Question: A long, thin, straight wire carrying an electric current I causes a magnetic field of flux density B at a perpendicular distance r from
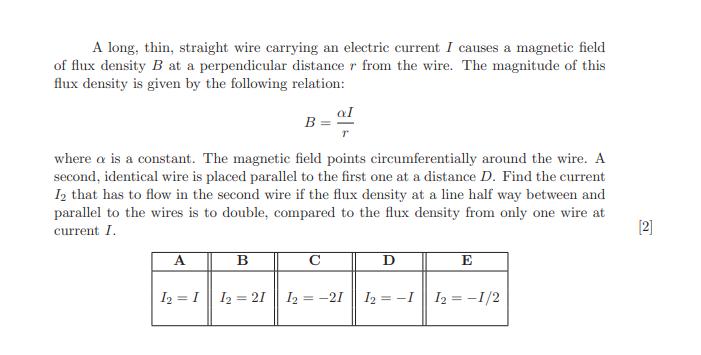
A long, thin, straight wire carrying an electric current I causes a magnetic field of flux density B at a perpendicular distance r from the wire. The magnitude of this flux density is given by the following relation: A where a is a constant. The magnetic field points circumferentially around the wire. A second, identical wire is placed parallel to the first one at a distance D. Find the current I that has to flow in the second wire if the flux density at a line half way between and parallel to the wires is to double, compared to the flux density from only one wire at current I. 12 = 1 B B 12=21 al D 12-21 12 = -1 E 1 = -1/2 [2]
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer let cur... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


