Question: b. State why this sound cannot be heard by human beings. . . . . .. ... .[1] c. The pulse of sound hits a

![. . . . .. ... .[1] c. The pulse of sound](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6672917ee54f8_3826672917ec2fb0.jpg)



![..................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1] 5. A small boat in a harbour is protected](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66729181b3c80_3856672918194d2c.jpg)

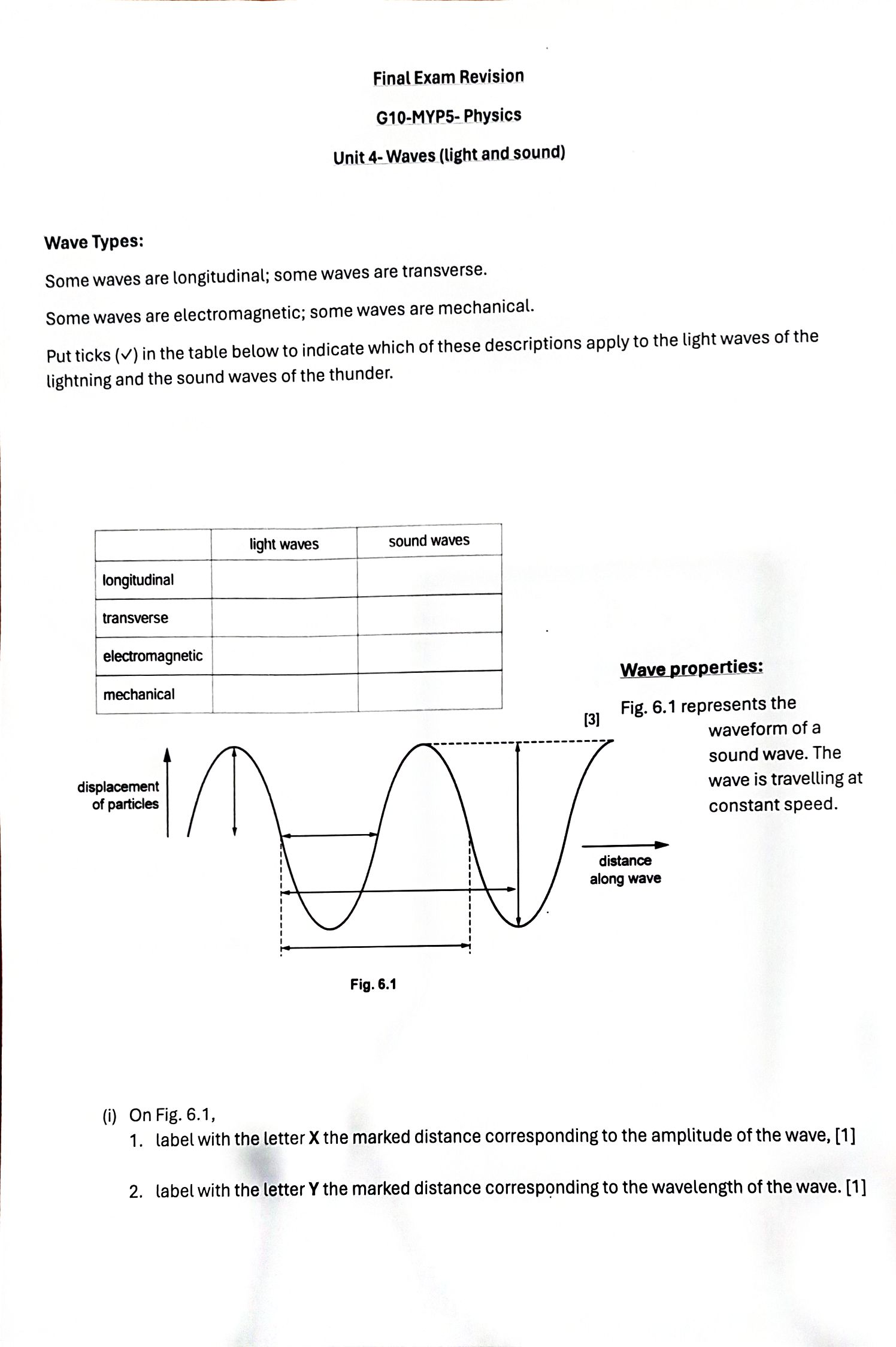

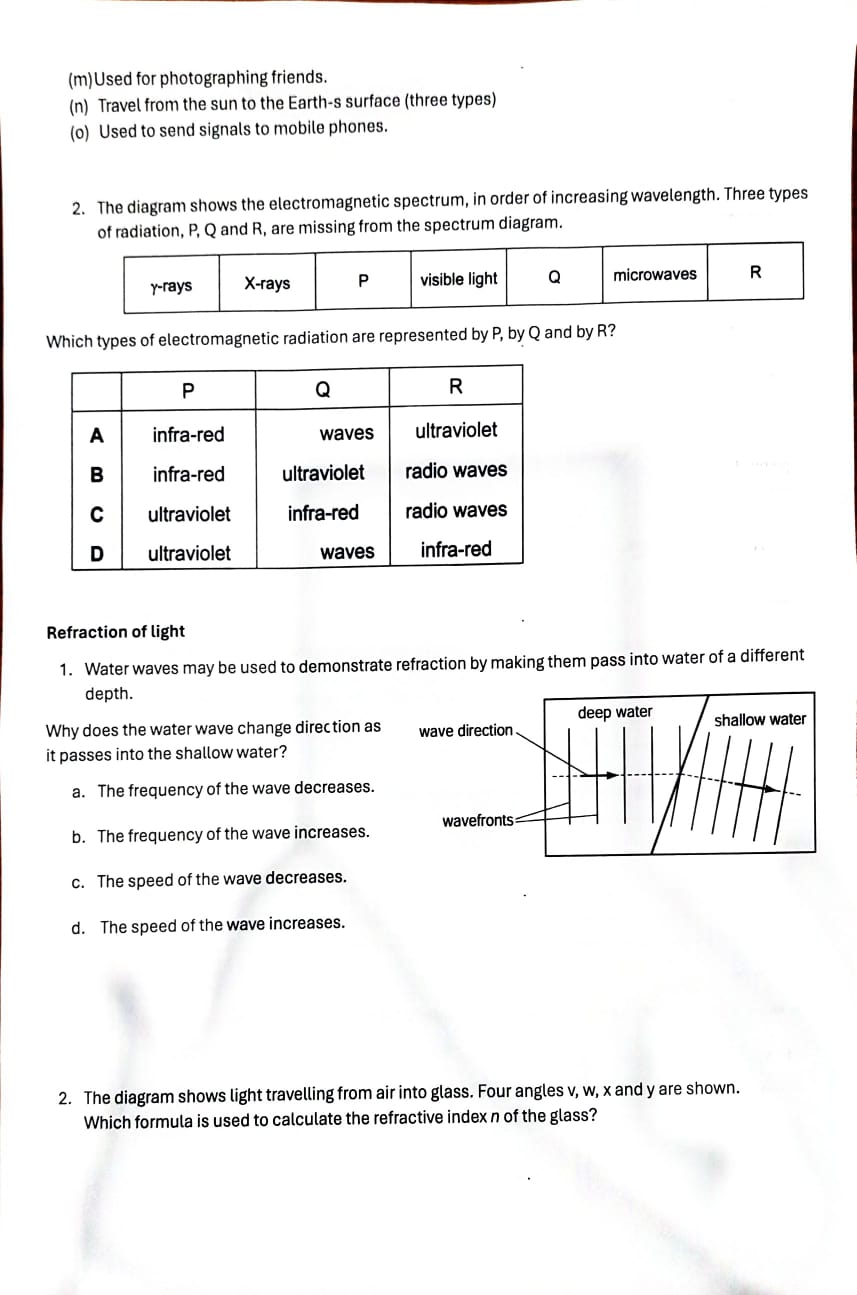

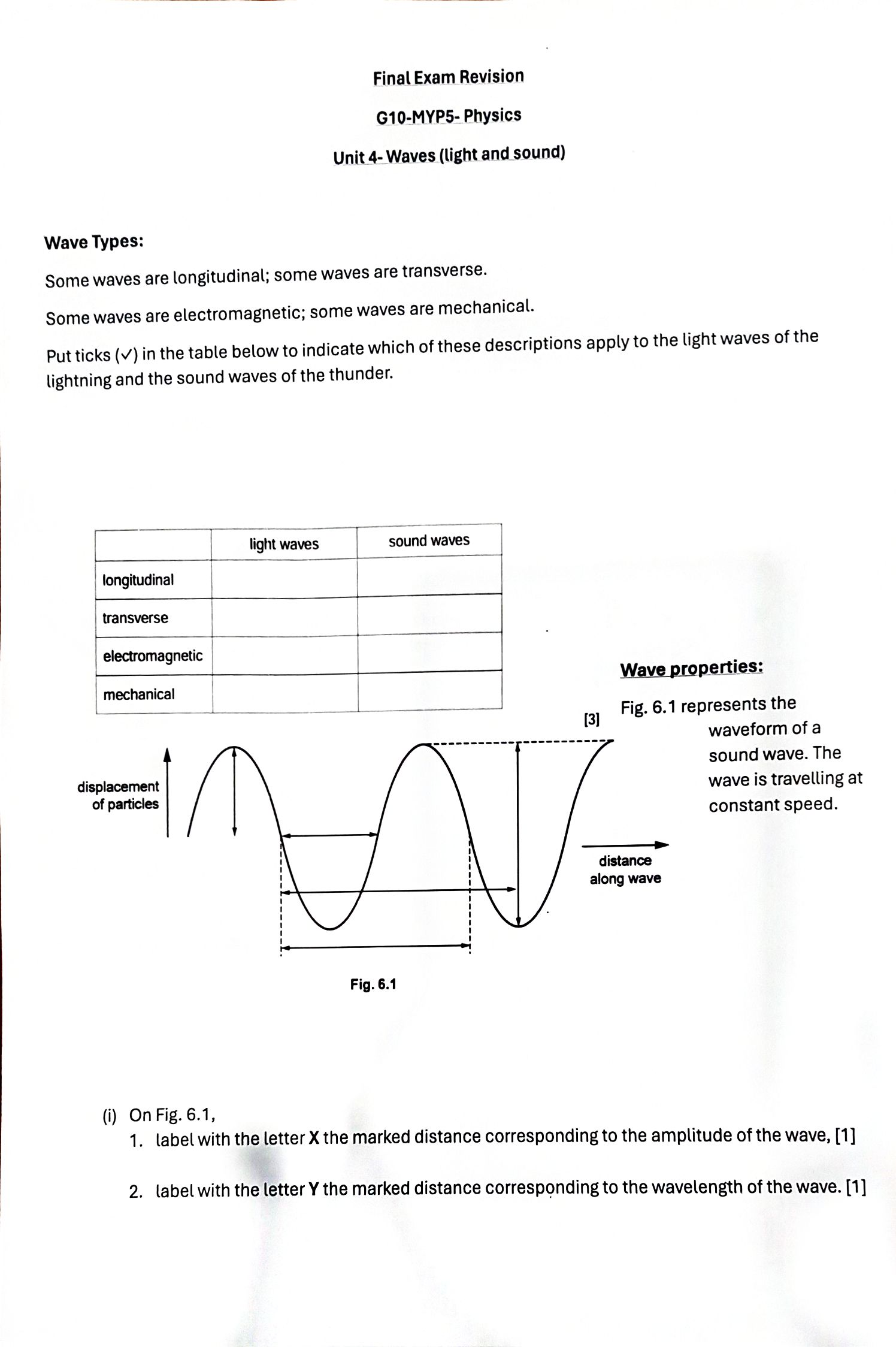
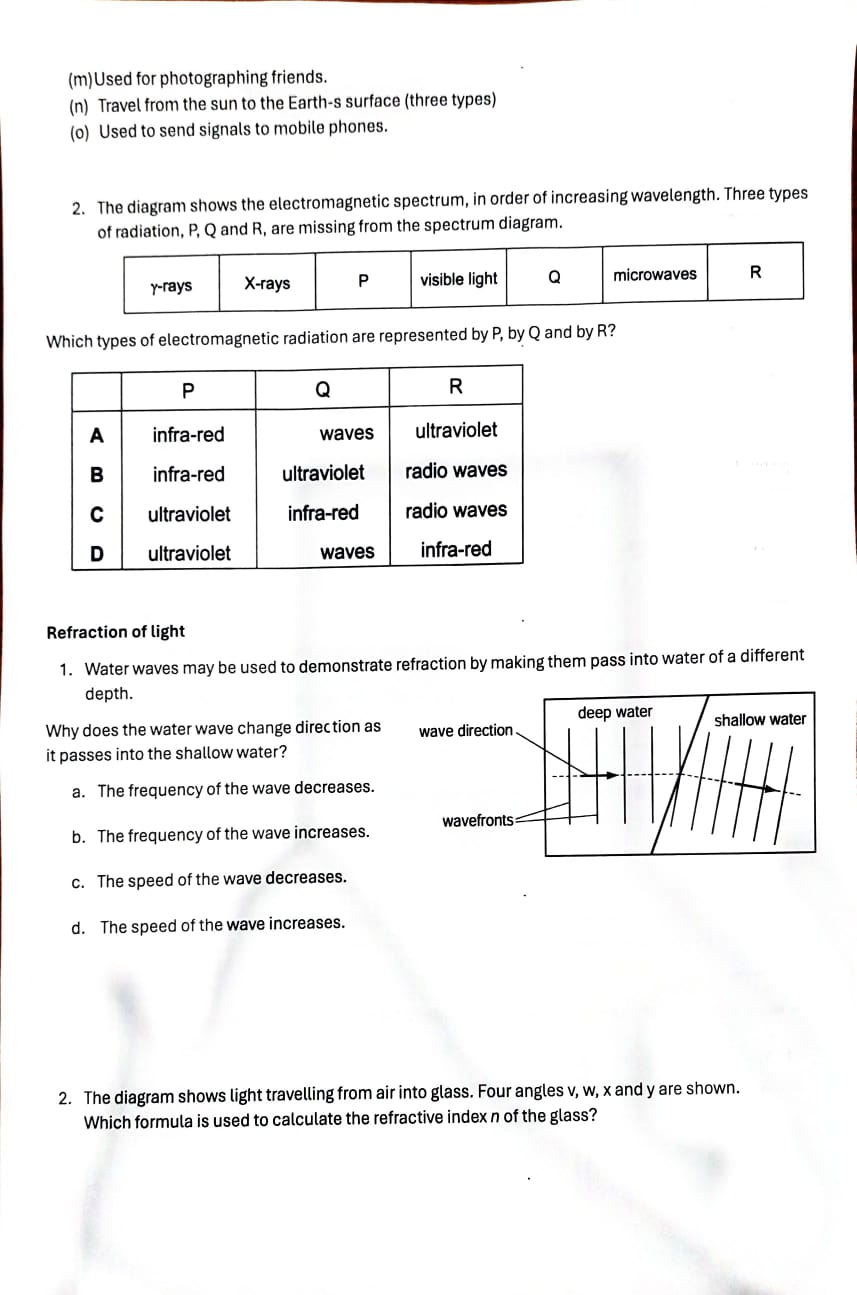
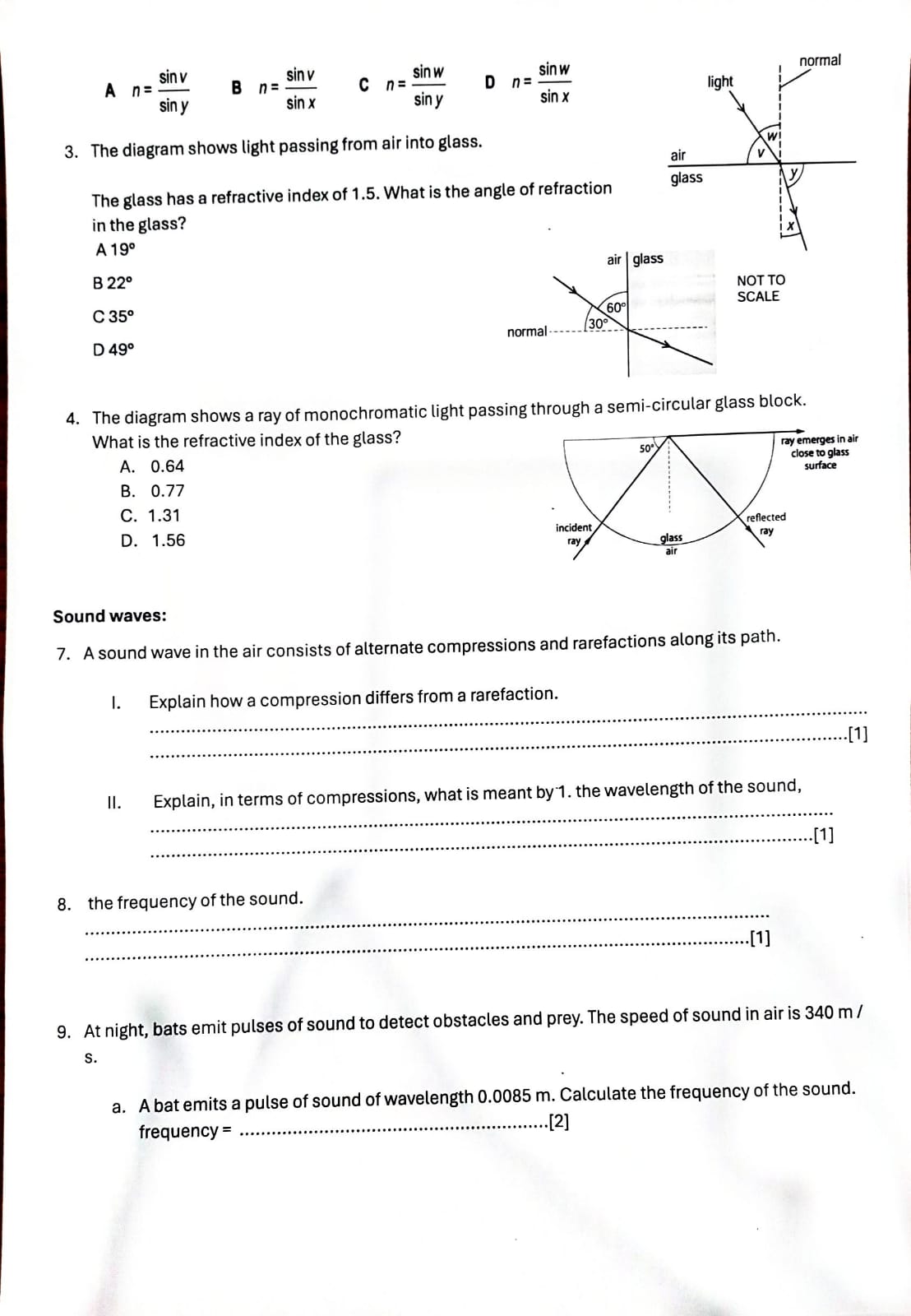
b. State why this sound cannot be heard by human beings. . . . . .. ... .[1] c. The pulse of sound hits a stationary object and is reflected back to the bat. The pulse is received by the bat 0. 12 s after it was emitted. Calculate the distance travelled by the pulse of sound during this time. distance = [2)4. During a thunderstorm, thunder and lightning are produced at the same time. (i) Apersonis some distance away from the storm. Explain why the person sees the lightning before hearing the thunder. .......................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (1] 5. A small boat in a harbour is protected from waves on the sea by harbor walls. \\ land e waves small boat harbour harbour walls 6. Some waves can curve round the harbour walls and reach the boat. What i effect? a. Adiffraction b. Bdispersion c. Creflection d. Drefraction Electromagnetic waves s the name of this 1. The electromagnetic spectrum includes seven types of radiation. What do you know about how they are produced, detected, and used? Name each type of electromagnetic ra Jiation described below. (a) detected by our eyes. (b) Given out by very hot objects (three types). (c) Given out by radioactive substances. (d) Used to show up broken bones. (e) Used in a T' remote control. (f) Used for broadcasting T' signals. (g) Has longer wavelengths than microwaves. (h) Used in airport security systems. (i) Used to cook food $two types%. () Used in satellite communications. (k) Has a range of frequencies between X-rays and visible light. () Used in invisible beams in security systems. ray of 40 light 50 ray of 50" light 50 C D ray of 40 ray of light 40 40 light 50 3. Fig. 7.1 is a top view of one wavefront of a water wave before it strikes a hard boundary boundary (i) Name the process that occurs as the wavefront strikes the boundary. ...... [1] (ii) (ii) Explain, in terms of wave theory, what occurs as the wavefront strikes the boundary. ....... ........ ......... . . ...... ....... [2] (iii) State whether there is an increase, a decrease or no change in the wavelength of the wave after it strikes the boundary. (iv) The speed of the wave is 3.0 m / s and its wavelength 7.0 cm. Calculate the frequency of the wave. frequency = .........Final Exam Revision G10-MYP5- Physics Unit 4- Waves (light and sound) Wave Types: Some waves are longitudinal; some waves are transverse. Some waves are electromagnetic; some waves are mechanical. Put ticks (v) in the table below to indicate which of these descriptions apply to the light waves of the lightning and the sound waves of the thunder. light waves sound waves longitudinal transverse electromagnetic Wave properties: mechanical [3] Fig. 6.1 represents the waveform of a sound wave. The displacement wave is travelling at of particles constant speed. distance along wave Fig. 6.1 (i) On Fig. 6.1, 1. label with the letter X the marked distance corresponding to the amplitude of the wave, [1] 2. label with the letter Y the marked distance corresponding to the wavelength of the wave. [1](ii) State what happens to the amplitude and the wavelength of the wave if 1. the loudness of the sound is increased at constant pitch, amplitude ......... ....... wavelength ............... 2. the pitch of the sound is increased at constant loudness. amplitude ... wavelength [1] Wave Behaviors: 1. The diagram shows a ray of light in air incident on a glass block. Some of the light is refracted, and some of the light is reflected. Two angles p and q are marked on the diagram. ray of Which row gives the angle of incidence and shows light whether the ray undergoes total internal reflection? air angle of glass total internal incidence reflection no B yes a no D a yes 2. Which diagram correctly shows a ray of light reflected by a plane mirror?(m)Used for photographing friends. (n) Travel from the sun to the Earth-s surface (three types) (0) Used to send signals to mobile phones. 2. The diagram shows the electromagnetic spectrum, in order of increasing wavelength. Three types of radiation, P, Q and R, are missing from the spectrum diagram. ultraviolet infra-red waves ultraviolet radio waves infra-red waves infra-red radio waves infra-red ultraviolet ultraviolet Refraction of light 1. Water waves may be used to demonstrate refraction by making them pass into water of a different depth. deep water Why does the water wave change direction as wave direction shallow water it passes into the shallow water? a. The frequency of the wave decreases. b. The frequency of the wave increases. c. The speed of the wave decreases. d. The speed of the wave increases. 2. The diagram shows light travelling from air into glass. Four angles v, w, xand y are shown. Which formula is used to calculate the refractive index n of the glass? An= - sin v B n= _ sin v C n= sin w D n=_ sin w normal light siny sin X sin y sin x 3. The diagram shows light passing from air into glass. air The glass has a refractive index of 1.5. What is the angle of refraction glass in the glass? A 190 B 220 air glass NOT TO C 350 60 SCALE normal - ----- 30 D 490 4. The diagram shows a ray of monochromatic light passing through a semi-circular glass block. What is the refractive index of the glass? A. 0.64 50. ray emerges in air close to glass B. 0.77 surface C. 1.31 D. 1.56 incident reflected glass Sound waves: 7. A sound wave in the air consists of alternate compressions and rarefactions along its path. I. Explain how a compression differs from a rarefaction. .......[1] Explain, in terms of compressions, what is meant by 1. the wavelength of the sound, -.......[1] 8. the frequency of the sound. ...[1] 9. At night, bats emit pulses of sound to detect obstacles and prey. The speed of sound in air is 340 m / S. a. A bat emits a pulse of sound of wavelength 0.0085 m. Calculate the frequency of the sound. frequency = .......... .[2]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


