Question
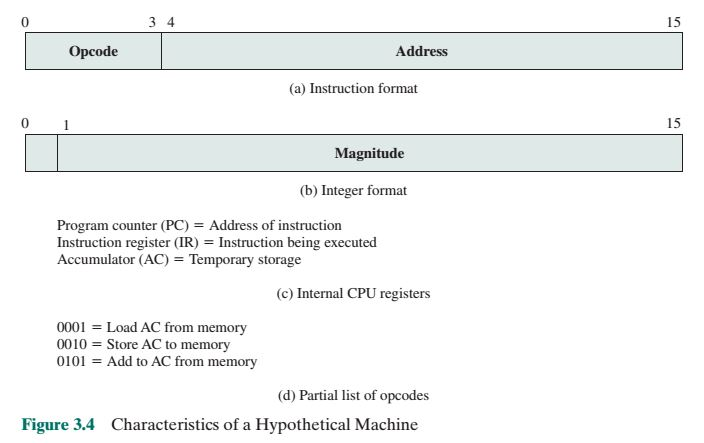
A hypothetical machine of Figure 3.4 as described in our lecture has two I/O instructions: 1101 (binary) = Load AC from I/O 0011 (binary) =
A hypothetical machine of Figure 3.4 as described in our lecture has two I/O instructions: 1101 (binary) = Load AC from I/O 0011 (binary) = Store AC to I/O In these cases, the 12bit address identifies a particular I/O device. Show the program execution for the following program (using the format of Figure 3.5 of the textbook as shown below) with clear explanation.
Load AC from device 15 (assume that the next balue retrieved from device 15 is 13)
Add contents of memory location 0x480. (assume that the content at location 0x480 is 24)
Store AC to device 48
Note: all numbers above should be treated as decimal number unless otherwise stated. Hexadecimal number has 0x as prefix, and the binary has a (binary) label after the number.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


