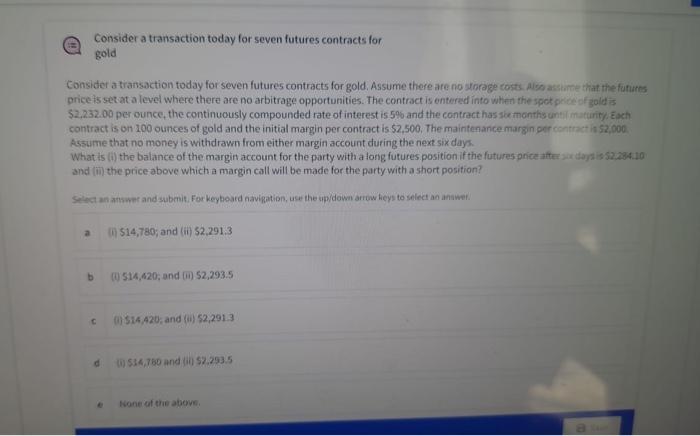
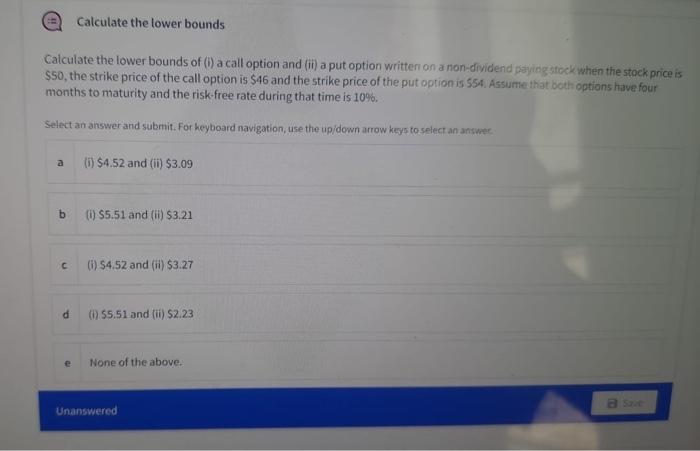
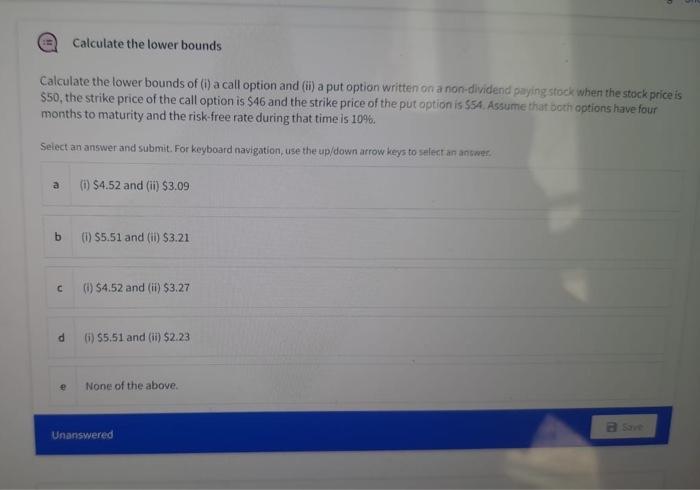
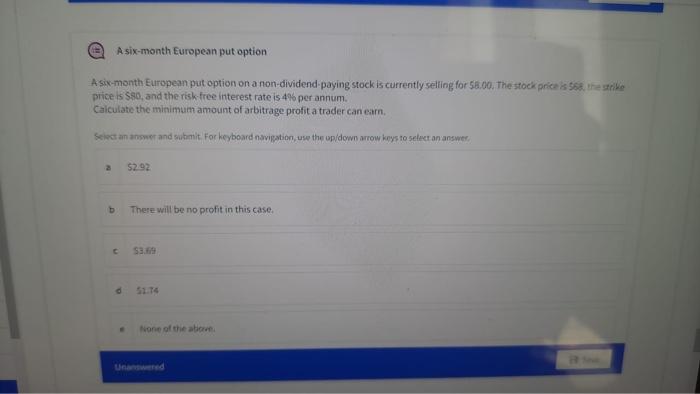
Consider a transaction today for seven futures contracts for gold Consider a transaction today for seven futures contracts for gold. Assume there are no storage costs. Also assume that the futures price is set at a level where there are no arbitrage opportunities. The contract is entered into when the spot price of gold is $2,232.00 per ounce, the continuously compounded rate of interest is 5% and the contract has six months until maturity. Each contract is on 100 ounces of gold and the initial margin per contract is $2,500. The maintenance margin per contract is $2,000 Assume that no money is withdrawn from either margin account during the next six days. What is (i) the balance of the margin account for the party with a long futures position if the futures price after six days is $2.284.10 and (ii) the price above which a margin call will be made for the party with a short position? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer a () $14,780; and (ii) $2,291.3 (0) 514,420; and () $2,293.5 () $14,420; and () $2,291.3 (0) 514,780 and (i) $2.293.5 None of the above. b C d Calculate the lower bounds Calculate the lower bounds of (i) a call option and (ii) a put option written on a non-dividend paying stock when the stock price is $50, the strike price of the call option is $46 and the strike price of the put option is $54. Assume that both options have four months to maturity and the risk-free rate during that time is 10%. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.09 (i) $5.51 and (ii) $3.21 (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.27 (i) $5.51 and (ii) $2.23 None of the above. a Save b C d e Unanswered Calculate the lower bounds Calculate the lower bounds of (i) a call option and (ii) a put option written on a non-dividend paying stock when the stock price is $50, the strike price of the call option is $46 and the strike price of the put option is $54. Assume that both options have four months to maturity and the risk-free rate during that time is 10%. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.09 (1) $5.51 and (ii) $3.21 (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.27 (i) $5.51 and (ii) $2.23 None of the above. Save b C d e Unanswered E A six-month European put option A six-month European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock is currently selling for $8.00. The stock price is 568, the strike price is $80, and the risk-free interest rate is 4% per annum. Calculate the minimum amount of arbitrage profit a trader can earn. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. 2 $2.92 b There will be no profit in this case. C $3.69 51.74 None of the above d . Consider a transaction today for seven futures contracts for gold Consider a transaction today for seven futures contracts for gold. Assume there are no storage costs. Also assume that the futures price is set at a level where there are no arbitrage opportunities. The contract is entered into when the spot price of gold is $2,232.00 per ounce, the continuously compounded rate of interest is 5% and the contract has six months until maturity. Each contract is on 100 ounces of gold and the initial margin per contract is $2,500. The maintenance margin per contract is $2,000 Assume that no money is withdrawn from either margin account during the next six days. What is (i) the balance of the margin account for the party with a long futures position if the futures price after six days is $2.284.10 and (ii) the price above which a margin call will be made for the party with a short position? Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer a () $14,780; and (ii) $2,291.3 (0) 514,420; and () $2,293.5 () $14,420; and () $2,291.3 (0) 514,780 and (i) $2.293.5 None of the above. b C d Calculate the lower bounds Calculate the lower bounds of (i) a call option and (ii) a put option written on a non-dividend paying stock when the stock price is $50, the strike price of the call option is $46 and the strike price of the put option is $54. Assume that both options have four months to maturity and the risk-free rate during that time is 10%. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.09 (i) $5.51 and (ii) $3.21 (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.27 (i) $5.51 and (ii) $2.23 None of the above. a Save b C d e Unanswered Calculate the lower bounds Calculate the lower bounds of (i) a call option and (ii) a put option written on a non-dividend paying stock when the stock price is $50, the strike price of the call option is $46 and the strike price of the put option is $54. Assume that both options have four months to maturity and the risk-free rate during that time is 10%. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. a (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.09 (1) $5.51 and (ii) $3.21 (i) $4.52 and (ii) $3.27 (i) $5.51 and (ii) $2.23 None of the above. Save b C d e Unanswered E A six-month European put option A six-month European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock is currently selling for $8.00. The stock price is 568, the strike price is $80, and the risk-free interest rate is 4% per annum. Calculate the minimum amount of arbitrage profit a trader can earn. Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. 2 $2.92 b There will be no profit in this case. C $3.69 51.74 None of the above d