Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
8-126 Two constant-pressure devices, each filled with 30 kg of air, have temperatures of 900 K and 300 K. A heat engine placed between
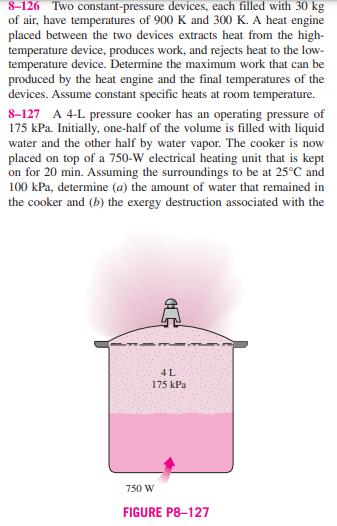
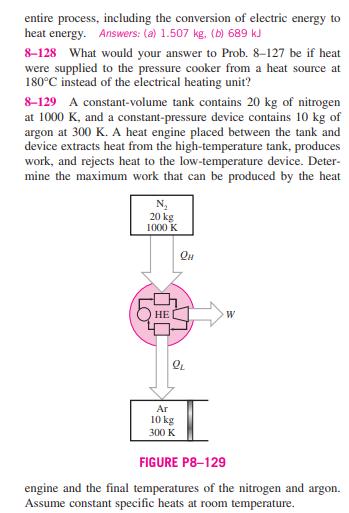

8-126 Two constant-pressure devices, each filled with 30 kg of air, have temperatures of 900 K and 300 K. A heat engine placed between the two devices extracts heat from the high- temperature device, produces work, and rejects heat to the low- temperature device. Determine the maximum work that can be produced by the heat engine and the final temperatures of the devices. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. 8-127 A 4-L pressure cooker has an operating pressure of 175 kPa. Initially, one-half of the volume is filled with liquid water and the other half by water vapor. The cooker is now placed on top of a 750-W electrical heating unit that is kept on for 20 min. Assuming the surroundings to be at 25C and 100 kPa, determine (a) the amount of water that remained in the cooker and (b) the exergy destruction associated with the C 4L 175 kPa 750 W FIGURE P8-127 entire process, including the conversion of electric energy to heat energy. Answers: (a) 1.507 kg. (b) 689 kJ 8-128 What would your answer to Prob. 8-127 be if heat were supplied to the pressure cooker from a heat source at 180C instead of the electrical heating unit? 8-129 A constant-volume tank contains 20 kg of nitrogen at 1000 K, and a constant-pressure device contains 10 kg of argon at 300 K. A heat engine placed between the tank and device extracts heat from the high-temperature tank, produces work, and rejects heat to the low-temperature device. Deter- mine the maximum work that can be produced by the heat N 20 kg 1000 K HE W Ar 10 kg 300 K FIGURE P8-129 engine and the final temperatures of the nitrogen and Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. argon. 8-130 A constant-volume tank has a temperature of 800 K and a constant-pressure device has a temperature of 290 K. Both the tank and device are filled with 20 kg of air. A heat engine placed between the tank and device receives heat from the high-temperature tank, produces work, and rejects heat to the low-temperature device. Determine the maximum work that can be produced by the heat engine and the final temper- atures of the tank and device. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. 8-126 Two constant-pressure devices, each filled with 30 kg of air, have temperatures of 900 K and 300 K. A heat engine placed between the two devices extracts heat from the high- temperature device, produces work, and rejects heat to the low- temperature device. Determine the maximum work that can be produced by the heat engine and the final temperatures of the devices. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. 8-127 A 4-L pressure cooker has an operating pressure of 175 kPa. Initially, one-half of the volume is filled with liquid water and the other half by water vapor. The cooker is now placed on top of a 750-W electrical heating unit that is kept on for 20 min. Assuming the surroundings to be at 25C and 100 kPa, determine (a) the amount of water that remained in the cooker and (b) the exergy destruction associated with the C 4L 175 kPa 750 W FIGURE P8-127 entire process, including the conversion of electric energy to heat energy. Answers: (a) 1.507 kg. (b) 689 kJ 8-128 What would your answer to Prob. 8-127 be if heat were supplied to the pressure cooker from a heat source at 180C instead of the electrical heating unit? 8-129 A constant-volume tank contains 20 kg of nitrogen at 1000 K, and a constant-pressure device contains 10 kg of argon at 300 K. A heat engine placed between the tank and device extracts heat from the high-temperature tank, produces work, and rejects heat to the low-temperature device. Deter- mine the maximum work that can be produced by the heat N 20 kg 1000 K HE W Ar 10 kg 300 K FIGURE P8-129 engine and the final temperatures of the nitrogen and Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. argon. 8-130 A constant-volume tank has a temperature of 800 K and a constant-pressure device has a temperature of 290 K. Both the tank and device are filled with 20 kg of air. A heat engine placed between the tank and device receives heat from the high-temperature tank, produces work, and rejects heat to the low-temperature device. Determine the maximum work that can be produced by the heat engine and the final temper- atures of the tank and device. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


