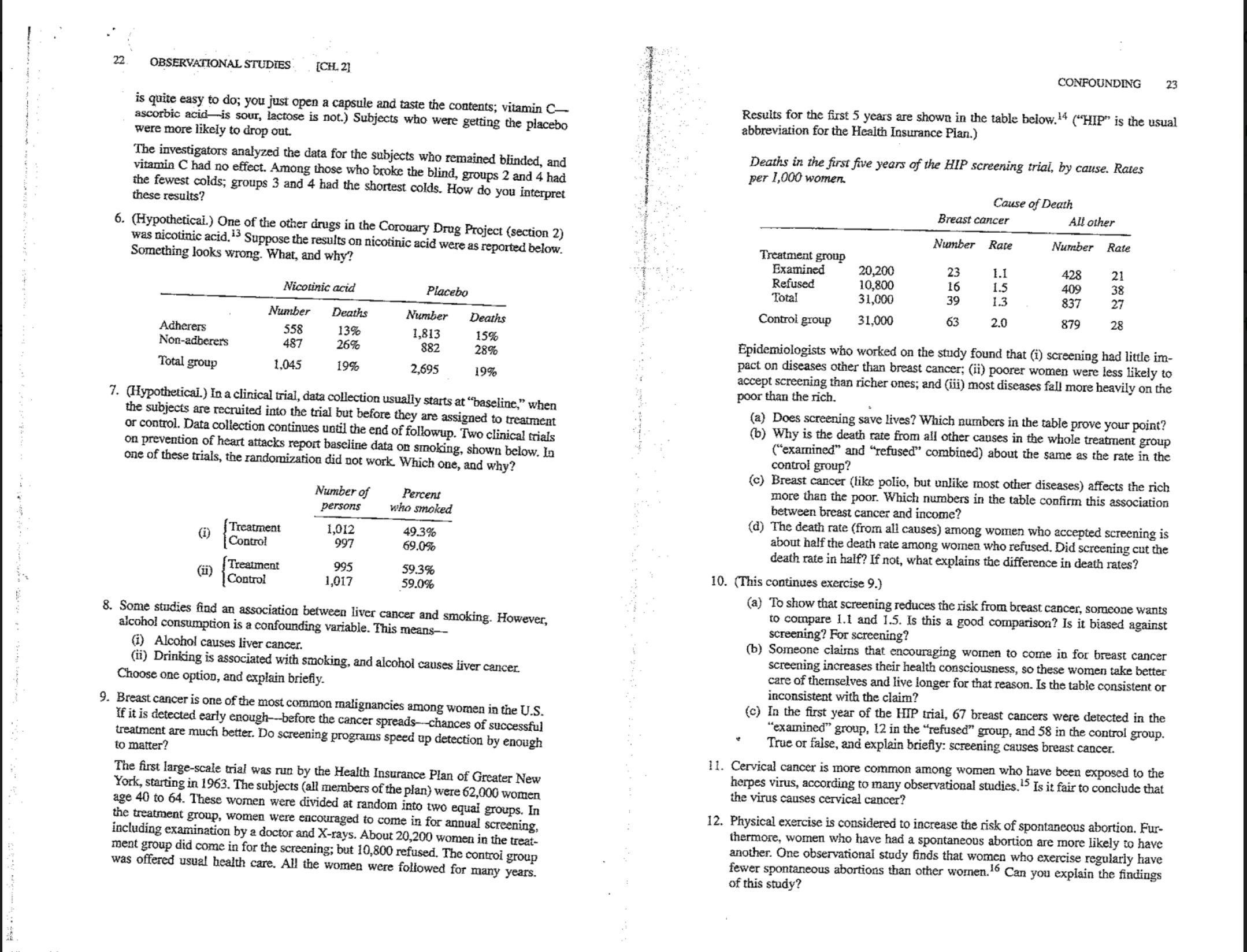
22 OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES . [CH. 2] CONFOUNDING 23 is quite easy to do; you just open a capsule and taste the contents; vitamin C- Results for the first 5 years are shown in the table below. " ("HIP" is the usual ascorbic acid-is sour, lactose is not.) Subjects who were getting the placebo abbreviation for the Health Insurance Plan.) were more likely to drop out. The investigators analyzed the data for the subjects who remained blinded, and Deaths in the first five years of the HIP screening trial, by cause. Rates vitamin C had no effect. Among those who broke the blind, groups 2 and 4 had per 1,000 women. the fewest colds; groups 3 and 4 had the shortest colds. How do you interpret Cause of Death these results? Breast cancer All other 6. (Hypothetical.) One of the other drugs in the Coronary Drug Project (section 2) Number Rate Number Rate was nicotinic acid. " Suppose the results on nicotinic acid were as reported below. Treatment group Something looks wrong. What, and why? Examined 20,200 25 1.I 428 21 Refused 10,800 16 1.5 409 38 Nicotinic acid Placebo Total 31,000 39 1.3 837 27 53 879 28 Number Deaths Number Deaths Control group 31,000 2.0 Adherers 558 13% 1,813 15% Non-adberers 487 Epidemiologists who worked on the study found that (i) screening had little im- 26% 882 28% pact on diseases other than breast cancer; (ii) poorer women were less likely to Total group 1,045 1990 2.695 19% accept screening than richer ones; and (ili) most diseases fall more heavily on the poor than the rich. 7. (Hypothetical.) In a clinical trial, data collection usually starts at "baseline," when the subjects are recruited into the trial but before they are assigned to treatment (a) Does screening save lives? Which numbers in the table prove your point? or control. Data collection continues until the end of followup. Two clinical trials b) Why is the death rate from all other causes in the whole treatment group on prevention of heart attacks report baseline data on smoking, shown below. In ("examined" and "refused" combined) about the same as the rate in the one of these trials, the randomization did not work. Which one, and why? control group? (c) Breast cancer (like polio, but unlike most other diseases) affects the rich Number of more than the poor. Which numbers in the table confirm this association Percent persons who smoked between breast cancer and income? d) The death rate (from all causes) among women who accepted screening is (i) Treatment 1,012 19.3% about half the death rate among women who refused. Did screening cut the Control 997 69.0% death rate in half? If not, what explains the difference in death rates? (ii) Treatment 995 59.3% 10. (This continues exercise 9.) Contro 1,017 59.0% a) To show that screening reduces the risk from breast cancer, someone wants 8. Some studies find an association between liver cancer and smoking. However, o compare 1.1 and 1.5. Is this a good comparison? Is it biased against alcohol consumption is a confounding variable. This means- screening? For screening? i) Alcohol causes liver cancer. (b) Someone claims that encouraging wornen to come in for breast cancer (ii) Drinking is associated with smoking, and alcohol causes liver cancer. screening increases their health consciousness, so these women take better care of themselves and live longer for that reason. Is the table consistent or Choose one option, and explain briefly. inconsistent with the claim? 9. Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies among women in the U.S. (c) In the first year of the HIP trial, 67 breast cancers were detected in the If it is detected early enough--before the cancer spreads-chances of successful 'examined" group, 12 in the "refused" group, and 58 in the control group. treatment are much better. Do screening programs speed up detection by enough True or false, and explain briefly: screening causes breast cancer. to matter? 11. Cervical cancer is more common among women who have been exposed to the The first large-scale trial was run by the Health Insurance Plan of Greater New herpes virus, according to many observational studies." Is it fair to conclude that York, starting in 1963. The subjects (all members of the plan) were 62,000 women the virus causes cervical cancer? age 40 to 64. These women were divided at random into two equal groups. In 12. Physical exercise is considered to increase the risk of spontaneous abortion. Fur- the treatment group, women were encouraged to come in for annual screening, thermore, women who have had a spontaneous abortion are more likely to have including examination by a doctor and X-rays. About 20,200 women in the treat- another. One observational study finds that women who exercise regularly have ment group did come in for the screening; but 10,800 refused. The control group fewer spontaneous abortions than other women. Can you explain the findings was offered usual health care. All the women were followed for many years. of this study