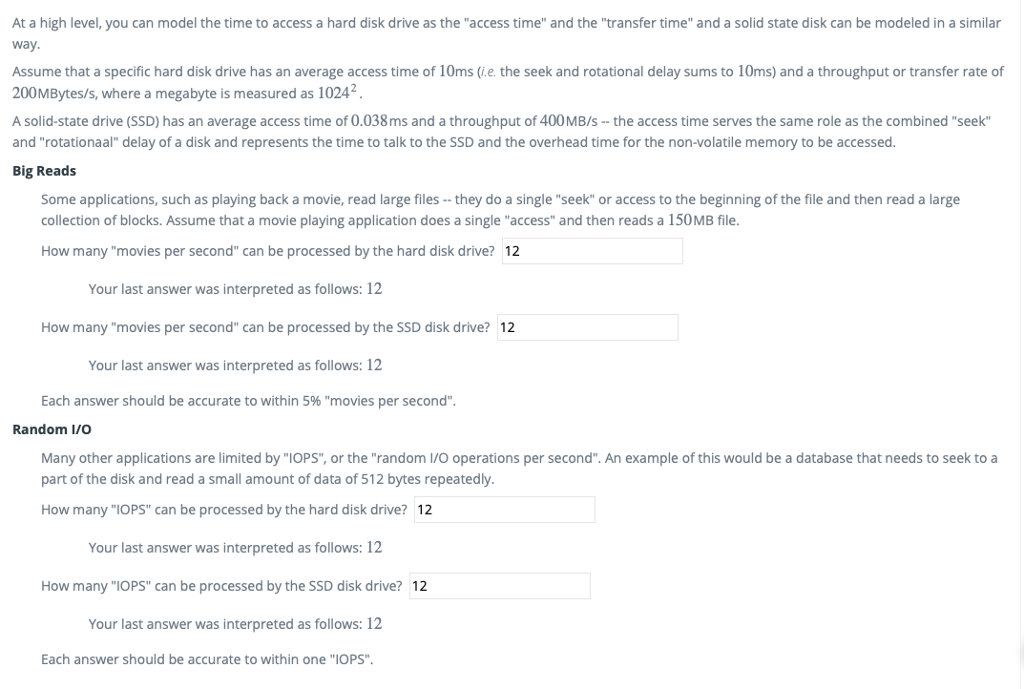
At a high level, you can model the time to access a hard disk drive as the "access time" and the "transfer time" and a solid state disk can be modeled in a similar way Assume that a specific hard disk drive has an average access time of 10ms (ie. the seek and rotational delay sums to 10ms) and a throughput or transfer rate of 200MBytes/s, where a megabyte is measured as 10242 A solid-state drive (SSD) has an average access time of 0.038ms and a throughput of 400MB/s- the access time serves the same role as the combined "seek" and "rotationaal" delay of a disk and represents the time to talk to the SSD and the overhead time for the non-volatile memory to be accessed. Big Reads Some applications, such as playing back a movie, read large files -they do a single "seek" or access to the beginning of the file and then read a large collection of blocks. Assume that a movie playing application does a single "access" and then reads a 150MB file How many "movies per second" can be processed by the hard disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 How many "movies per second" can be processed by the SSD disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 Each answer should be accurate to within 5% "movies per second" Random I/O Many other applications are limited by "IOPS", or the "random I/O operations per second". An example of this would be a database that needs to seek to a part of the disk and read a small amount of data of 512 bytes repeatedly How many "IOPS" can be processed by the hard disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 How many "IOPS" can be processed by the SSD disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 Each answer should be accurate to within one "IOPS". At a high level, you can model the time to access a hard disk drive as the "access time" and the "transfer time" and a solid state disk can be modeled in a similar way Assume that a specific hard disk drive has an average access time of 10ms (ie. the seek and rotational delay sums to 10ms) and a throughput or transfer rate of 200MBytes/s, where a megabyte is measured as 10242 A solid-state drive (SSD) has an average access time of 0.038ms and a throughput of 400MB/s- the access time serves the same role as the combined "seek" and "rotationaal" delay of a disk and represents the time to talk to the SSD and the overhead time for the non-volatile memory to be accessed. Big Reads Some applications, such as playing back a movie, read large files -they do a single "seek" or access to the beginning of the file and then read a large collection of blocks. Assume that a movie playing application does a single "access" and then reads a 150MB file How many "movies per second" can be processed by the hard disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 How many "movies per second" can be processed by the SSD disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 Each answer should be accurate to within 5% "movies per second" Random I/O Many other applications are limited by "IOPS", or the "random I/O operations per second". An example of this would be a database that needs to seek to a part of the disk and read a small amount of data of 512 bytes repeatedly How many "IOPS" can be processed by the hard disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 How many "IOPS" can be processed by the SSD disk drive? 12 Your last answer was interpreted as follows: 12 Each answer should be accurate to within one "IOPS







