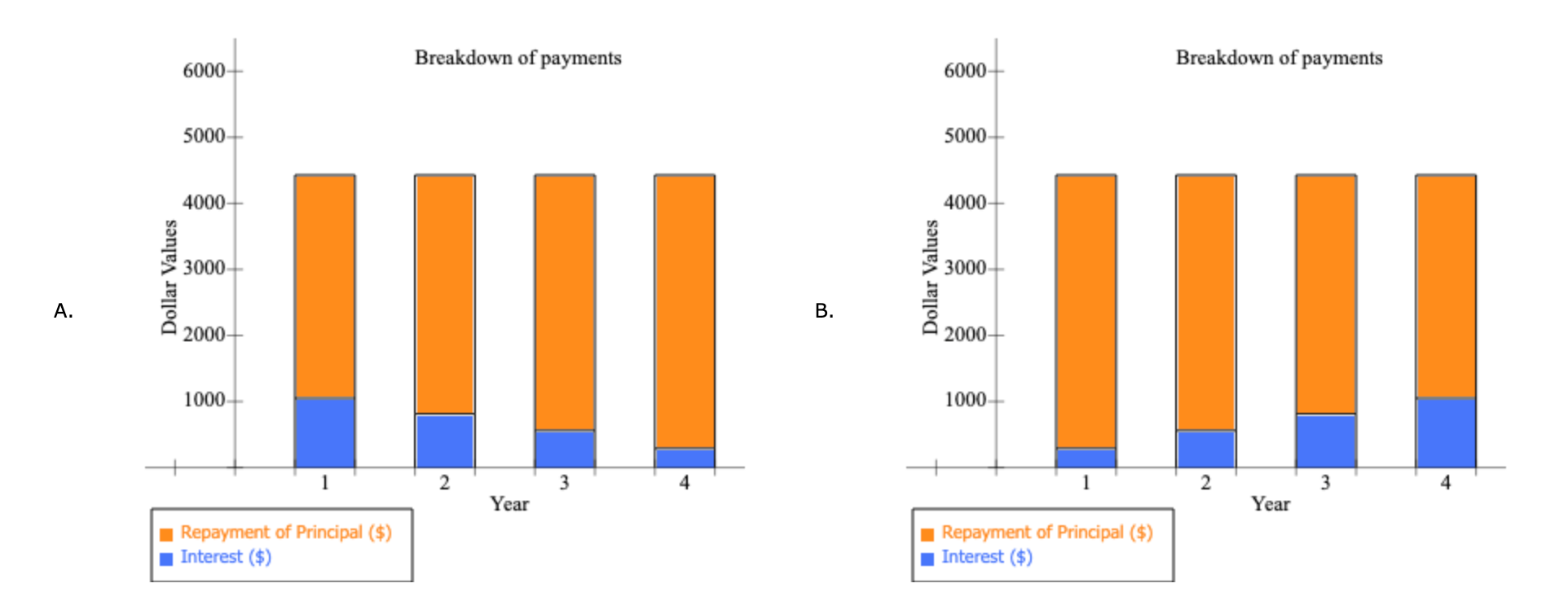
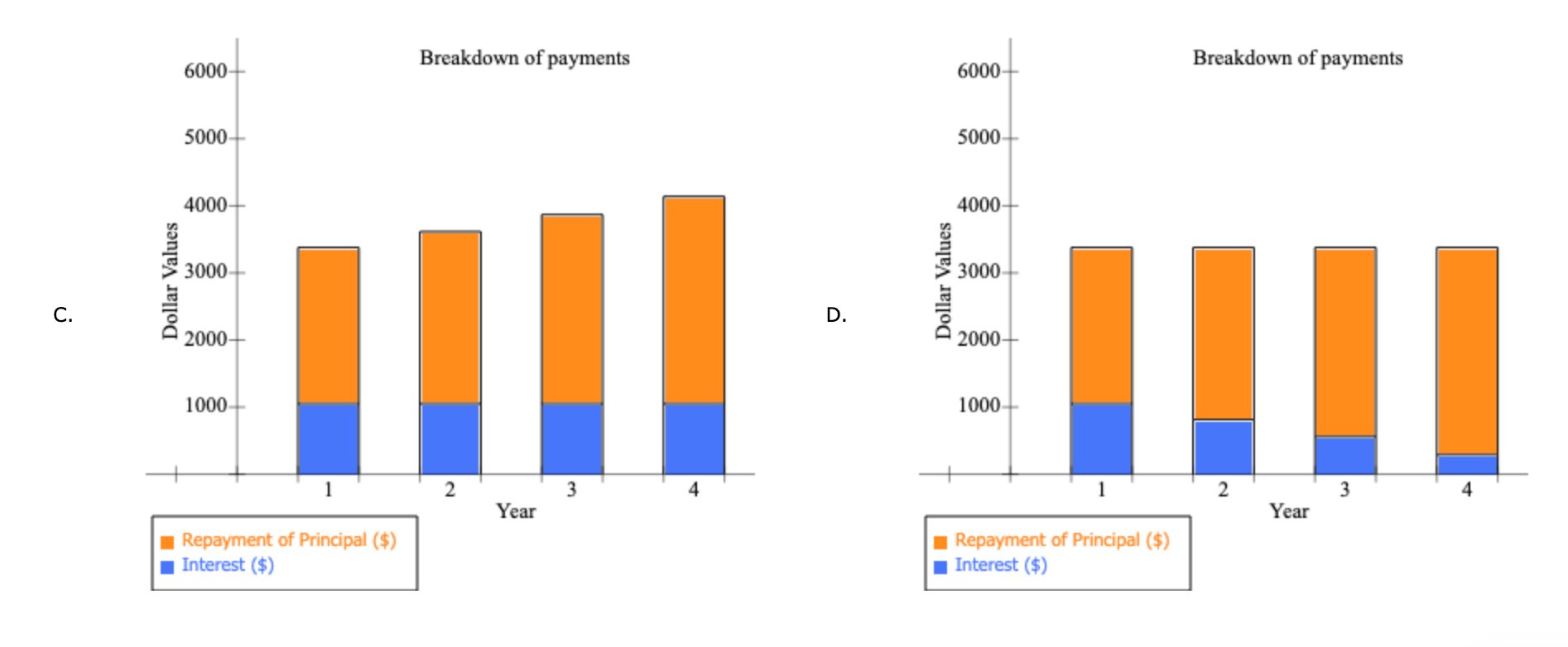
1 Time value of money 2 3 a. Finding FV 4. Investment (PV) $1,000 5 Interest rate (1) 8% 6 Number of years (N) 6 Formula 7 Future value (FV) #N/A 8 9 b. Creating a table with FVs at various interest rates and time periods using Data Table 10 Year (B6) Interest Rate (B5) 11 0% 4% 25% 12 0 13 1 14 2 15 3 16 4 17 5 18 19 Creating a graph with years on the horizontal axis and FV on the vertical axis 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 DO #N/A 39 C. Finding PV 40 Future value (FV) $1,000 41 Discount rate (1) 8% 42 Number of years (N) 6 Formulas 43 Present value (PV) #N/A 44 45 d. Finding the rate of return provided by the security 46 Cost of security (PV) $1,000 47 Future value of security (FV) $3,000 48 Number of years (N) 6 49 Rate of return (1) #N/A 50 51 e. Calculating the number of years required to double the population 52 Current population in millions (PV) 35 53 Growth rate (1) 4% 54 Doubled population in millions (FV) #N/A 55 Number of years required to double (N) 56 57 f. Finding the PV and FV of an ordinary annuity 58 Annuity (PMT) $1,000 59 Interest rate (1) 11% 60 Number of years (N) 6 61 Present value of ordinary annuity (PV) #N/A 62 Future value of ordinary annuity (FV) #N/A 63 64 g. Recalculating the PV and FV for part f if the annuity is an annuity due 65 Present value of annuity due (PV) #N/A 66 Future value of annuity due (FV) #N/A 67 68 h. Recalculating the PV and the FV for parts a and c if the interest rate is semiannually compounded 69 Future value (FV) #N/A 70 Present value (PV) #N/A 71 72 i. Finding the annual payments for an ordinary annuity and an annuity due 73 Present value (PV) $1,000 74 Discount rate (1) 7% 75 Number of years (N) 12 76 Annual payment for ordinary annuity (PMT1) #N/A 77 Annual payment for annuity due (PMT2) #N/A #N/A 79 j. Finding the PV and the FV of an investment that makes the following end-of-year payments 80 Year Payment 81 1 $100 82 2 $200 83 3 3 $400 84 04 85 Interest rate (1) 7% 86 Present value of investment (PV) #N/A 87 Future value of investment (FV) 88 89 k. Five banks offer the same nominal rate on deposits, but A pays interest annually, B pays semiannually, C pays quarterly, D pays monthly, and E pays daily. 90 (1) Calculating the effective annual rate for each bank and the future values of the deposit at the end of 1 year and 2 years 91 Nominal rate (INOM) 5% 92 Deposit (PV) $4,500 93 Number of days per year 365 94 Formulas 95 A B D D E 96 EAR EAR 97 FV after 1 year FV after 1 year 98 FV after 2 years FV after 2 years 99 100 (2) Calculating the nominal rates that will cause all of the banks to provide the same effective annual rate as Bank A 101 B C D E 102 Nominal rate (INOM) Nominal rate (INOM) 103 104 (3) Calculating the amount of payment to be made annually for A, semiannually for B, quarterly for C, monthly for D, and daily for E 105 Needed amount (FV) $4,500 106 Number of years (N) 1 107 108 A B D E 109 Payment (PMT) Payment (PMT) 110 111 I. Setting up the amortization schedule 112 Original amount of mortgage (PV) $15,000 113 Interest rate (1) 7% 114 Term to maturity, years (N) 4 115 Formula 116 Annual payment (PMT) #N/A 117 Formulas 111 I. Setting up the amortization schedule 112 Original amount of mortgage (PV) $15,000 113 Interest rate (1) 7% 114 Term to maturity, years (N) 4 115 Formula 116 Annual payment (PMT) #N/A 117 Repayment of 118 Year Beginning Balance Payment Interest Principal Ending Balance 119 1 120 2 121 3 122 4 123 124 Creating a graph that shows how the payments are divided between interest and principal repayment over time 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 Excel Activity: Time value of money The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel file below. Download the spreadsheet and perform the required analysis to answer the questions below. Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as positive values. X Download spreadsheet Time value of money-4d655b.xlsx a. Find the FV of $1,000 invested to earn 8% after 6 years. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ b. What is the investment's FV at rates of 0%, 4%, and 25% after 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years? Round your answers to the nearest cent. Interest Rate Year 0% 4% 25% 0 $ 1000 $ 1000 $ 1000 1 $ 1000 2 $ 1000 $ $ 3 $ 1000 $ 4 1000 $ $ $ 5 1000 $ Choose the correct graph of future value as a function of time and rate. Note: blue line is for 0%, orange line is for 4%, and grey line is for 25%. The correct graph is 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) A. 3000 2000 1000 Year 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) B. 3000 2000 1000 Year 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) C. 3000 2000- 1000 2 5 Year 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) D. 3000 2000 1000 C+ 2 ut Year c. Find the PV of $1,000 due in 6 years if the discount rate is 8%. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ d. A security has a cost of $1,000 and will return $3,000 after 6 years. What rate of return does the security provide? Round your answer to two decimal places. % e. Suppose California's population is 35.0 million people, and its population is expected to grow by 4% annually. How long will it take for the population to double? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. years f. Find the PV of an ordinary annuity that pays $1,000 each of the next 6 years if the interest rate is 11%. Then find the FV of that same annuity. Round your answers to the nearest cent. PV of ordinary annuity: $ FV of ordinary annuity: $ g. How will the PV and FV of the annuity in part f change if it is an annuity due rather than an ordinary annuity? Round your answers to the nearest cent. PV of annuity due: $ FV of annuity due: $ h. What will the FV and the PV for parts a and c be if the interest rate is 8% with semiannual compounding rather than 8% with annual compounding? Round your answers to the nearest cent. FV with semiannual compounding: $ PV with semiannual compounding: $ i. Find the annual payments for an ordinary annuity and an annuity due for 12 years with a PV of $1,000 and an interest rate of 7%. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Annual payment for ordinary annuity: $ Annual payment for annuity due: j. Find the PV and the FV of an investment that makes the following end-of-year payments. The interest rate is 7%. Year Payment 1 2 $100 $200 $400 3 Round your answers to the nearest cent. PV of investment: $ FV of investment: $ k. Five banks offer nominal rates of 5% on deposits, but A pays interest annually, B pays semiannually, C pays quarterly, D pays monthly, and E pays daily. Assume 365 days in a year. 1. What effective annual rate does each bank pay? If you deposit $4,500 in each bank today, how much will you have in each bank at the end of 1 year? 2 years? Round your answers to two decimal places. A B D E EAR % % % % % $ $ $ $ $ FV after 1 year FV after 2 years $ $ $ $ 2. If the TVM is the only consideration, what nominal rate will cause all of the banks to provide the same effective annual rate as Bank A? Round your answers to two decimal places. B c E Nominal rate % % % % 3. Suppose you don't have the $4,500 but need it at the end of 1 year. You plan to make a series of deposits - annually for A, semiannually for B, quarterly for C, monthly for D, and daily for E - with payments beginning today. How large must the payments be to each bank? Round your answers to the nearest cent. B D E Payment $ $ $ $ $ 4. Even if the five banks provided the same effective annual rate, would a rational investor be indifferent between the banks? It is more likely that an investor would prefer the bank that compounded frequently. 1. Suppose you borrow $15,000. The interest rate is 7%, and it requires 4 equal end-of-year payments. Set up an amortization schedule that shows the annual payments, interest payments, principal repayments, and beginning and ending loan balances. Round your answers to the nearest cent. If your answer is zero, enter "0". Ending Beginning Balance Repayment of Principal Year Payment Interest Balance 1 $ $ 2 $ $ $ $ $ 3 $ $ $ $ 4 $ Choose the correct graph that shows how the payments are divided between interest and principal repayment over time. The correct graph is Breakdown of payments Breakdown of payments 6000 6000 5000 5000 4000 4000 Dollar Values 3000 Dollar Values 3000 A. B. 2000 2000 1000 1000 1 3 4 1 2 3 4 Year Year Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) Breakdown of payments Breakdown of payments 6000 6000 5000 5000 4000 4000 3000 3000 Dollar Values Dollar Values C. D. 2000 . 2000 IIII 1000 1000 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Year Year Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) 1 Time value of money 2 3 a. Finding FV 4. Investment (PV) $1,000 5 Interest rate (1) 8% 6 Number of years (N) 6 Formula 7 Future value (FV) #N/A 8 9 b. Creating a table with FVs at various interest rates and time periods using Data Table 10 Year (B6) Interest Rate (B5) 11 0% 4% 25% 12 0 13 1 14 2 15 3 16 4 17 5 18 19 Creating a graph with years on the horizontal axis and FV on the vertical axis 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 DO #N/A 39 C. Finding PV 40 Future value (FV) $1,000 41 Discount rate (1) 8% 42 Number of years (N) 6 Formulas 43 Present value (PV) #N/A 44 45 d. Finding the rate of return provided by the security 46 Cost of security (PV) $1,000 47 Future value of security (FV) $3,000 48 Number of years (N) 6 49 Rate of return (1) #N/A 50 51 e. Calculating the number of years required to double the population 52 Current population in millions (PV) 35 53 Growth rate (1) 4% 54 Doubled population in millions (FV) #N/A 55 Number of years required to double (N) 56 57 f. Finding the PV and FV of an ordinary annuity 58 Annuity (PMT) $1,000 59 Interest rate (1) 11% 60 Number of years (N) 6 61 Present value of ordinary annuity (PV) #N/A 62 Future value of ordinary annuity (FV) #N/A 63 64 g. Recalculating the PV and FV for part f if the annuity is an annuity due 65 Present value of annuity due (PV) #N/A 66 Future value of annuity due (FV) #N/A 67 68 h. Recalculating the PV and the FV for parts a and c if the interest rate is semiannually compounded 69 Future value (FV) #N/A 70 Present value (PV) #N/A 71 72 i. Finding the annual payments for an ordinary annuity and an annuity due 73 Present value (PV) $1,000 74 Discount rate (1) 7% 75 Number of years (N) 12 76 Annual payment for ordinary annuity (PMT1) #N/A 77 Annual payment for annuity due (PMT2) #N/A #N/A 79 j. Finding the PV and the FV of an investment that makes the following end-of-year payments 80 Year Payment 81 1 $100 82 2 $200 83 3 3 $400 84 04 85 Interest rate (1) 7% 86 Present value of investment (PV) #N/A 87 Future value of investment (FV) 88 89 k. Five banks offer the same nominal rate on deposits, but A pays interest annually, B pays semiannually, C pays quarterly, D pays monthly, and E pays daily. 90 (1) Calculating the effective annual rate for each bank and the future values of the deposit at the end of 1 year and 2 years 91 Nominal rate (INOM) 5% 92 Deposit (PV) $4,500 93 Number of days per year 365 94 Formulas 95 A B D D E 96 EAR EAR 97 FV after 1 year FV after 1 year 98 FV after 2 years FV after 2 years 99 100 (2) Calculating the nominal rates that will cause all of the banks to provide the same effective annual rate as Bank A 101 B C D E 102 Nominal rate (INOM) Nominal rate (INOM) 103 104 (3) Calculating the amount of payment to be made annually for A, semiannually for B, quarterly for C, monthly for D, and daily for E 105 Needed amount (FV) $4,500 106 Number of years (N) 1 107 108 A B D E 109 Payment (PMT) Payment (PMT) 110 111 I. Setting up the amortization schedule 112 Original amount of mortgage (PV) $15,000 113 Interest rate (1) 7% 114 Term to maturity, years (N) 4 115 Formula 116 Annual payment (PMT) #N/A 117 Formulas 111 I. Setting up the amortization schedule 112 Original amount of mortgage (PV) $15,000 113 Interest rate (1) 7% 114 Term to maturity, years (N) 4 115 Formula 116 Annual payment (PMT) #N/A 117 Repayment of 118 Year Beginning Balance Payment Interest Principal Ending Balance 119 1 120 2 121 3 122 4 123 124 Creating a graph that shows how the payments are divided between interest and principal repayment over time 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 Excel Activity: Time value of money The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel file below. Download the spreadsheet and perform the required analysis to answer the questions below. Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers as positive values. X Download spreadsheet Time value of money-4d655b.xlsx a. Find the FV of $1,000 invested to earn 8% after 6 years. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ b. What is the investment's FV at rates of 0%, 4%, and 25% after 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years? Round your answers to the nearest cent. Interest Rate Year 0% 4% 25% 0 $ 1000 $ 1000 $ 1000 1 $ 1000 2 $ 1000 $ $ 3 $ 1000 $ 4 1000 $ $ $ 5 1000 $ Choose the correct graph of future value as a function of time and rate. Note: blue line is for 0%, orange line is for 4%, and grey line is for 25%. The correct graph is 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) A. 3000 2000 1000 Year 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) B. 3000 2000 1000 Year 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) C. 3000 2000- 1000 2 5 Year 7000 FV as Function of Time and Rate 6000 5000 4000 Future Value (S) D. 3000 2000 1000 C+ 2 ut Year c. Find the PV of $1,000 due in 6 years if the discount rate is 8%. Round your answer to the nearest cent. $ d. A security has a cost of $1,000 and will return $3,000 after 6 years. What rate of return does the security provide? Round your answer to two decimal places. % e. Suppose California's population is 35.0 million people, and its population is expected to grow by 4% annually. How long will it take for the population to double? Round your answer to the nearest whole number. years f. Find the PV of an ordinary annuity that pays $1,000 each of the next 6 years if the interest rate is 11%. Then find the FV of that same annuity. Round your answers to the nearest cent. PV of ordinary annuity: $ FV of ordinary annuity: $ g. How will the PV and FV of the annuity in part f change if it is an annuity due rather than an ordinary annuity? Round your answers to the nearest cent. PV of annuity due: $ FV of annuity due: $ h. What will the FV and the PV for parts a and c be if the interest rate is 8% with semiannual compounding rather than 8% with annual compounding? Round your answers to the nearest cent. FV with semiannual compounding: $ PV with semiannual compounding: $ i. Find the annual payments for an ordinary annuity and an annuity due for 12 years with a PV of $1,000 and an interest rate of 7%. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Annual payment for ordinary annuity: $ Annual payment for annuity due: j. Find the PV and the FV of an investment that makes the following end-of-year payments. The interest rate is 7%. Year Payment 1 2 $100 $200 $400 3 Round your answers to the nearest cent. PV of investment: $ FV of investment: $ k. Five banks offer nominal rates of 5% on deposits, but A pays interest annually, B pays semiannually, C pays quarterly, D pays monthly, and E pays daily. Assume 365 days in a year. 1. What effective annual rate does each bank pay? If you deposit $4,500 in each bank today, how much will you have in each bank at the end of 1 year? 2 years? Round your answers to two decimal places. A B D E EAR % % % % % $ $ $ $ $ FV after 1 year FV after 2 years $ $ $ $ 2. If the TVM is the only consideration, what nominal rate will cause all of the banks to provide the same effective annual rate as Bank A? Round your answers to two decimal places. B c E Nominal rate % % % % 3. Suppose you don't have the $4,500 but need it at the end of 1 year. You plan to make a series of deposits - annually for A, semiannually for B, quarterly for C, monthly for D, and daily for E - with payments beginning today. How large must the payments be to each bank? Round your answers to the nearest cent. B D E Payment $ $ $ $ $ 4. Even if the five banks provided the same effective annual rate, would a rational investor be indifferent between the banks? It is more likely that an investor would prefer the bank that compounded frequently. 1. Suppose you borrow $15,000. The interest rate is 7%, and it requires 4 equal end-of-year payments. Set up an amortization schedule that shows the annual payments, interest payments, principal repayments, and beginning and ending loan balances. Round your answers to the nearest cent. If your answer is zero, enter "0". Ending Beginning Balance Repayment of Principal Year Payment Interest Balance 1 $ $ 2 $ $ $ $ $ 3 $ $ $ $ 4 $ Choose the correct graph that shows how the payments are divided between interest and principal repayment over time. The correct graph is Breakdown of payments Breakdown of payments 6000 6000 5000 5000 4000 4000 Dollar Values 3000 Dollar Values 3000 A. B. 2000 2000 1000 1000 1 3 4 1 2 3 4 Year Year Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) Breakdown of payments Breakdown of payments 6000 6000 5000 5000 4000 4000 3000 3000 Dollar Values Dollar Values C. D. 2000 . 2000 IIII 1000 1000 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Year Year Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($) Repayment of Principal ($) Interest ($)




















