Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
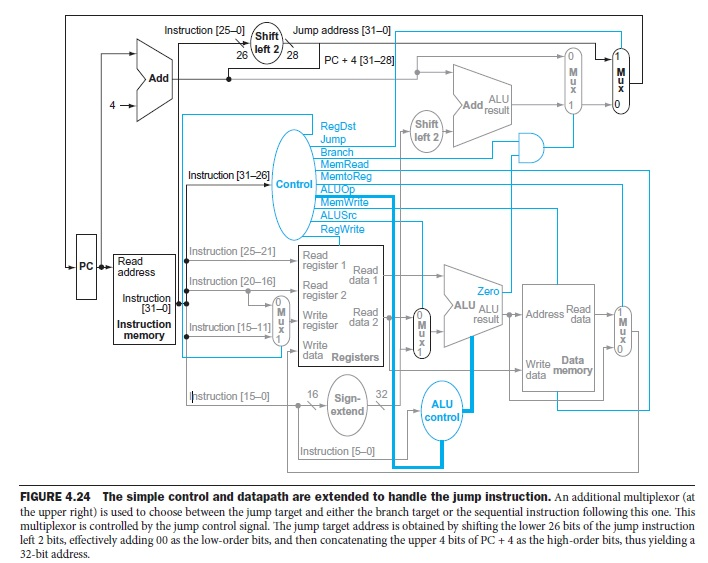
Assume we want to execute the following new instruction on the given MIPS single-cycle data path figure below. mov R[rt], R[rs]; This instruction uses I-format
Assume we want to execute the following new instruction on the given MIPS single-cycle data path figure below.
mov R[rt], R[rs]; This instruction uses I-format and performs: R[rt] R[rs]
The opcode of the mov instruction is 001001. Modify the data path and identify the values of the following control signals needed for this instruction. Then modify the control unit to implement the control signals. Assume that you are not allowed to change ALU operations.
| RegDst | ALUSrc | MemtoReg | RegWrite | MemRead | MemWrite | Newsignal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


