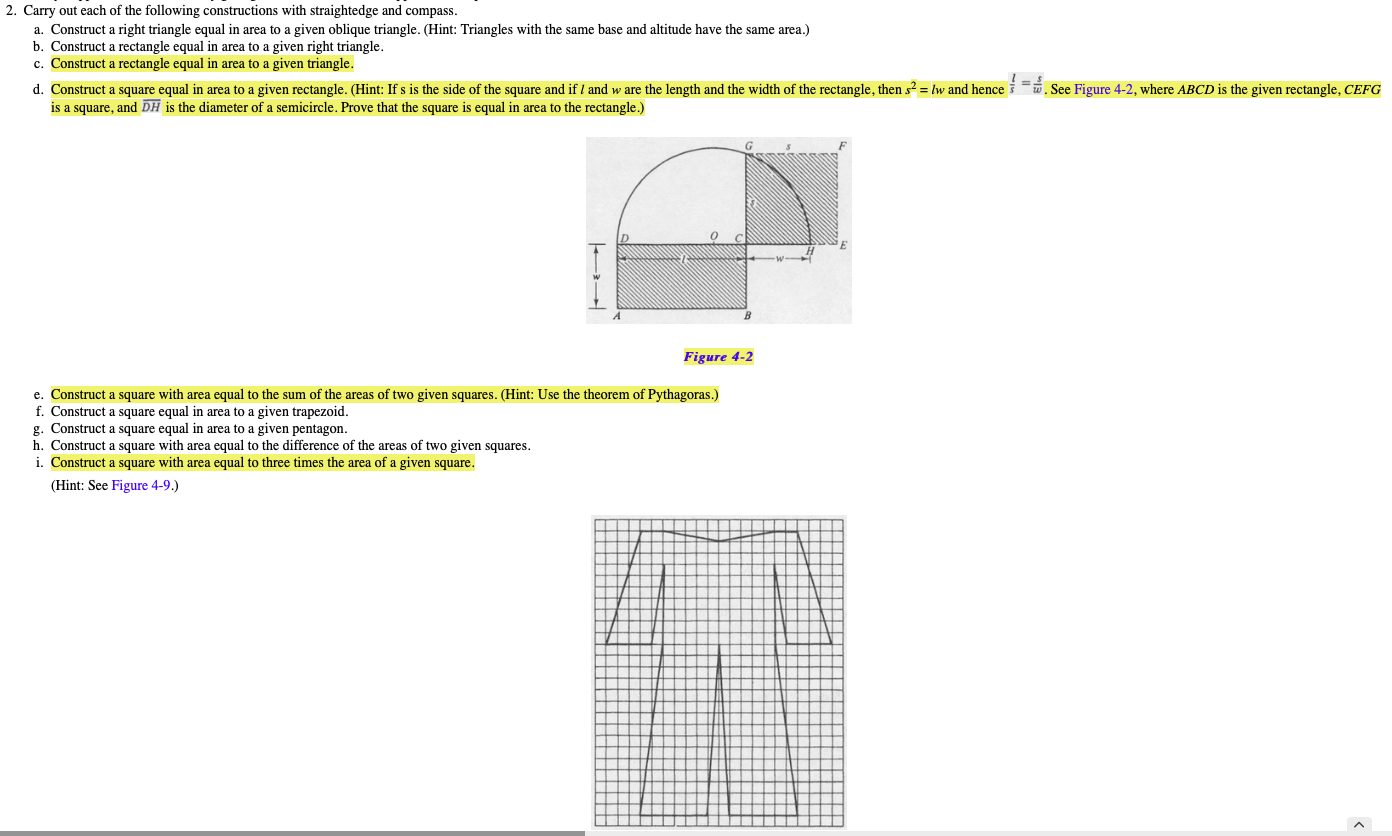
2. Carry out each of the following constructions with straightedge and compass. a. Construct a right triangle equal in area to a given oblique triangle. (Hint: Triangles with the same base and altitude have the same area.) b. Construct a rectangle equal in area to a given right triangle. c. Construct a rectangle equal in area to a given triangle. d. Construct a square equal in area to a given rectangle. (Hint: If s is the side of the square and if I and w are the length and the width of the rectangle, then s2 = lw and hence } = See Figure 4-2, where ABCD is the given rectangle, CEFG is a square, and DH is the diameter of a semicircle. Prove that the square is equal in area to the rectangle.) - Figure 4-2 e. Construct a square with area equal to the sum of the areas of two given squares. (Hint: Use the theorem of Pythagoras.) f. Construct a square equal in area to a given trapezoid. g. Construct a square equal in area to a given pentagon. h. Construct a square with area equal to the difference of the areas of two given squares. i. Construct a square with area equal three times the of a given square. (Hint: See Figure 4-9.) 2. Carry out each of the following constructions with straightedge and compass. a. Construct a right triangle equal in area to a given oblique triangle. (Hint: Triangles with the same base and altitude have the same area.) b. Construct a rectangle equal in area to a given right triangle. c. Construct a rectangle equal in area to a given triangle. d. Construct a square equal in area to a given rectangle. (Hint: If s is the side of the square and if I and w are the length and the width of the rectangle, then s2 = lw and hence } = See Figure 4-2, where ABCD is the given rectangle, CEFG is a square, and DH is the diameter of a semicircle. Prove that the square is equal in area to the rectangle.) - Figure 4-2 e. Construct a square with area equal to the sum of the areas of two given squares. (Hint: Use the theorem of Pythagoras.) f. Construct a square equal in area to a given trapezoid. g. Construct a square equal in area to a given pentagon. h. Construct a square with area equal to the difference of the areas of two given squares. i. Construct a square with area equal three times the of a given square. (Hint: See Figure 4-9.)







