
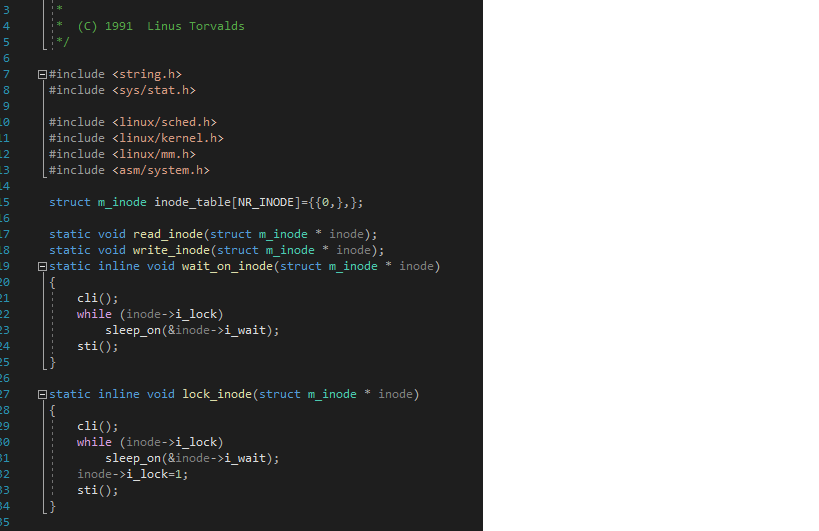








Experiment 1 1. Experimental requirements Read and analyze the ROMFS file system code (inode.c) in Linux, explain the functions and implementation ideas of each function, add comments to the code, and draw a flowchart. 2. Experimental tools Word, Visual Studio Experiment 2 1. Experimental requirements Design and implement a mock file system that requires directories, common files, and storage files. The directory structure of the file system uses a Linux-like tree structure. Operations that require simulation include: (1) Add, delete, and rename directories; (2) Display of the directory (list) (3) Add, delete, and rename files (4) Copy of files and directories (5) File read and write operations (6) Display the list of available commands when the user enters; display the help documentation for all commands when the user enters help; display the instructions for that command when entering a "command +?" (Such as "help +?"). (7) The user exits the system when entering exit. In addition, you need to write experimental design instructions, such as flowcharts, class diagrams, and so on. Key screenshots of experimental program operation (attach operating instructions if necessary). 2. Experimental tools Word, Linux, C compiler Note The experimental implementation is based on the LINUX platform. The development language must use C /C++, not Java. The experimental report does not use a uniform template, but the requirements must include the following: Experimenter identity information, such as class name, etc., and complete relevant content as required. ** (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds #include
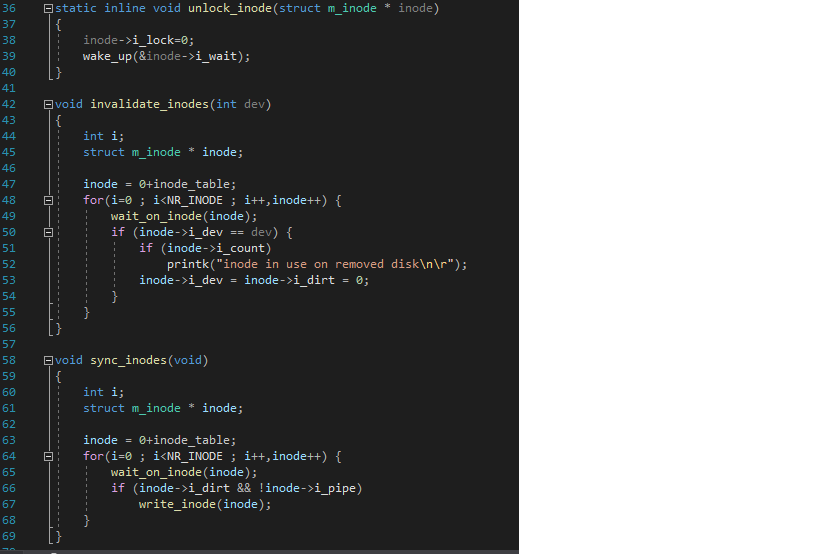
#include #include #include #include [ #include struct m_inode inode_table(NR_INODE ]={{@,},}; static void read_inode (struct m_inode * inode); static void write inode struct m_inode * inode); static inline void wait_on_inode (struct m_inode * inode), cli(); while (inode->i_lock) sleep_on(&inode->i_wait); sti(); static inline void lock inode (struct minode * inode) cli(); while (inode->i_lock) sleep_on(&inode->i_wait); inode->i_lock=1; sti(); static inline void unlock_inode (struct m_inode * inode) inode->i_lock=0; wake_up(&inode->i_wait); void invalidate_inodes(int dev) int i; struct m_inode * inode; inode = @+inode_table; for(i=0; ii_dev == dev) { if (inode->i_count) printk("inode in use on removed disk "); inode->i_dev = inode->i_dirt = 0; void sync_inodes (void) int i; struct m_inode * inode; inode = +inode_table; for(i=0; ii_dirt && !inode->i_pipe) write_inode (inode); static int _bmap(struct m_inode * inode, int block, int create) struct buffer_head * bh; int i; if (block= 7+512+512*512) panic("_bmap: block>big"); if (blocki_zone[block]) if (inode->i_zone[block]=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { inode->i_ctime=CURRENT_TIME; inode->i_dirt=1; return inode->i_zone[block]; block -= 7; if (blocki_zone[7]) if (inode->i_zone [7]=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { inode->i_dirt=1; i inode->i_ctime=CURRENT_TIME; 98 99 100 if (!inode->i_zone[7]) return 0; if (!(bh = bread (inode->i_dev, inode->i_zone [7]))) return ; i = ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data) [block]; if (create && !i) if (i=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data)[block]=i; bh->b_dirt=1; 101 LO3 104 105 brelse (bh); No issues found - ady brelse (bh); return i; 195 106 197 108 109 block -= 512; if (create && !inode->i_zone[8]) if (inode->i_zone[8]=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { inode->i_dirt=1; inode->i_ctime=CURRENT_TIME; 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 if (!inode->i_zone[8]) return ; if (!(bh=bread (inode->i_dev, inode->i_zone[8]))) return ; i = ((unsigned short *)bh->b_data)[block>>9]; if (create && !i) if (i=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data) [block>>9)-i: bh->b_dirt=1; brelse (bh); if (!i) return; if (!(bh=bread(inode->i_dev,i))) return 0; i = ((unsigned short *)bh->b_data)[block&511]; if (create && !i) if (i=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data)[block8511]-i: 1 bh->b_dirt=1; brelse (bh); return i; Gint bmap(struct m_inode * inode, int block) 139 . No issues found return _bmap(inode, block, 0); 148 141 142 143 nt create_block(struct m_inode * inode, int block) 145 return _bmap(inode, block,1); void iput(struct m_inode * inode) if (!inode) return; wait_on_inode (inode); if (!inode->i_count) panic("iput: trying to free free inode"); if (inode->i_pipe) { wake_up(&inode->i_wait); if (--inode->i_count) return; free_page(inode->i_size); inode->i_count=0; inode->i_dirt=0; inode->i_pipe=0; return; 158 if (!inode->i_dev) { inode->i_count--; return; } (S_ISBLK(inode->i_mode)) { sync_dev(inode->i_zone[@]); wait_on_inode (inode); repeat: 174 175 176 177 178 if (inode->i_count>1) { inode->i_count--; return; 179 if (!inode->i_nlinks) { truncate(inode); free_inode (inode); return; 180 181 182 183 184 185 if (inode->i_dirt) { write_inode (inode); /* we can sleep - so do again */ wait_on_inode(inode); goto repeat; 186 187 188 inode->i count--; return; struct m_inode * get_empty_inode (void) struct m inode * inode; static struct m_inode * last_inode = inode_table; int i; 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 du { inode = NULL; for (i = NR_INODE; i; i--) { if (++last inode >= inode table + NR INODE) last_inode = inode_table; if (!last_inode->i_count) { inode = last_inode; ir (!iriode->i_dirl && !irude->i_luck) break; 205 206 207 if (!inode) { 208 - No issues found for (i=0; ii_dirt) { write_inode (inode); wait_on_inode (inode); } while (inode->i_count); memset(inode,,sizeof(*inode)); inode->i_count = 1; return inode; struct m_inode * get_pipe_inode (void) struct m_inode * inode; if (!(inode = get_empty_inode())) return NULL; if (!(inode->i_size=get_free_page()) { inode->i_count = 0; ; return NULL; inode->i_count = 2; /* sum of readers/writers */ PIPE_HEAD(*inode) = PIPE_TAIL(*inode) = 0; inode->i_pipe = 1; return inode; struct m_inode * iget(int dev,int nr) No issues found struct m_ noue Inoue, empty; 244 245 if (!dev) panic("iget with dev==0"); empty - get_empty_inode(); inode = inode_table; while (inode i_dev != dev || inode->i_num != nr) { inode++; continue; 251 252 253 254 255 256 wait_on_inode (inode); if (inode->i dev != dev | inode->inum != nr) { inode = inode_table; continue; 259 260 261 inode->i_count++; if (inode->i_mount) { int i; 64 for (i = 0; i= NR_SUPER) { printk("Mounted inode hasn't got sb "); if (empty) iput(empty); return inode; iput(inode); dev = super_block[i].s_dev; nr = ROOT_INO; inode = inode_table; continue; No issues found - ady Tune here to search if (empty) iput(empty); return inode; if (!empty) return (NULL); inode=empty; inode->i_dev = dev; inode->i_num = nr; read_inode (inode); return inode; static void read_inode (struct m_inode * inode), struct super_block * sb; struct buffer_head * bh; int block; lock_inode(inode); if (!(sb-get_super(inode->i_dev))) panic("trying to read inode without dev"); block = 2 + sb->s_imap_blocks + 5b->5_zmap_blocks + (inode->i_num-1)/INODES_PER_BLOCK; if (!(bh=bread (inode->i_dev, block))) panic("unable to read i-node block"); *(struct d_inode *)inode = ((struct d_inode *)bh->b_data) [(inode->i_num-1)XINODES_PER_BLOCK]; brelse (bh); unlock_inode(inode); Estatic void write inode (struct m_inode * inode), 311 312 313 314 315 316 struct super_block * sb; struct buffer_head * bh; int block; 317 318 319 320 321 lock_inode (inode); if (!inode->i_dirt || !inode->i_dev) { unlock_inode (inode); return; 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 if (!(sb-get_super(inode->i_dev))) panic("trying to write inode without device") block = 2 + sb->s_imap_blocks + sb->S_zmap_blocks (inode->i_num-1)/INODES_PER_BLOCK; if (!(bh=bread(inode->i_dev, block))) panic("unable to read i-node block"); ((struct d_inode *)bh->b_data) [(inode->i_num-1)%INODES_PER_BLOCK] = *(struct d_inode *)inode; bh->b_dirt=1; inode->i_dirt=0; brelse (bh); unlock_inode (inode); 330 331 333 334 335 336 337 Experiment 1 1. Experimental requirements Read and analyze the ROMFS file system code (inode.c) in Linux, explain the functions and implementation ideas of each function, add comments to the code, and draw a flowchart. 2. Experimental tools Word, Visual Studio Experiment 2 1. Experimental requirements Design and implement a mock file system that requires directories, common files, and storage files. The directory structure of the file system uses a Linux-like tree structure. Operations that require simulation include: (1) Add, delete, and rename directories; (2) Display of the directory (list) (3) Add, delete, and rename files (4) Copy of files and directories (5) File read and write operations (6) Display the list of available commands when the user enters; display the help documentation for all commands when the user enters help; display the instructions for that command when entering a "command +?" (Such as "help +?"). (7) The user exits the system when entering exit. In addition, you need to write experimental design instructions, such as flowcharts, class diagrams, and so on. Key screenshots of experimental program operation (attach operating instructions if necessary). 2. Experimental tools Word, Linux, C compiler Note The experimental implementation is based on the LINUX platform. The development language must use C /C++, not Java. The experimental report does not use a uniform template, but the requirements must include the following: Experimenter identity information, such as class name, etc., and complete relevant content as required. ** (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds #include #include #include #include #include [ #include struct m_inode inode_table(NR_INODE ]={{@,},}; static void read_inode (struct m_inode * inode); static void write inode struct m_inode * inode); static inline void wait_on_inode (struct m_inode * inode), cli(); while (inode->i_lock) sleep_on(&inode->i_wait); sti(); static inline void lock inode (struct minode * inode) cli(); while (inode->i_lock) sleep_on(&inode->i_wait); inode->i_lock=1; sti(); static inline void unlock_inode (struct m_inode * inode) inode->i_lock=0; wake_up(&inode->i_wait); void invalidate_inodes(int dev) int i; struct m_inode * inode; inode = @+inode_table; for(i=0; ii_dev == dev) { if (inode->i_count) printk("inode in use on removed disk "); inode->i_dev = inode->i_dirt = 0; void sync_inodes (void) int i; struct m_inode * inode; inode = +inode_table; for(i=0; ii_dirt && !inode->i_pipe) write_inode (inode); static int _bmap(struct m_inode * inode, int block, int create) struct buffer_head * bh; int i; if (block= 7+512+512*512) panic("_bmap: block>big"); if (blocki_zone[block]) if (inode->i_zone[block]=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { inode->i_ctime=CURRENT_TIME; inode->i_dirt=1; return inode->i_zone[block]; block -= 7; if (blocki_zone[7]) if (inode->i_zone [7]=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { inode->i_dirt=1; i inode->i_ctime=CURRENT_TIME; 98 99 100 if (!inode->i_zone[7]) return 0; if (!(bh = bread (inode->i_dev, inode->i_zone [7]))) return ; i = ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data) [block]; if (create && !i) if (i=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data)[block]=i; bh->b_dirt=1; 101 LO3 104 105 brelse (bh); No issues found - ady brelse (bh); return i; 195 106 197 108 109 block -= 512; if (create && !inode->i_zone[8]) if (inode->i_zone[8]=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { inode->i_dirt=1; inode->i_ctime=CURRENT_TIME; 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 if (!inode->i_zone[8]) return ; if (!(bh=bread (inode->i_dev, inode->i_zone[8]))) return ; i = ((unsigned short *)bh->b_data)[block>>9]; if (create && !i) if (i=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data) [block>>9)-i: bh->b_dirt=1; brelse (bh); if (!i) return; if (!(bh=bread(inode->i_dev,i))) return 0; i = ((unsigned short *)bh->b_data)[block&511]; if (create && !i) if (i=new_block(inode->i_dev)) { ((unsigned short *) (bh->b_data)[block8511]-i: 1 bh->b_dirt=1; brelse (bh); return i; Gint bmap(struct m_inode * inode, int block) 139 . No issues found return _bmap(inode, block, 0); 148 141 142 143 nt create_block(struct m_inode * inode, int block) 145 return _bmap(inode, block,1); void iput(struct m_inode * inode) if (!inode) return; wait_on_inode (inode); if (!inode->i_count) panic("iput: trying to free free inode"); if (inode->i_pipe) { wake_up(&inode->i_wait); if (--inode->i_count) return; free_page(inode->i_size); inode->i_count=0; inode->i_dirt=0; inode->i_pipe=0; return; 158 if (!inode->i_dev) { inode->i_count--; return; } (S_ISBLK(inode->i_mode)) { sync_dev(inode->i_zone[@]); wait_on_inode (inode); repeat: 174 175 176 177 178 if (inode->i_count>1) { inode->i_count--; return; 179 if (!inode->i_nlinks) { truncate(inode); free_inode (inode); return; 180 181 182 183 184 185 if (inode->i_dirt) { write_inode (inode); /* we can sleep - so do again */ wait_on_inode(inode); goto repeat; 186 187 188 inode->i count--; return; struct m_inode * get_empty_inode (void) struct m inode * inode; static struct m_inode * last_inode = inode_table; int i; 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 du { inode = NULL; for (i = NR_INODE; i; i--) { if (++last inode >= inode table + NR INODE) last_inode = inode_table; if (!last_inode->i_count) { inode = last_inode; ir (!iriode->i_dirl && !irude->i_luck) break; 205 206 207 if (!inode) { 208 - No issues found for (i=0; ii_dirt) { write_inode (inode); wait_on_inode (inode); } while (inode->i_count); memset(inode,,sizeof(*inode)); inode->i_count = 1; return inode; struct m_inode * get_pipe_inode (void) struct m_inode * inode; if (!(inode = get_empty_inode())) return NULL; if (!(inode->i_size=get_free_page()) { inode->i_count = 0; ; return NULL; inode->i_count = 2; /* sum of readers/writers */ PIPE_HEAD(*inode) = PIPE_TAIL(*inode) = 0; inode->i_pipe = 1; return inode; struct m_inode * iget(int dev,int nr) No issues found struct m_ noue Inoue, empty; 244 245 if (!dev) panic("iget with dev==0"); empty - get_empty_inode(); inode = inode_table; while (inode i_dev != dev || inode->i_num != nr) { inode++; continue; 251 252 253 254 255 256 wait_on_inode (inode); if (inode->i dev != dev | inode->inum != nr) { inode = inode_table; continue; 259 260 261 inode->i_count++; if (inode->i_mount) { int i; 64 for (i = 0; i= NR_SUPER) { printk("Mounted inode hasn't got sb "); if (empty) iput(empty); return inode; iput(inode); dev = super_block[i].s_dev; nr = ROOT_INO; inode = inode_table; continue; No issues found - ady Tune here to search if (empty) iput(empty); return inode; if (!empty) return (NULL); inode=empty; inode->i_dev = dev; inode->i_num = nr; read_inode (inode); return inode; static void read_inode (struct m_inode * inode), struct super_block * sb; struct buffer_head * bh; int block; lock_inode(inode); if (!(sb-get_super(inode->i_dev))) panic("trying to read inode without dev"); block = 2 + sb->s_imap_blocks + 5b->5_zmap_blocks + (inode->i_num-1)/INODES_PER_BLOCK; if (!(bh=bread (inode->i_dev, block))) panic("unable to read i-node block"); *(struct d_inode *)inode = ((struct d_inode *)bh->b_data) [(inode->i_num-1)XINODES_PER_BLOCK]; brelse (bh); unlock_inode(inode); Estatic void write inode (struct m_inode * inode), 311 312 313 314 315 316 struct super_block * sb; struct buffer_head * bh; int block; 317 318 319 320 321 lock_inode (inode); if (!inode->i_dirt || !inode->i_dev) { unlock_inode (inode); return; 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 if (!(sb-get_super(inode->i_dev))) panic("trying to write inode without device") block = 2 + sb->s_imap_blocks + sb->S_zmap_blocks (inode->i_num-1)/INODES_PER_BLOCK; if (!(bh=bread(inode->i_dev, block))) panic("unable to read i-node block"); ((struct d_inode *)bh->b_data) [(inode->i_num-1)%INODES_PER_BLOCK] = *(struct d_inode *)inode; bh->b_dirt=1; inode->i_dirt=0; brelse (bh); unlock_inode (inode); 330 331 333 334 335 336 337

















