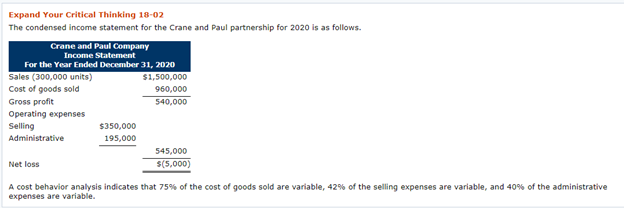
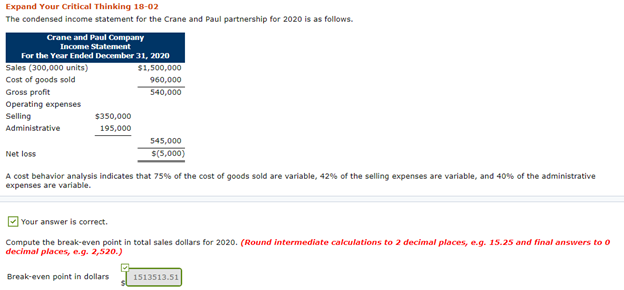

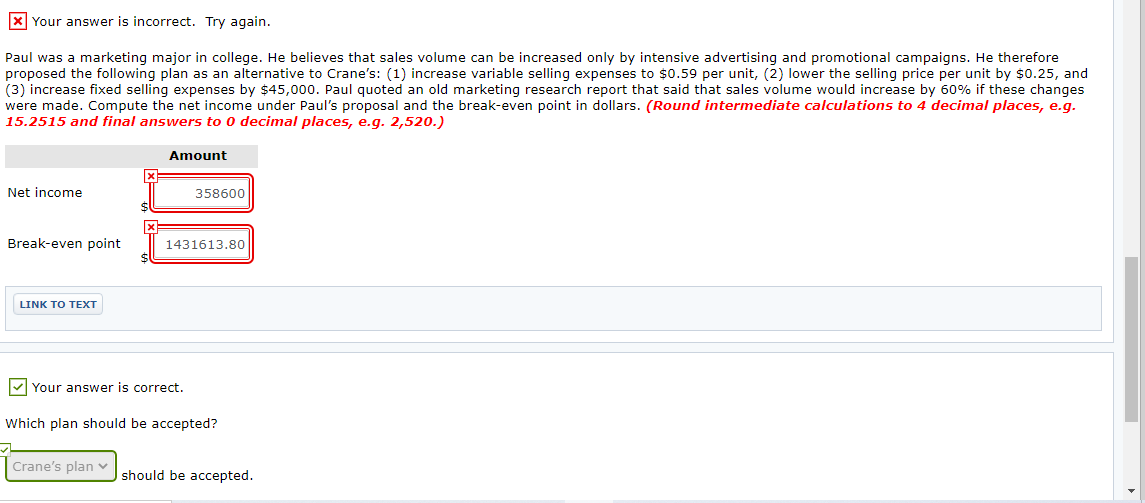

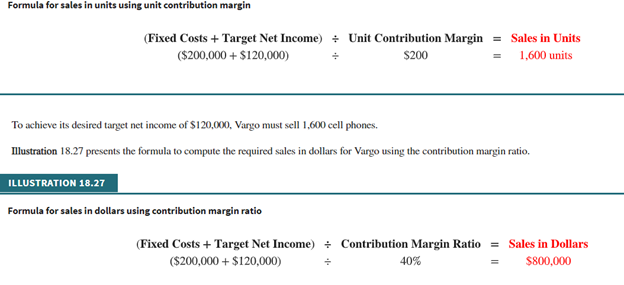
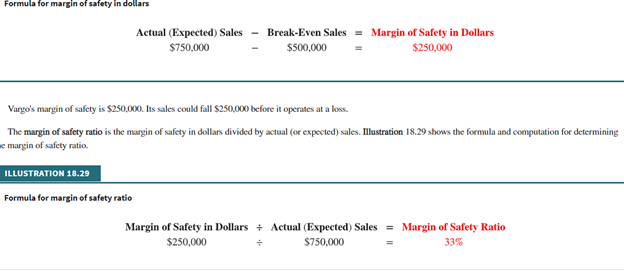
Expand Your Critical Thinking 18-02 The condensed income statement for the Crane and Paul partnership for 2020 is as follows. Crane and Paul Company Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 Sales (300,000 units) $1,500,000 Cost of goods sold 960,000 Gross profit 540,000 Operating expenses Selling $350,000 Administrative 195,000 545,000 Net loss $(5,000) A cost behavior analysis indicates that 75% of the cost of goods sold are variable, 42% of the selling expenses are variable, and 40% of the administrative expenses are variable. Expand Your Critical Thinking 18-02 The condensed income statement for the Crane and Paul partnership for 2020 is as follows. Crane and Paul Company Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 Sales (300,000 units) $1,500,000 Cost of goods sold 960,000 Gross profit 540,000 Operating expenses Selling $350,000 Administrative 195,000 545,000 Net loss $(5,000) A cost behavior analysis indicates that 75% of the cost of goods sold are variable, 42% of the selling expenses are variable, and 40% of the administrative expenses are variable. your answer is correct Compute the break-even point in total sales dollars for 2020. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25 and final answers to o decimal places, e.g. 2,520.) Break-even point in dollars 1513513.51 Your answer is correct. Crane has proposed a plan to get the partnership "out of the red" and improve its profitability. She feels that the quality of the product could be substantially improved by spending $0.25 more per unit on better raw materials. The selling price per unit could be increased to only $5.25 because of competitive pressures. Crane estimates that sales volume will increase by 25%. Compute the net income under Crane's proposal and the break-even point in dollars. (Round intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places, e.g. 15.2515 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 2,520.) Amount Net income 133750 Break-even point 1589189.19 x Your answer is incorrect. Try again. Paul was a marketing major in college. He believes that sales volume can be increased only by intensive advertising and promotional campaigns. He therefore proposed the following plan as an alternative to Crane's: (1) increase variable selling expenses to $0.59 per unit, (2) lower the selling price per unit by $0.25, and (3) increase fixed selling expenses by $45,000. Paul quoted an old marketing research report that said that sales volume would increase by 60% if these changes were made. Compute the net income under Paul's proposal and the break-even point in dollars. (Round intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places, e.g. 15.2515 and final answers to o decimal places, e.g. 2,520.) Amount Net income 358600 x Break-even point 1431613.80 LINK TO TEXT Your answer is correct. Which plan should be accepted? Crane's plan should be accepted. Formula for sales to meet target net income Sales Variable Costs Fixed Costs Target Net Income Formula for sales in units using unit contribution margin (Fixed Costs + Target Net Income) Unit Contribution Margin = Sales in Units ($200,000+ $120,000) $200 1,600 units To achieve its desired target net income of $120,000, Vargo must sell 1,600 cell phones. Illustration 18.27 presents the formula to compute the required sales in dollars for Vargo using the contribution margin ratio. ILLUSTRATION 18.27 Formula for sales in dollars using contribution margin ratio (Fixed Costs + Target Net Income) Contribution Margin Ratio = Sales in Dollars ($200,000+ $120,000) 40% $800.000 . Formula for margin of safety in dollars Actual (Expected) Sales $750,000 Break-Even Sales = Margin of Safety in Dollars $500,000 $250,000 Vargo's margin of safety is $250,000. Its sales could fall $250,000 before it operates at a loss. The margin of safety ratio is the margin of safety in dollars divided by actual (or expected) sales. Illustration 18.29 shows the formula and computation for determining e margin of safety ratio ILLUSTRATION 18.29 Formula for margin of safety ratio Margin of Safety in Dollars Actual (Expected) Sales = Margin of Safety Ratio $250,000 $750,000 33%













