



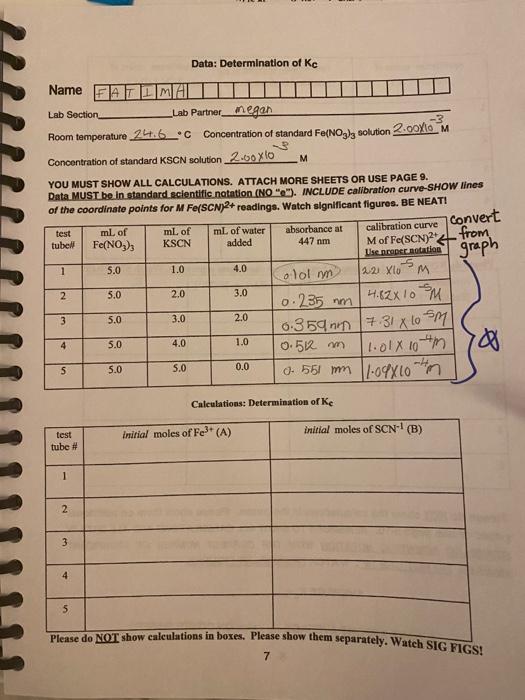

Experiment #5: THE DETERMINATION OF THE EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT FOR A CHEMICAL REACTION PURPOSE In this experiment you will study the equilibrium properties of the reaction between iron (II) lon and the thiocyanate ion: Fe3+ (aq) + SCN1(aq) FeSCN2+ (aq) (1) You will prepare several solutions containing known concentrations of iron (IHI) nitrate Fe(NO3)3 and potassium thiocyanate KSCN. These variously prepared solutions, when analyzed, will demonstrate that Kc has the same value in each of the mixtures. Objectives THEORY: When solutions containing Fe3+ ion and thiocyanate lon, SCN-1, are mixed, reaction (1) occurs to some extent forming the FeSCN2+ complex ion, which has a deep red color. For every mole of FeSCN2+ that is formed, one mole of Fe3+ and one mole of SCN-1 will react. Regardless of the initial reactant concentrations, when equilibrium is reached, each of the three species will have a concentration such that the Kc expression at a given temperature will always yield the same numerical value tok Ko The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is: [FeSCN2+1 [Fe "*TSCN-T; - Kc (2) The concentration of the FeSCN2+ in each sample can be determined by using a spectrophotometer at 447 nm. By knowing the initial concentrations of the reactants and the equilibrium concentration of the product, you can then calculate the equilibrium concentration of the reactants. Kc is then calculated by placing the equilibrium concentrations in the equilibrium expression (2). PROCEDURE: ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES! You should work in partners. **You must calibrate the Spec-20 prior to using it. See page 3 for Instructions** Obtain 2 cuvettes (from front)-1 for a blank and 1 for all solutions, Label 5 large test tubes (from your drawer (1 to 5) in succession on your test tube rack. Pour approximately 30 mL of 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe(NO3)3 which has been dissolved in 1 M HNO3, into a dry 100 ml beaker. CAUTION: Since these reagents are dissolved in 1M HNO3 any of this liquid on your clothing it will result in acid holes, and the iron (III) present will cause a brown stain, 1 Add approximately 20 mL 2.00 x 103 M KSCN to another dry 100 mL beaker. The pipettes supplied are calibrated to deliver. Do not push out the small volume remaining in the pipette after it has drained. Remove the GREEN plunger and let it drain by gravity. Pipet 5.0 mL of the standard 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe(NO3)3 into each of the 5 test tubes. Pipet 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mL of the standard 2.00 X 10-3 M KSCN into each of the corresponding test tubes labeled 1 to 5) Then pipette the proper number of mL of deionized water into each test tube to bring the total volume in each tube to 10.0 mL Stir dach solution thoroughly with a stirring rod, being sure to wipe the stirring rod before placing it in a second solution Alternatively your instructor may demonstrate a "inger- swirling technique to mix the reagents. the volumes of reagents to be added tube are summarized below. Note: Test tube #5 has NO water in it, each 1.0 3.0 2.0 4.0 mL of water 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 mL of KSCN 1.0 5.0 ml of Fe(NO3)3 5 mixture # 2 3 Use the same spectrophotometer for all absorbance measurements. SET the wavelength control to 447 nm, and zero the instrument using a cuvette that contains a "blank" solution. The blank is made up using 5.0 mL of the standard 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe(NO3), and 5.0 mL of distilled water. Follow the instructions on "Operating a Spectronic 20" on the next page. Remember to SET BOTH left and right maximums for the blankll PREPARE ALL ORIGINAL SOLUTIONS IN LARGE TEST TUBES. PLEASE NOTE: ONLY CUVETTES (SPECIAL TEST TUBES) GO INTO THE SPEC 20. You must do steps #2 through #8 on the next page. Step #1 has been already done. READ SPECTROPHOTOMETER AND GRAPH TO 3 DIGITS!!!!!! 2 op am hat rati ant ite Operating a Spectronic 20 ***NEED 2 POINTS OF CALIBRATION RIGHT and LEFT adjustments 1. Turn the instrument on using the left knob on front of the case. A red indicator light will appear when the instrument is on. Allow 15 minutes warm-up time. **2 LEET: With the sample compartment empty and the door closed, adjust the instrument with the left knob on front of the case so that the needle points to 0% T (or A). To avoid a parallax error, position your eye so that the needle and its Image line up each time a reading is made. 3. Check that the instrument is adjusted to a wavelength of 447 nanometers (10-meters). **4. RIGHT Prepare a blank. In A CLEAN LARGE TEST TUBE pipette 5.0 mL of the standard 2.00 X 103 M Fe(NO3)3 and pipette 5.00 mL of delonized water. Stir the mixture then pour some (up to the "Power") of this solution into a clean cuvette (pre-rinsed with deionized water). Wipe the outside of the cuvette with a kimwipe and place it in the sample holder so that the trademark on the cuvette lines up with the mark on the sample holder. Push the cuvette down until it bottoms in the holder. Close the door and set the instrument to read 100% I (zero A) by turning the right front knob. 5. Remove the blank. Insert another cuvette with solution 1 up to the midway of the "flower". Be sure to dry and position the cuvette as in step 4. Read absorbance as quickly as possible straight-on 8. Repeat with EACH of the other 4 mixtures. 7. When finished with the instrument turn the power off unless someone else is waiting. Wash all cuvettes, rinse them with deionized water and return them to the supply containers. They cost $5 each and are NOT to be returned to your.lab drawer. 8 meter wavelength adjust sample holder cover 100% T (and O A) adjust on-off and 0% T adjust 3 CALCULATIONS: (see sample calculation included p 6) MUST SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS AND CORRECT SIGNIFICANT FIGURES. BE NEAT. The determination of K is straight forward if you follow these steps: Step 1: Find the initial number of moles of each reactant: number moles Fe3+=# moles A= ( Molarity A) * (* Liters A) (3) number moles SCN-1 = #moles 3 = ( Molarity B)* (#Liters B) Step 2: Find the number of moles of product at equilibrium: Need to read graph. will need to converteguilibrium concentration to standard scientific notation on graph. The concentration (M) of the FeSCN2at equilibrium will be determined directly from the calibration curve graph on the next page. Use an equation similar to equation #3 to convert M of FeSCN2+ to moles. number moles FeSCN2+ = #moles c= (Molarity c) * (# Liters c) Step 3: Find the number of moles of each reactant at equilibrium: For every FeSCN2+ ion that is formed, one ion each of Fe3+ and SCN-1 is consumed. Fe3+ + SCN-1 FeSCN2+ Step 1, initial A moles B moles Step 2 C moles Step 3, at equil. (A-C) moles (B-C) moles C moles Step 4: Convert the number of moles of all species at equilibrium to CONCENTRATION IN MOUL, M, by dividing the number of moles by the total volume in liters. [Fe3+1 = (A-C) moles / total volume in L [SCN-'] = (B-C) moles / total volume in L [FeSCN241 = C moles / total volume in L Step 5: Find Ke by putting the concentration (mol/L) of each species into the proper equilibrium constant expression and solving for Kc Report must include: calibration curve with coordination lines, correct scientific notation SAMPLE CALCULATION FOR MIXTURE 1: Note all data is in standard scientific notation. Step 1: Find the initial number of moles of each reactant: number molos F03+moles A - (2.00 x 108m) x (5.0 x 10-3 L) = 1.0 x 10-5 molo. number moles SC #moles 3 = (2.00 x 10M)x(1.0 x 10L) - 2.0 x 10 mole Step 2: Find the number of moles of product at equilibrium: * number moles FeSCN2+ = # molesc (Molarity c) * (Liters c) "must convert From the graph: it the absorbance for mixture 1 = 0.12, then the (FeSCN2+leq = 0.24 x 10+M = 24 x 105 M (see the graph) and the total volume in the cuvette at equilibrium = 10 ml = 0.010 L number moles FeSCN2+ = #molesc (2.4x 106m) (1.0 x 10L) = 2.4 x 10-7 mol. from graph Step 3: Find the number of moles of each reactant at equilibrium: Fe3+ SCN-1 FeSCN2+ Step 1, initial 1.0 x 10-5 mol 2.0 x 10-6 mol Step 2 2.4 x 10-7 mol Step 3, at equil. (1.0 x 10-5-2.4 x 107 moles =9.76 x 10-6 moles (2.0 x 10-6-24 x 10-7) moles = 1.76 x 10-6 moles 24x 107 moles Step 4: Convert number of moles of all species at equilibrium to CONCENTRATION in moVL, by dividing the number of moles by the total volume in liters. [Fe3+] - 9.76 x 10-6 moles/1.0 x 102 L=9.76 x 10*M (SCN: 1) = 1.76 x 10 moles / 1.0 x 10-2 L = 1.76 x 10-4M FeSCN2+1 = 24 x 107 moles/1.0 x 102L-24x10M Step 5: Find Kc by putting the concentration (mol/L) of each species into the proper equilibrium constant expression and solving for Ke convert to standard scientific notation [FeSCN2 = 2.4 x 10-6 M7119.76 * 10+ M)(1.76 x 10+M)- 1.4 x 102 = (FeSCN1 (From graph Data: Determination of Ke Name ATLMAI Lab Section _Lab Partner_megan -3 Room temperature 24.6C Concentration of standard Fo/NO3), solution 2.00/10 M Concentration of standard KSCN solution 2.60 xlo M YOU MUST SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS. ATTACH MORE SHEETS OR USE PAGE 9. Data MUST be in standard scientific notation (NO""). INCLUDE calibration curve-SHOW lines of the coordinate points for M Fe(SCN)2+ readings. Watch significant figures. BE NEATI test ml of ml Convert mL of water calibration curve absorbance at tube! Fe(NO3)3 KSCN added 447 nm Mof Fe(SCN)2 from User per sotation 1 1.0 4.0 -5 ololm 121 Xlo M 2 5.0 2.0 3.0 0.235 mm 4.82x 10 m 3 5.0 3.0 2.0 0.35ann 7.31 x 0 sm 4 5.0 4.0 1.0 0.56 m 1.01x 10m 5 5.0 5.0 0.0 0. 551 mm 1.09x10m graph 5.0 5 Calculations: Determination of Ke initial moles of Fe3+ (A) initial moles of SCN1 (B) test tube # 1 2 3 4 5 Please do NOT show calculations in boxes. Please show them separately. Watch SIG FIGS! 7 equilibrium moles of equilibrium moles of Fet (A-C) equilibrium moles of FeSCN2(C) SCN) (B-C) 2 3 5 Please do NOT show calculations in boxes. Please show them separately. Watch SIG FIGS! equilibrium equilibrium [Fe3") equilibrium (SCN) K. [FeSCN1 2 3 4 5 Please do NOT show the calculations in the boxes. Please show them on additional paper or use page 9-10. REMEMBER TO SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS AND ALL DATA IN STANDARD SCIENTIFIC NOTATION WITH THE CORRECT NUMBER OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES. DO NOT USE "e". WATCH SIGNIFICANT FIGURES. AVERAGEK PLEASE REPORT AVERAGE Kc Value ON COVER SHEET. 8













