Question
Convert C language to Assembly Language for Assembly Simulator Assembly Instructions : Program should count the taxicab distance of the empty space (in this case
Convert C language to Assembly Language for Assembly Simulator
Assembly Instructions :
Program should count the taxicab distance of the empty space (in this case represented by the number 16) to the last index.
Start Position -> 8000h
Result -> R1
If error return FFFFh in R1
Rules :
Program should end as follow -> END: JMP END ;END OF PROGRAM
C code :
#include
int main () { int array[] = {9, 7, 1, 6, 13, 3, 12, 2, 11, 15, 10, 14, 5, 16, 8, 4}; int i, row, rowcounter = 1, columncounter = 1, nrOfcolumns = 4, nrOfrows = 4, result = 0; for( i = 0; i 4) columncounter = 1; // Calculate row if(array[i] == 16) { if(rowcounter
Example of another working assembly program for P3 Simulator. Try to keep the same code configuration
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; EP1A1 (Example 1) ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Function EP1A1(N) ; res = 0 ; For i=1 To N ; res=res+i ; Next ; EP1A1=res ; End Function ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 1. Arguments in memory, away from the start of the program ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
ORIG 1000h
_N WORD 10
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; If the program reaches 1000h, overlaps ; the memory value of _N, that at the moment is ; 10. ; As it's a small program, the risk of that happening ; is very small. ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 2. Allocate the program in the beggining fof the memory ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; the returned value stays at R1 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
ORIG 0000h
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 3. Inititate R1 that is res with value 0 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
EP1A1: MOV R1,R0 ; R1
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 4. Initiate R2 that is the iterator variable i ; with the value 0 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
MOV R2,R0 ; R2
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 5. for each step of the cicle, increase the variable ;iterator value ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
Cicle: INC R2
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 6. Add the iterator variable i (R2) ; to the result res (R1) ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
ADD R1, R2
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 7. Check if iterator variable i (R2) ; have reached the limit that we are interested in _N ; Note that the access to _N is M[_N] as we are interested ; in having the value of _N, and not the memory ; position of _N, that is 1000h ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
CMP R2,M[_N] ; i!=_N
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 8. If the limit is not being reached, ; continue to the next cycle ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
BR.NZ Cicle
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; 9. The limit has been reached ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
End: JMP End ; End of program
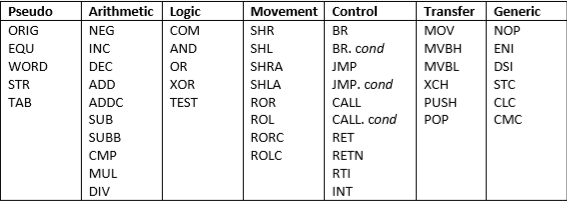
Arithmetic Logic Movement Control Pseudo Transfer Generic ORIG NEG COM SHR BR MOV NOP EQU BR. cond INC AND SHL MVBH ENI SHRA WORD DEC OR JMP MVBL DSI STR JMP. cond ADD XOR SHLA XCH STC TAB TEST ROR CALL PUSH ADDC CLC CALL. cond ROL SUB POP CMC SUBB RORC RET CMP ROLC RETN MUL RTI DIV INTStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


