Question: Consider the following numbers in a Python list: [28, 24, 23, 9, 1] In the hash table below of size 7 ([None, None, None, None,
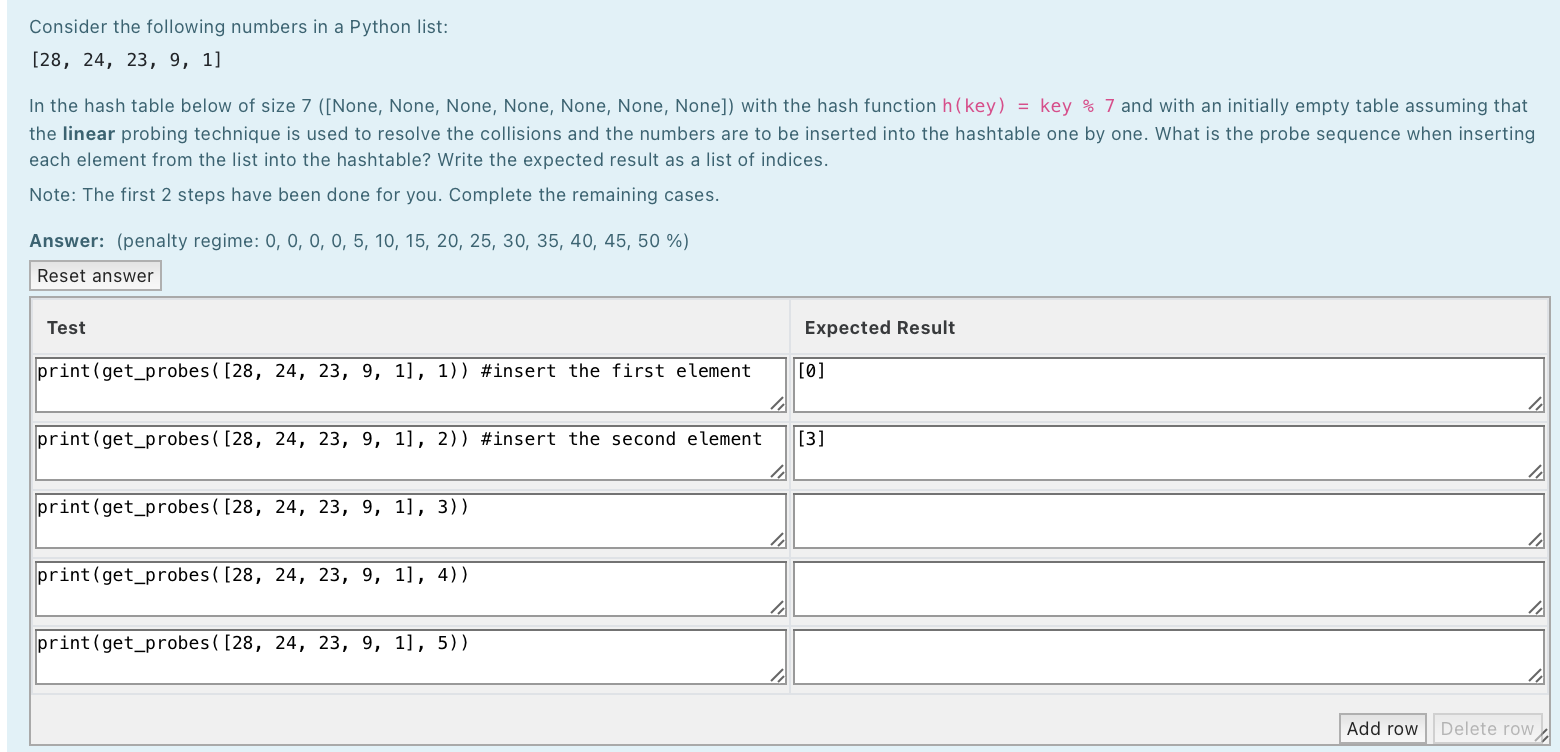
![9, 1] In the hash table below of size 7 ([None, None,](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f39b5126eeb_04066f39b50803e2.jpg)
![None, None, None, None, None]) with the hash function h(key) = key](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f39b51e19e7_04166f39b516ad67.jpg)
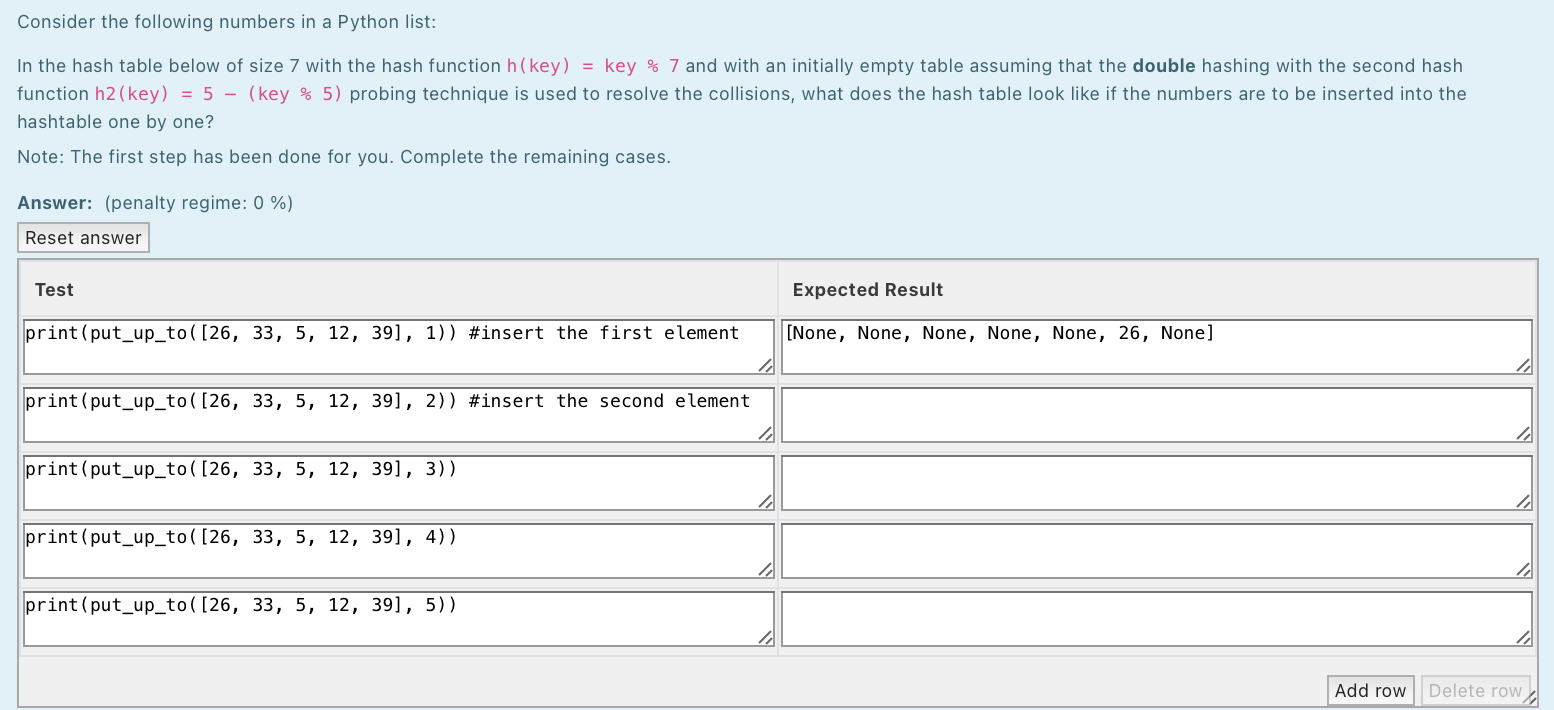
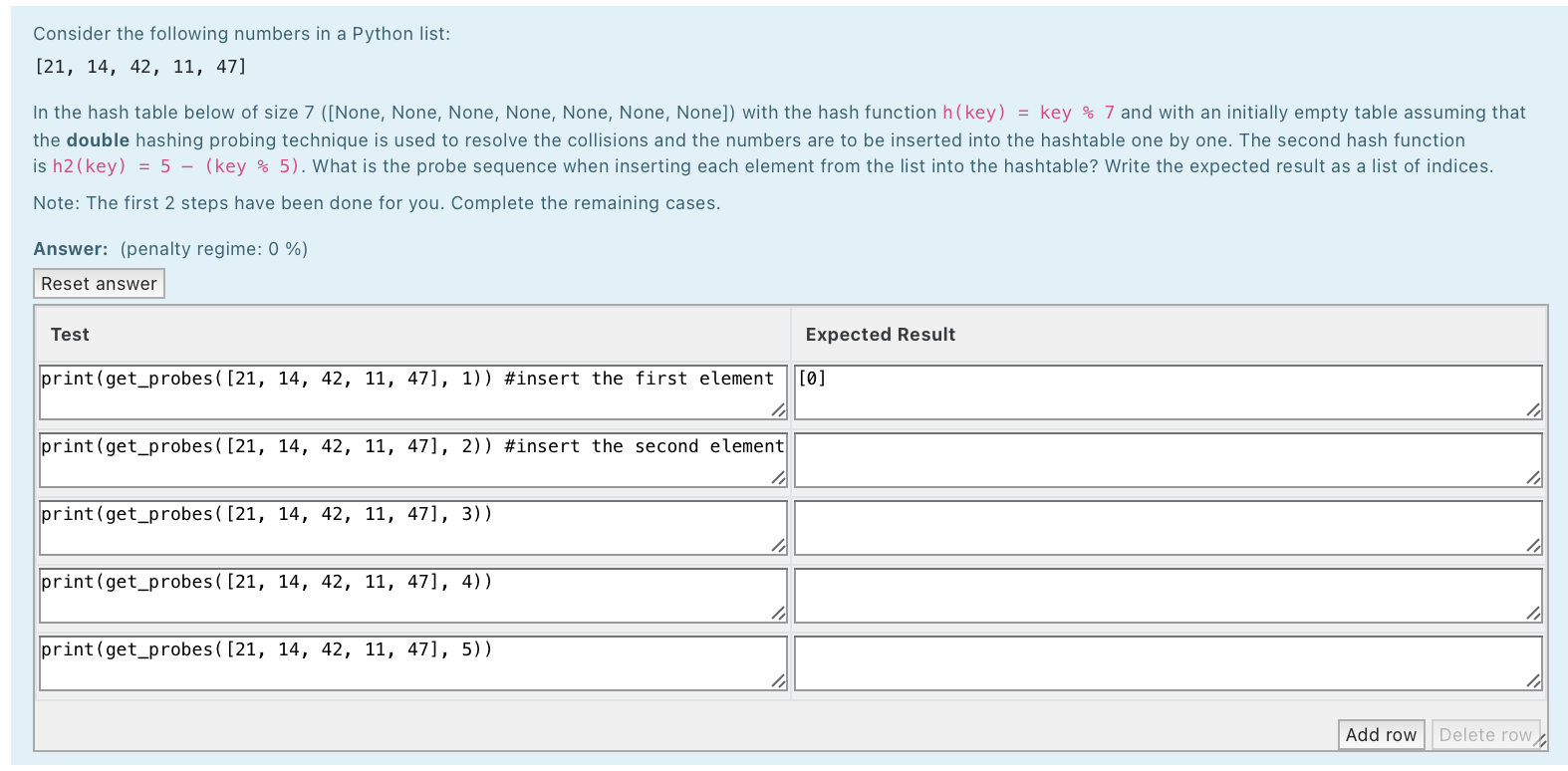
Consider the following numbers in a Python list: [28, 24, 23, 9, 1] In the hash table below of size 7 ([None, None, None, None, None, None, None]) with the hash function h(key) = key % 7 and with an initially empty table assuming that the linear probing technique is used to resolve the collisions and the numbers are to be inserted into the hashtable one by one. What is the probe sequence when inserting each element from the list into the hashtable? Write the expected result as a list of indices. Note: The first 2 steps have been done for you. Complete the remaining cases. Answer: (penalty regime: 0, 0, 0, 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 %) Reset answer Test Expected Result print (get_probes ( [28, 24, 23, 9, 1], 1)) #insert the first element [0] print(get_probes ( [28, 24, 23, 9, 1), 2)) #insert the second element [3] print(get_probes ( [28, 24, 23, 9, 1], 3)) print (get_probes ( [28, 24, 23, 9, 1], 4)) print(get_probes ( [28, 24, 23, 9, 1], 5)) Add row Delete row Consider the following numbers in a Python list: [28, 14, 7, 38, 31] In the hash table below of size 7 with the hash function h(key) = key % 7 and with an initially empty table assuming that the quadratic probing technique is used to resolve the collisions, what does the hash table look like if the numbers are to be inserted into the hashtable one by one? Note: The first step has been done for you. Complete the remaining cases. Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) Reset answer Test Expected Result print (put_up_to( [28, 14, 7, 38, 31], 1)) #insert the first element [28, None, None, None, None, None, None] print (put_up_to( [28, 14, 7, 38, 31), 2)) #insert the second element print (put_up_to( [28, 14, 7, 38, 31), 3)) print (put_up_to( [28, 14, 7, 38, 31], 4)) print (put_up_to ( [28, 14, 7, 38, 31], 5)) Add row Delete row Consider the following numbers in a Python list: [26, 33, 5, 12, 39] In the hash table below of size 7 ([None, None, None, None, None, None, None]) with the hash function h(key) = key % 7 and with an initially empty table assuming that the quadratic probing technique is used to resolve the collisions and the numbers are to be inserted into the hashtable one by one. What is the probe sequence when inserting each element from the list into the hashtable? Write the expected result as a list of indices. Note: The first 2 steps have been done for you. Complete the remaining cases. Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) Reset answer Test Expected Result print (get_probes ( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39], 1)) #insert the first element [5] print(get_probes ( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39), 2)) #insert the second element [5, 6] print (get_probes ( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39), 3)) print (get_probes ( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39], 4)) print (get_probes ( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39], 5)) Add row Delete row Consider the following numbers in a Python list: In the hash table below of size 7 with the hash function h(key) = key % 7 and with an initially empty table assuming that the double hashing with the second hash function h2 (key) = 5 (key % 5) probing technique is used to resolve the collisions, what does the hash table look like if the numbers are to be inserted into the hashtable one by one? Note: The first step has been done for you. Complete the remaining cases. Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) Reset answer Test Expected Result print(put_up_to( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39], 1)) #insert the first element [None, None, None, None, None, 26, None] print (put_up_to( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39), 2)) #insert the second element print (put_up_to( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39], 3)) print (put_up_to( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39), 4)) print (put_up_to( [26, 33, 5, 12, 39), 5)) Add row Delete rowy Consider the following numbers in a Python list: [21, 14, 42, 11, 47] In the hash table below of size 7 ([None, None, None, None, None, None, None]) with the hash function h(key) = key % 7 and with an initially empty table assuming that the double hashing probing technique is used to resolve the collisions and the numbers are to be inserted into the hashtable one by one. The second hash function is h2(key) = 5 - (key % 5). What is the probe sequence when inserting each element from the list into the hashtable? Write the expected result as a list of indices. Note: The first 2 steps have been done for you. Complete the remaining cases. Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) Reset answer Test Expected Result print (get_probes ( [21, 14, 42, 11, 47], 1)) #insert the first element [0] print (get_probes ( [21, 14, 42, 11, 47], 2)) #insert the second element print (get_probes ( [21, 14, 42, 11, 47], 3)) print (get_probes ( [21, 14, 42, 11, 47], 4)) print(get_probes ( [21, 14, 42, 11, 47], 5)) Add row Delete row
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


