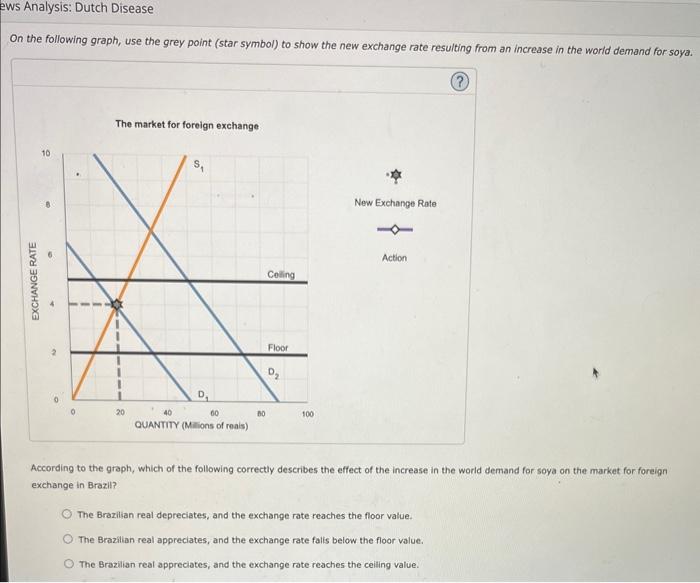
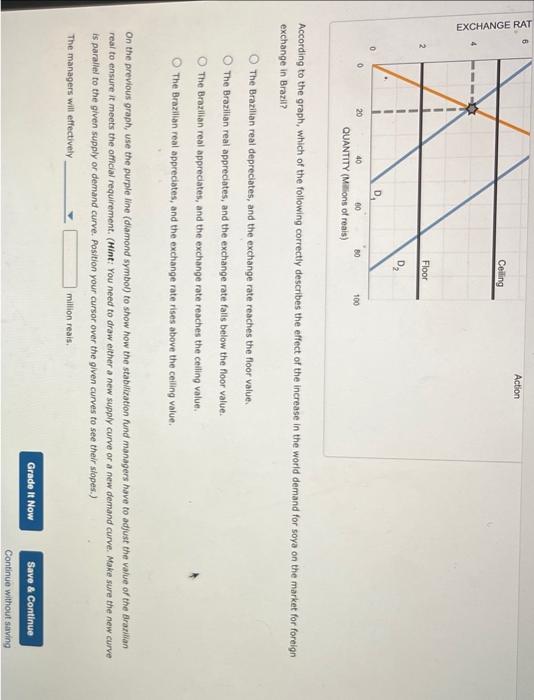
3. The currency stabilization fund Suppose the Brazilian government recognizes that its reliance on soya exports makes it vulnerable to the Dutch Disease. On the one hand, if soya prices increase, the Brazilian real will appreciate, the real exchange rate will increase, and the nation's exports will become more expensive for other countries to buy, On the other hand, if soya prices fall, the Brazilian real will depreciate, and the country's revenues will decline. The Brazilian government creates a currency stabilization fund to maintain a stable exchange rate to avoid a negative outcome. To stabilize the value of a currency within a certain range, the stabilization fund managers take one of the following actions: - If the real depreciates below some threshold value (a floor) per real, the fund managers will purchase the excess supply of reais in the international exchange market to increase the value of the real to at least the floor value. - If the real appreciates above some threshold value (a ceiling) per real, the fund managers will sell the excess supply of reais to lower its value to at least the ceiling value. Consider the following scenario: Brazil establishes a currency stabilization fund to keep the exchange rate between $2 per Brazilian real and $5 per Brazilian real. Initially, the market exchange rate is within the allowed range at $4 per Brazlian real, as shown by the intersection of the demand ( D1) and supply (S1) curves for the Brazilian real on the following graph. Suppose thot due to an increase in the worla demand for soya, Brazil is able to export more soya, and the demand for the Brazilion real increases from D1 to D2. On the following graph, use the grey point (star symbol) to show the new exchange rate resulting from an increase in the world demand for soya. According to the graph, which of the following correctly describes the effect of the increase in the world demand for soya on the market for foreign exchange in Brazil? The Brazilian real depreciates, and the exchange rate reaches the floor value. The Brazilian real appreciates, and the exchange rate falis below the floor value. The Brazilian real appreciates, and the exchange rate reaches the ceiling value. According to the graph, which of the following correctly describes the effect of the increase in the world demand for soya on the market for foreign exchange in Brazil? The Brazilian real depreciates, and the exchange rate reaches the floor value. The Brazilian real appreciates, and the exchange rate falls below the floor value. The Brazilian real appreciates, and the exchange rate reaches the ceiling value. The Brazilian real appreciates, and the exchange rate rises above the ceiling value, On the previous graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to show how the stabilization fund managers have to adjust the value of the Arazikan real to ensure it meets the official requirement. (Mint: You need to draw either a new supply curve or a new demand curve. Make sure the new curve. is paraliel to the given supply or demand curve. Position your cursor over the given curves to see their sibpes.) The managers will effectively million reais