Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
4 Factor Rank Click a factor to learn more High, Medium, Low Barriers to Entry Economies of Scale and Scope Capital Requirements and High
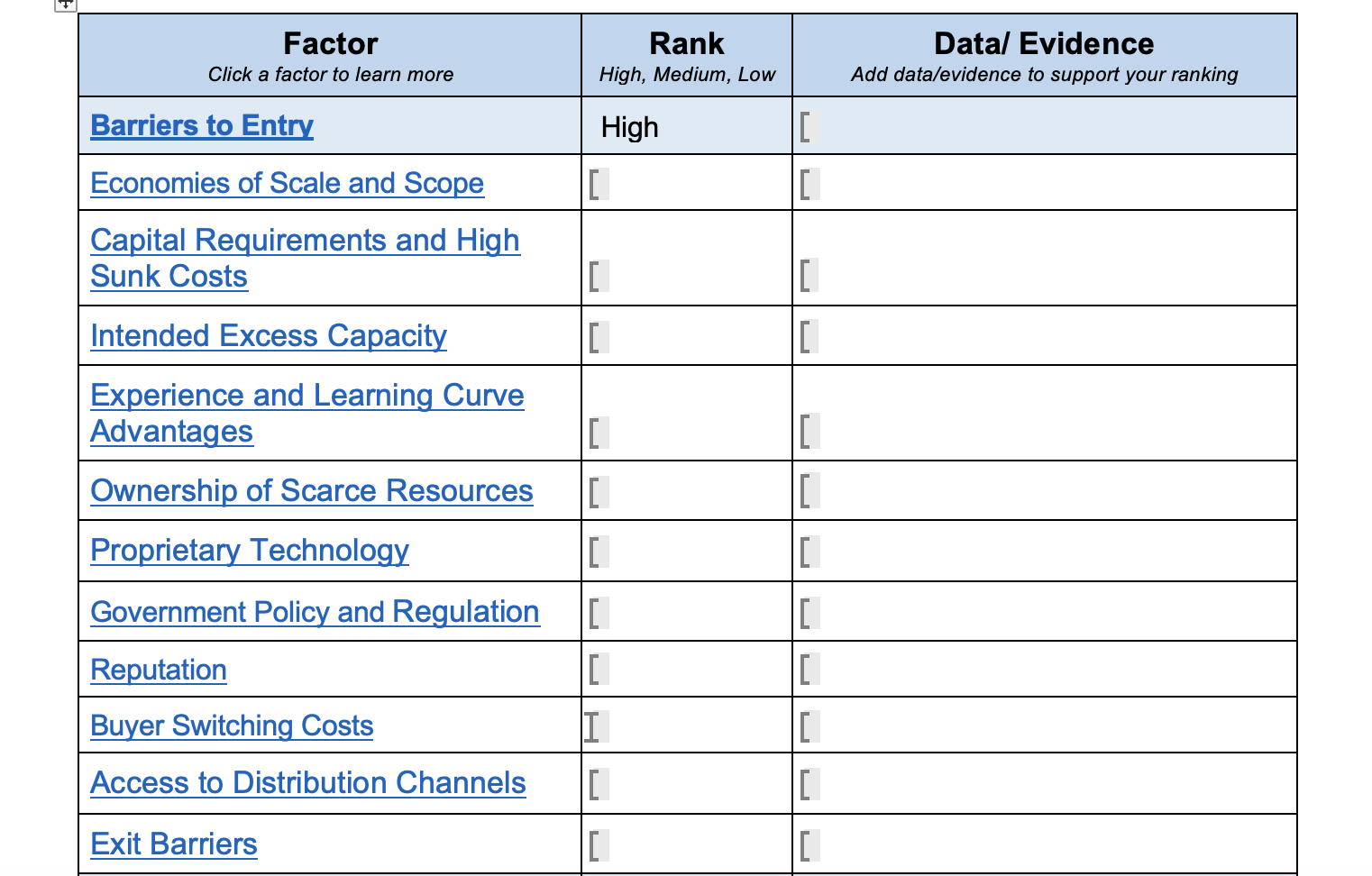
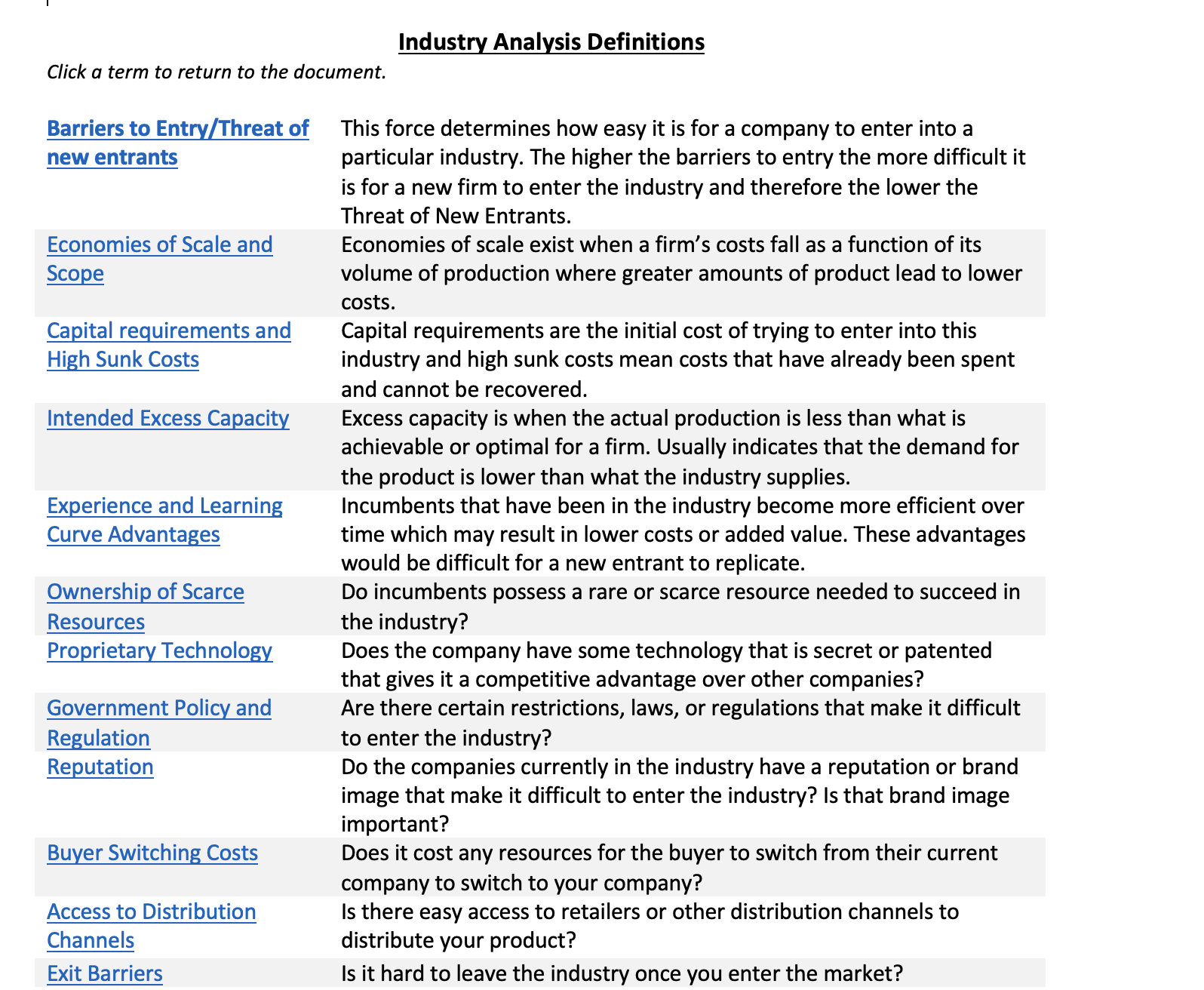
4 Factor Rank Click a factor to learn more High, Medium, Low Barriers to Entry Economies of Scale and Scope Capital Requirements and High Sunk Costs High [ [ [ [ Intended Excess Capacity [ Experience and Learning Curve Advantages Ownership of Scarce Resources Proprietary Technology ] Government Policy and Regulation [ Reputation [ Buyer Switching Costs IT [ Access to Distribution Channels [ [ Exit Barriers [ Data/ Evidence Add data/evidence to support your ranking Click a term to return to the document. Barriers to Entry/Threat of new entrants Economies of Scale and Scope Capital requirements and High Sunk Costs Intended Excess Capacity Experience and Learning Curve Advantages Ownership of Scarce Resources Proprietary Technology Government Policy and Regulation Reputation Buyer Switching Costs Access to Distribution Channels Exit Barriers Industry Analysis Definitions This force determines how easy it is for a company to enter into a particular industry. The higher the barriers to entry the more difficult it is for a new firm to enter the industry and therefore the lower the Threat of New Entrants. Economies of scale exist when a firm's costs fall as a function of its volume of production where greater amounts of product lead to lower costs. Capital requirements are the initial cost of trying to enter into this industry and high sunk costs mean costs that have already been spent and cannot be recovered. Excess capacity is when the actual production is less than what is achievable or optimal for a firm. Usually indicates that the demand for the product is lower than what the industry supplies. Incumbents that have been in the industry become more efficient over time which may result in lower costs or added value. These advantages would be difficult for a new entrant to replicate. Do incumbents possess a rare or scarce resource needed to succeed in the industry? Does the company have some technology that is secret or patented that gives it a competitive advantage over other companies? Are there certain restrictions, laws, or regulations that make it difficult to enter the industry? Do the companies currently in the industry have a reputation or brand image that make it difficult to enter the industry? Is that brand image important? Does it cost any resources for the buyer to switch from their current company to switch to your company? Is there easy access to retailers or other distribution channels to distribute your product? Is it hard to leave the industry once you enter the market?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


