Congrats! You got a job as a CFO in UK. You are asked to recommend how a company can eliminate the risk of holding a
Congrats! You got a job as a CFO in UK. You are asked to recommend how a company can eliminate the risk of holding a foreign bond using the information provided below
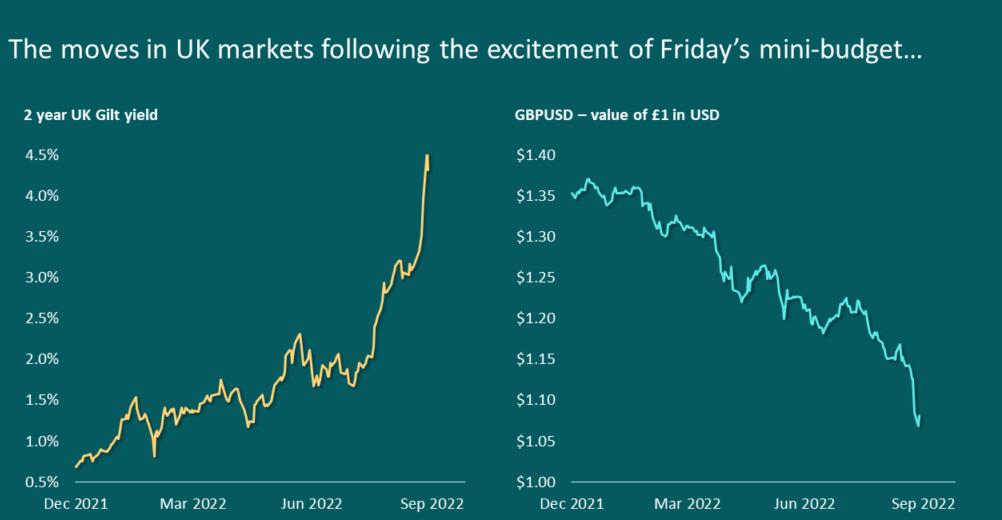
In all the excitement about last Friday’s mini-Budget sending sterling down to a record low against the US dollar, and sending gilt yields rocketing (2 year gilt yields rose by 1% over two days), there’s a dangerous technical factor lurking in UK bond markets that we mustn’t ignore. Toby Nangle, formerly a multi-asset fund manager, identified it in an excellent Financial Times article in July this year. The piece points out that there are £1.5 trillion of assets held by UK pensions that have been hedged in so-called LDI trades. LDI (Liability Driven Investment) helps to match pension funds’ liabilities (future payments to pensioners) with the schemes’ assets. In a simple model this matching could be done by buying gilts of similar durations to the liabilities – if you owe your retired employees a collective £1 million in 2046, then you could buy a gilt maturing in that year. Or if you buy a quality corporate bond with a higher yield (a lower price) you can assign less capital to that liability, and use the extra cash to invest in a growth asset like equity, property, or private assets. Going further, you could use interest rate swaps or inflation swaps to match your duration liabilities. This means that you only have to put up some initial margin for the trade, and pay or receive collateral as market yields change (think of it like a contract for difference on a yield). If yields fall you would receive margin, and if yields rise the 1 pension fund must pay margin to the counterparty. Using swaps gives the pension scheme far more capital to assign to those more interesting asset classes with high potential returns rather than having it tied up in boring gilts. As Toby points out, the rise in gilt yields over the past year or so has been beneficial for many underfunded pension schemes – the value of future liabilities has fallen, so underfunded schemes become less underfunded (see this document from the Pension Protection Fund for the current situation). But a sudden rise in gilts has significant implications for pension funds using swaps to hedge liabilities. Collateral calls for margin payments will be large given the scale of the move in long dated bond yields, so this means that many schemes may have to raise cash by selling physical assets elsewhere in their portfolios – and in the dash for higher yields and higher returns, some of these will be in less liquid asset classes, perhaps leading to spread widening and discounts from expected value on sale. To quote Toby, ‘while rising yields are good news for pension scheme funding levels, they look a likely catalyst for a further liquidation of risky assets’. Whilst this is a dynamic specific to pension funds using swaps, there’s a wider collateral implication from the recent turmoil in UK assets – and I’ve no real idea of its scale. Most UK based investors, and especially bond investors, buy overseas assets and hedge away the currency risk. The sterling corporate bond market has shrunk dramatically relative to other global capital markets, thanks mainly to the continued growth of the euro-denominated credit markets over the past years, and many issuers no longer borrow in pounds. UK corporate bond investors will therefore routinely look globally for the most attractive credit yields in either euros or dollars once hedging costs or gains are considered. Like interest rate and inflation swaps though, hedging is done via the use of derivatives – often foreign exchange forward contracts. As an example, I might buy a bond issued in euros by Telefonica. To eliminate the risk that the euro falls in value and thus wipes out the additional return I anticipated, or more, I sell euros of a similar value to the bond I bought in the forward FX market, and buy sterling. Fund investors are therefore exposed only to the pound rather than to FX movements. Like other derivatives though, changes in price of the underlying asset lead to collateral movements. Given the 20% fall in the pound against the US dollar this year, and the recent sharp falls in the past week, if you had bought a dollar bond and hedged it, the dollars that you have effectively sold ‘short’ against sterling as the hedge have rallied, and the counterparty to the FX hedge will call for a collateral payment. Whilst most funds will hold some cash and extremely liquid government bonds against such moves, the size of the recent turmoil probably means that many investors will be having to liquidate credit and other less liquid assets in order to meet these collateral calls. Whilst inflation, central banks, and *cough* government fiscal decisions will determine the overall direction of bond yields over coming months, don’t discount the technical dynamics too. The dash for collateral could be a big factor in the short term for the UK.
Please answer the following questions.
(a) What is a UK gilt?
(b) What happened to gilt prices from Dec 2021 to Sept 2022?
(c) Did you observe an appreciation or depreciation of the pound in the same time period?
(d) Why has the rise in gilt yields over the past year or so has been beneficial for many underfunded pension schemes?
(e) Sara collected data from the term structure of interest rates for the following 4 semesters, (note that effective semiannual rate is the rate posted divided by 2). c ( 0 . 0 5 4 , 0. 0 6 , 0. 0 5 4 4 , 0. 0 6 1 8 )
(f) What is the duration of a bond that can pay these rates as a coupon rate?
(g) Her friend, Nicole, offered a new fixed income instrument that pays a fixed coupon rate of 5.5%. If Sara takes a long position in the fixed rate instrument and a short position in the floating one, write the effect of this strategy in terms of duration. (Note: Compute the duration of each position separately, and compare the values). 2
(h) Using your result above, discuss why some investors adopt such strategies.
(i) Trading in assets is risky, and therefore the market usually asks for a reserve or a collateral to be put in an account. If the position of one side of the market deteriorates, then that party receives a margin call, meaning that more cash needs to be put in the account. Discuss why you think some investors are getting margin calls when swapping interest rates. (j) Another risk that a company is subject to is the exchange rate risk (currency risk). Sara noticed that her company (based in UK) bought Euro bonds. What strategy do you recommend to hedge the exchange risk of holding Euro bonds?
The moves in UK markets following the excitement of Friday's mini-budget... 2 year UK Gilt yield 4.5% 4.0% 3.5% 3.0% 2.5% 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% Dec 2021 ymw Mar 2022 Jun 2022 Sep 2022 GBPUSD - value of 1 in USD $1.40 $1.35 $1.30 $1.25 $1.20 $1.15 $1.10 $1.05 $1.00 Dec 2021 Mar 2022 Jun 2022 Sep 2022
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a A UK gilt is a government bond issued by the United Kingdom government It is a type of fixedincome security meaning that it pays a fixed interest rate to investors Gilts are considered to be very sa...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


