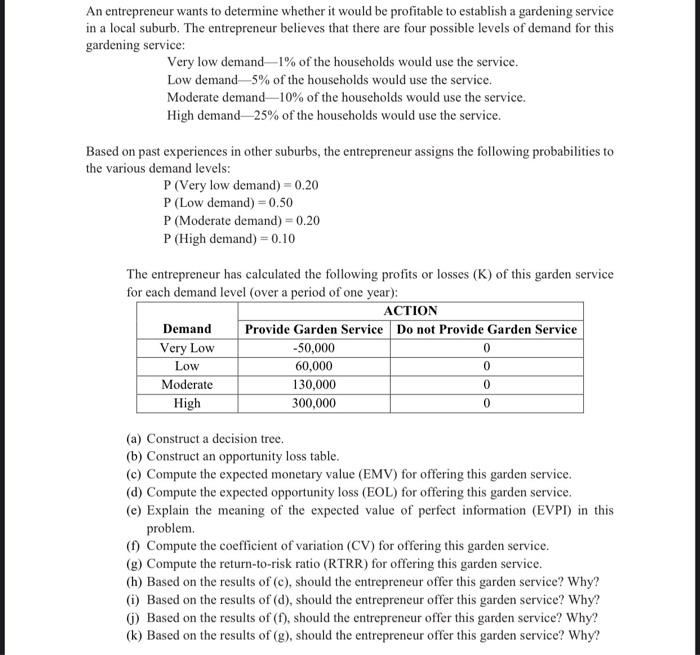
An entrepreneur wants to determine whether it would be profitable to establish a gardening service in a local suburb. The entrepreneur believes that there are four possible levels of demand for this gardening service: Very low demand- 1% of the households would use the service. Low demand 5% of the households would use the service. Moderate demand 10% of the households would use the service. High demand 25% of the households would use the service. Based on past experiences in other suburbs, the entrepreneur assigns the following probabilities to the various demand levels: P(Verylowdemand)=0.20P(Lowdemand)=0.50P(Moderatedemand)=0.20P(Highdemand)=0.10 The entrepreneur has calculated the following profits or losses (K) of this garden service for each demand level (over a period of one year): (a) Construct a decision tree. (b) Construct an opportunity loss table. (c) Compute the expected monetary value (EMV) for offering this garden service. (d) Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for offering this garden service. (e) Explain the meaning of the expected value of perfect information (EVPI) in this problem. (f) Compute the coefficient of variation (CV) for offering this garden service. (g) Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for offering this garden service. (h) Based on the results of (c), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? (i) Based on the results of (d), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? (j) Based on the results of ( f), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? (k) Based on the results of (g), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? An entrepreneur wants to determine whether it would be profitable to establish a gardening service in a local suburb. The entrepreneur believes that there are four possible levels of demand for this gardening service: Very low demand- 1% of the households would use the service. Low demand 5% of the households would use the service. Moderate demand 10% of the households would use the service. High demand 25% of the households would use the service. Based on past experiences in other suburbs, the entrepreneur assigns the following probabilities to the various demand levels: P(Verylowdemand)=0.20P(Lowdemand)=0.50P(Moderatedemand)=0.20P(Highdemand)=0.10 The entrepreneur has calculated the following profits or losses (K) of this garden service for each demand level (over a period of one year): (a) Construct a decision tree. (b) Construct an opportunity loss table. (c) Compute the expected monetary value (EMV) for offering this garden service. (d) Compute the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for offering this garden service. (e) Explain the meaning of the expected value of perfect information (EVPI) in this problem. (f) Compute the coefficient of variation (CV) for offering this garden service. (g) Compute the return-to-risk ratio (RTRR) for offering this garden service. (h) Based on the results of (c), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? (i) Based on the results of (d), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? (j) Based on the results of ( f), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why? (k) Based on the results of (g), should the entrepreneur offer this garden service? Why