

Chapter 13
Critical Concept - The Trustee's Responsibility
How does the failure of an organization to prepare for equipment replacement at the end of its useful life impact the overall operations of the organization and its patients?
Chapter 14
Critical concept - Creating a Financial Analysis
Ratio analysis - in your opinion, shouldn't the organization already know how it's doing without exploring financial analysis? How can you trust the organization's interpretation of the numbers generated by the financial analysis?
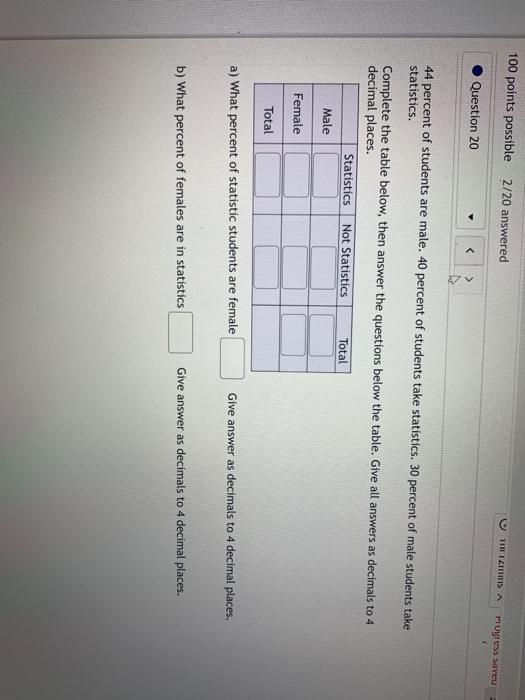
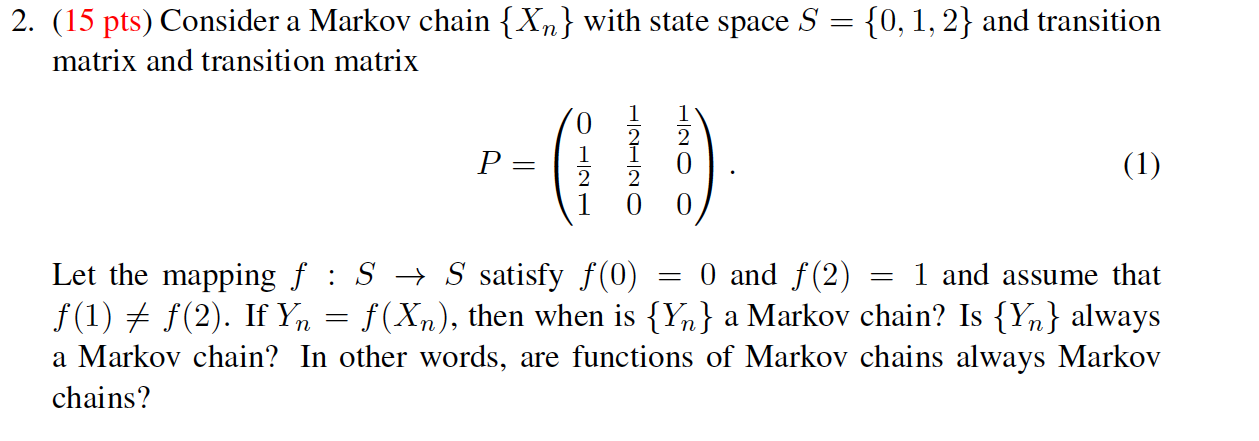
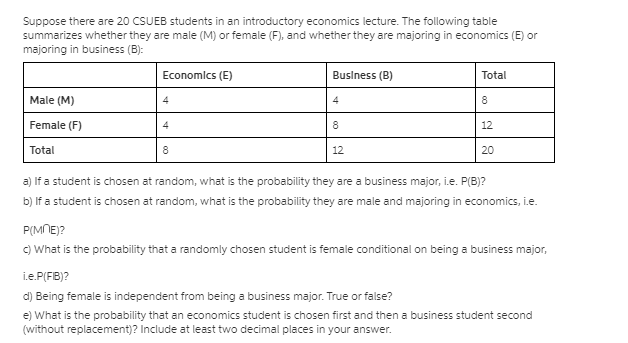
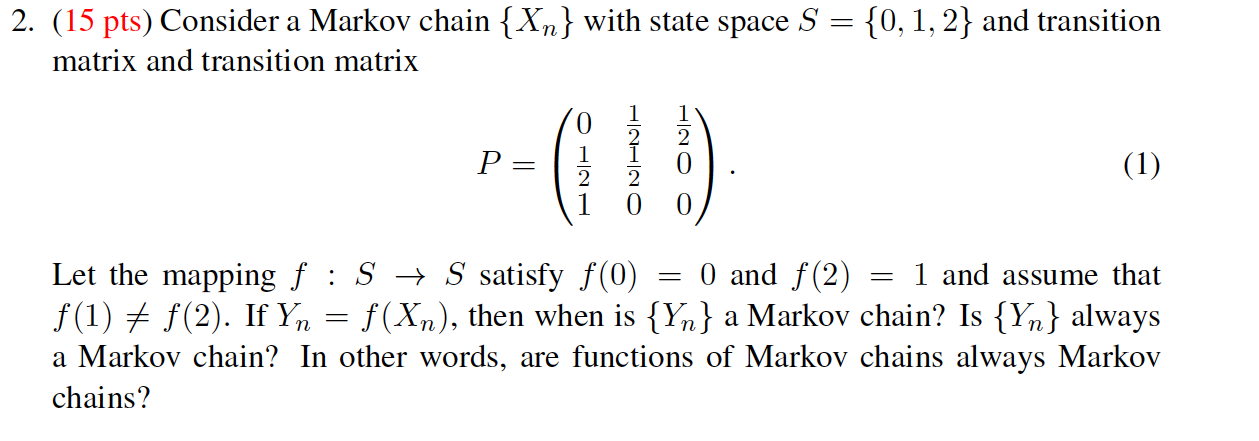
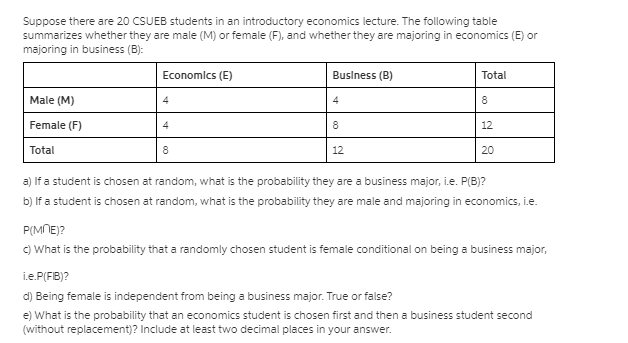
100 points possible 2/20 answered ImiamiIs A Hugeas Savey Question 20 4 44 percent of students are male. 40 percent of students take statistics. 30 percent of male students take statistics. Complete the table below, then answer the questions below the table. Give all answers as decimals to 4 decimal places. Statistics Not Statistics Total Male Female Total a) What percent of statistic students are female Give answer as decimals to 4 decimal places. b) What percent of females are in statistics Give answer as decimals to 4 decimal places.2. (15 pts) Consider a Markov chain { Xn } with state space S = {0, 1, 2} and transition matrix and transition matrix P = O ON/H HNIH O (1) Let the mapping f : S - S satisfy f(0) = 0 and f(2) = 1 and assume that f(1) + f(2). If Yn = f(Xn), then when is { Yn } a Markov chain? Is { Yn } always a Markov chain? In other words, are functions of Markov chains always Markov chains?Consider a standard chessboard with an 8 x 8 grid of possible locations. We define a Markov chain by randomly moving a single chess piece on this board. The initial location Xo is sampled uniformly among the 82 = 64 squares. At time t, the piece then chooses Xt+1 by sampling uniformly from the set of legal moves given its current location Xt. For a description of legal chess moves, see: http://en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Rules_of_chess#Basic_moves. a) Suppose the chess piece is a king, which can move to any of the 8 adjacent squares. Is the Markov chain irreducible? Is the Markov chain aperiodic? b) Suppose the chess piece is a bishop. Is the Markov chain irreducible? Is the Markov chain aperiodic? c) Suppose the chess piece is a knight. Is the Markov chain irreducible? Is the Markov chain aperiodic?Simple Interest: I = Prt Simple Interest Future Value: FV = P(1 + rt) Compound Interest: FV = P(1 + r)nt Annual Yield: APY = (1+ ")" - 1 Ordinary Annuity (payments due at the end of each period): FV. = punt . (In)"t - 1 n Annuity Due (payments due in the beginning of each period): FVa = pymt . (1 +%)nt - 1 ( 1 + " ) Present Value of Annuity: P(1 + ")nt = FV(annuity) Simple Interest Amortized Loan: pymt (1 + h )"-1= p(1+ 1)n n Simple Interest Amortized Loan Unpaid Balance (after t years): P(1 + " )nt - pymt (1 +m)nt - 1 n Payout Annuity: P(1 + ")nt = pymt . (1+")nt - 1 T n 1+c 1 - 1tr Payout Annuity with COLA: P = pymt . r - CSuppose there are 20 CSUEB students in an introductory economics lecture. The following table summarizes whether they are male (M) or female (F), and whether they are majoring in economics (B) or majoring in business (B): Economics (E) Business (B) Total Male (M) 4 4 Female (F) 4 8 12 Total 8 12 20 al If a student is chosen at random, what is the probability they are a business major, i.e. P(B)? bj If a student is chosen at random, what is the probability they are male and majoring in economics, i.e. P(ME)? c) What is the probability that a randomly chosen student is female conditional on being a business major, i.e.P(FIB)? d) Being female is independent from being a business major. True or false? e) What is the probability that an economics student is chosen first and then a business student second (without replacement)? Include at least two decimal places in your