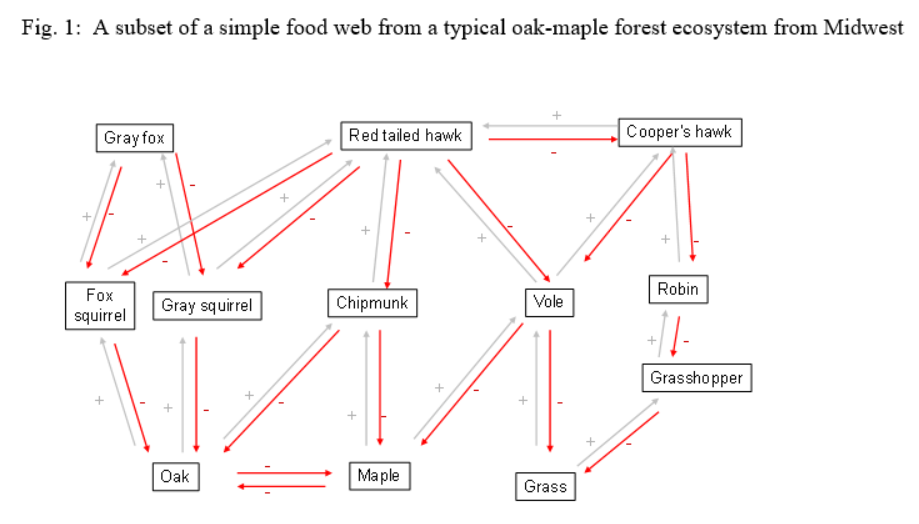
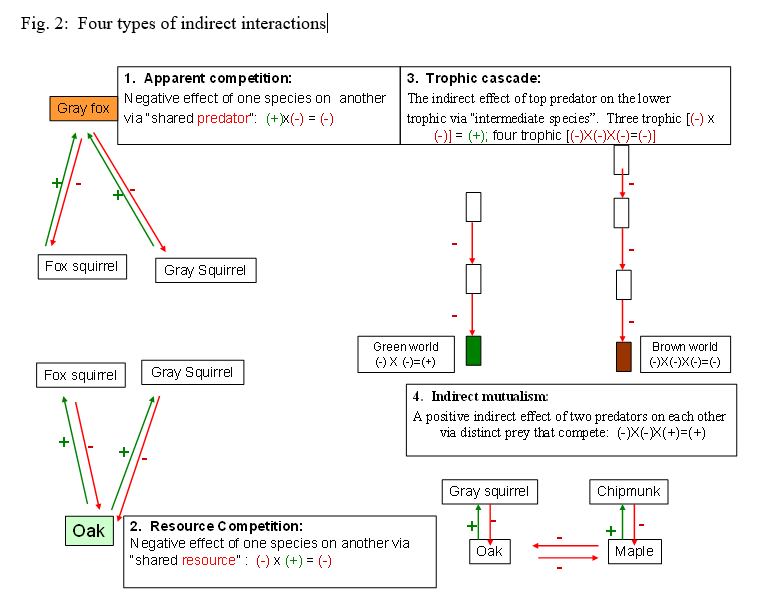

Fig. 1: A subset of a simple food web from a typical oak-maple forest ecosystem from Midwest Gray fox Red tailed hawk Cooper's hawk + Robin Fox squirrel Gray squirrel Chipmunk Vole Grasshopper Oak Maple Grass Fig. 2: Four types of indirect interactions Gray fox 1. Apparent competition: Negative effect of one species on another via"shared predator": (+ X(-) = (-) 3. Trophic cascade: The indirect effect of top predator on the lower trophic via "intermediate species. Three trophic [(-) X 0)] = (+); four trophic [(-)X(-)X(-)=(-)) Fox squirrel Gray Squirrel Greenworld (-) X (-)=(+) Brown world (-)X(-)X(-)=(-) Fox squirrel Gray Squirrel 4. Indirect mutunlism: A positive indirect effect of two predators on each other via distinct prey that compete: (-)X-X(+)=(+) + Gray squirrel Chipmunk Oak 2. Resource Competition: Negative effect of one species on another via "shared resource": (-) (+) = (-) + Maple Oak answer these questions using the food web for the Midwestern oak-maple community (Fig. 1). Explanations of the different types of indirect interactions are provided in Fig. 2. 1. List all the apparent competition interactions, using the format prey 1 shared predator prey 2 (e.g., fox squirrel gray fox - gray squirrel) 2. List all the resource competition interactions, using the format predator 1 shared prey predator 2" (e.g., fox squirrel - oak - gray squirrel) 3. List a minimum of ten trophic cascades, using the format predator prey prey...etc. (e.g., gray fox -fox squirrel - oak) 4. List all the indirect mutualism interactions, using the format predator 1 prey 1 prey 2 - predator 2" (e.g., gray squirrel oak - maple - chipmunk) Fig. 1: A subset of a simple food web from a typical oak-maple forest ecosystem from Midwest Gray fox Red tailed hawk Cooper's hawk + Robin Fox squirrel Gray squirrel Chipmunk Vole Grasshopper Oak Maple Grass Fig. 2: Four types of indirect interactions Gray fox 1. Apparent competition: Negative effect of one species on another via"shared predator": (+ X(-) = (-) 3. Trophic cascade: The indirect effect of top predator on the lower trophic via "intermediate species. Three trophic [(-) X 0)] = (+); four trophic [(-)X(-)X(-)=(-)) Fox squirrel Gray Squirrel Greenworld (-) X (-)=(+) Brown world (-)X(-)X(-)=(-) Fox squirrel Gray Squirrel 4. Indirect mutunlism: A positive indirect effect of two predators on each other via distinct prey that compete: (-)X-X(+)=(+) + Gray squirrel Chipmunk Oak 2. Resource Competition: Negative effect of one species on another via "shared resource": (-) (+) = (-) + Maple Oak answer these questions using the food web for the Midwestern oak-maple community (Fig. 1). Explanations of the different types of indirect interactions are provided in Fig. 2. 1. List all the apparent competition interactions, using the format prey 1 shared predator prey 2 (e.g., fox squirrel gray fox - gray squirrel) 2. List all the resource competition interactions, using the format predator 1 shared prey predator 2" (e.g., fox squirrel - oak - gray squirrel) 3. List a minimum of ten trophic cascades, using the format predator prey prey...etc. (e.g., gray fox -fox squirrel - oak) 4. List all the indirect mutualism interactions, using the format predator 1 prey 1 prey 2 - predator 2" (e.g., gray squirrel oak - maple - chipmunk)









