Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
............... FloatArrays.java : ckage csi213.lab05; import java.util.Arrays; /** * This {@code FloatArrays} class provides methods for manipulating {@code Float} arrays. */ public class FloatArrays {
...............
FloatArrays.java :
ckage csi213.lab05;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* This {@code FloatArrays} class provides methods for manipulating {@code Float} arrays.
*/
public class FloatArrays {
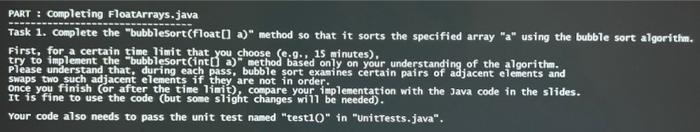
/**
* Sorts the specified array using the bubble sort algorithm.
*
* @param a
* an {@code Float} array
*/
public static void bubbleSort(float[] a) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
for (int last = a.length - 1; last >= 1; last--) {
// TODO: add some code here
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
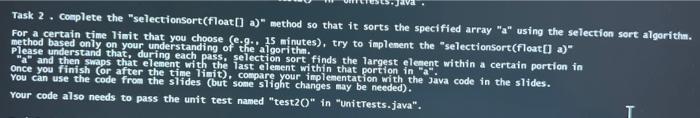
/**
* Sorts the specified array using the selection sort algorithm.
*
* @param a
* an {@code Float} array
* @param out
* a {@code PrintStream} to show the array at the end of each pass
*/
public static void selectionSort(float[] a) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
for (int last = a.length - 1; last >= 1; last--) {
// TODO: add some code here
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
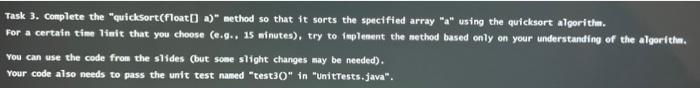
/**
* Sorts the specified array using the quick sort algorithm.
*
* @param a
* an {@code Float} array
* @param out
* a {@code PrintStream} to show the array at the end of each pass
*/
public static void quickSort(float[] a) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
for (int index = 1; index
// TODO: add some code here
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
/**
* The main method of the {@code FloatArrays} class.
*
* @param args
* the program arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
float[] a = { 5.3F, 3.8F, 1.2F, 2.7F, 4.99F };
bubbleSort(Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length));
System.out.println();
selectionSort(Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length));
System.out.println();
quickSort(Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length));
System.out.println();
}
}
.....................
UnitTests.java :
package csi213.lab05;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* {@code UnitTests} tests the Lab 5 implementations.
*
*/
public class UnitTests {
static float[] a = { 5, 3, 1, 2, 4 };
static float[] b = { 7, 6, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4 };
/**
* Tests the Task 1 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
float[] a1 = Arrays.copyOf(a,a.length);
FloatArrays.bubbleSort(a1);
compare(a,a1);
float[] b1 = Arrays.copyOf(b,b.length);
FloatArrays.bubbleSort(b1);
compare(b,b1);
}
/**
* Tests the Task 2 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
float[] a1 = Arrays.copyOf(a,a.length);
FloatArrays.selectionSort(a1);
compare(a,a1);
float[] b1 = Arrays.copyOf(b,b.length);
FloatArrays.selectionSort(b1);
compare(b,b1);
}
/**
* Tests the Task 3 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
float[] a1 = Arrays.copyOf(a,a.length);
FloatArrays.quickSort(a1);
compare(a,a1);
float[] b1 = Arrays.copyOf(b,b.length);
FloatArrays.quickSort(b1);
compare(b,b1);
}
/**
* Compares the two specified {@code float} arrays.
*
* @param a
* a {@code float} array
* @param b
* a {@code float} array
*/
protected void compare(float[] original, float[] sorted) {
assertEquals(original.length, sorted.length);
float[] temp = Arrays.copyOf(original,original.length);
Arrays.sort(temp);
for (int i = 0; i
assertEquals(temp[i], sorted[i],.001f);
}
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


