Question
6. Ricardian equivalence and the government budget constraint: Consider the intertemporal budget constraint in equation (18.5). , pdv of spending + initial debt = pdv
6. Ricardian equivalence and the government budget constraint: Consider the intertemporal budget constraint in equation (18.5). 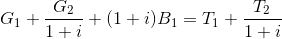 , pdv of spending + initial debt = pdv of taxes.
, pdv of spending + initial debt = pdv of taxes.
Assume the interest rate is i = 5%.
(a) Suppose the government cuts taxes today by $100 billion. Describe three possible ways the government can change spending and taxes to satisfy its budget constraint.
(b) Suppose consumers obey the permanent-income hypothesis (discussed in Chapter 10). Would their consumption rise, fall, or stay the same for each of the alternatives considered in part (a)?
(c) What happens to private saving, total saving, and investment in the three scenarios? Why? (Assume foreign saving does not change.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


