
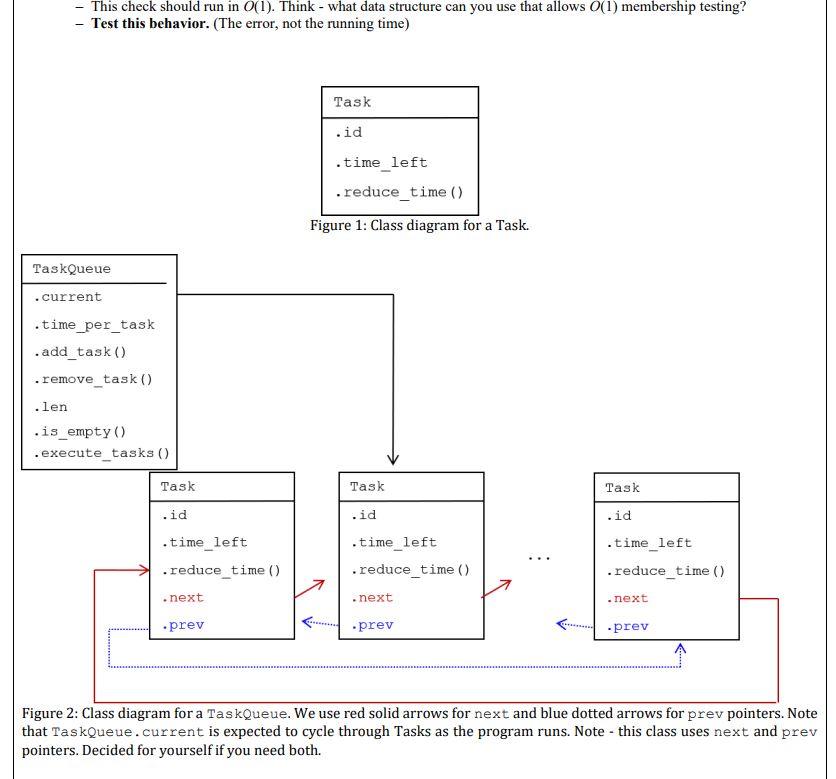


b. Programming Exercise (2/2) - Circular Linked Data Structure Not all linked data structures are linear - it is often helpful to have nodes that link to multiple nodes (as in Trees and Graphs), or nodes that link together in other non-linear ways. In this assignment, we build a circular linked data structure - a list that loops around on itself. This is useful when we need to repeatedly loop through a series of nodes. For instance, an operating system may keep such a circular list of tasks that need CPU time, and continually cycle through the list of tasks. We will implement two classes: - Task - a task for the operating system to complete. Each task has the following attributes, in addition to any "linking" attributes (like next or prev) you decide are necessary: - id - a unique identifier (an int) - time_left - the amount of time necessary to complete this task - reduce_time () - reduces time_left by the appropriate amount - TaskQueue - A circular data structure with attributes: - current - the current task to process - time_per_task - the amount of time to dedicate to each task before moving to the next one. This has a default value of 1 , but should be a parameter a user can specify when creating a TaskQueue. - add_task ( ) - adds a task immediately before current. Should be O(1). - remove_task()-removes the task with a given id. Should be O(n). - len - the number of tasks in the TaskQueue. O(1). - is_empty () - returns True if the TaskQueue is empty; false otherwise. O(1). - execute_tasks() * executes tasks cyclically. Each task will run for time_per_task or the amount of time it has remaining, whichever is lower. This should print out information whenever a task is finished (see examples for string formatting). At the end, return the total time it took to execute all tasks. You do not need to test the print outs but should test the return value. See next page for class diagrams. Special Behavior - If a task is reduced to 0 seconds by reduce_time, then the TaskQueue should remove that task from the queue and print out info - the task id and the time it finished (see Examples below for formatting) - If a user tries to remove a task with an id that is not in the TaskQueve, you should raise a RuntimeError with an appropriate string. - This check should run in O(1). Think - what data structure can you use that allows O(1) membership testing? Figure 2: Class diagram for a TaskQueue. We use red solid arrows for next and blue dotted arrows for prev pointers. Note that TaskQueve.current is expected to cycle through Tasks as the program runs. Note - this class uses next and prev pointers. Decided for yourself if you need both. Examples Any examples below are intended to be illustrative, not exhaustive. Your code may have bugs even if it behaves as below. Write your own tests, and think carefully about edge cases. from TaskQueue import p1 = Task (id=1, time_left =3) p = Task (id=2, time_left =1) t 3= Task (id=3, time_left =5) tasks =[t1,t2,t3] TQ = TaskQueue(time_per_task=1) for task in tasks: External Modules Do not use any imported modules (math, collections,...) when implementing functionality. It is okay to use imported modules for testing; e.g. the random and string modules for generating random items. It is okay to import modules you write yourself for this assignment; e.g. any data structures you write yourself. Submission At a minimum, submit the following files on GradeScope under "Assignment 1 - Programming (2/2)" category: - TaskQueue.py - TestTaskqueue.py Grading Code readability matters. Code that is difficult to read (no comments, poor variable/function names, not enough whitespace) will incur a penalty of 10 points. Most of this assignment is manually graded, including tests. Use test driven development - write tests for functionality, run those tests to verify they fail, then implement the functionality










