Question
Harriston Electronics builds circuit boards for a variety of applications in industrial equipment. The firm was founded in 1986 by two electrical engineers who left
Harriston Electronics builds circuit boards for a variety of applications in industrial equipment. The firm was founded in 1986 by two electrical engineers who left their jobs with General Electric (GE) Corporation. Harriston Electronics balance sheet for year-end 2014 describes a firm with $1,184,841,000 in assets (book values) and invested capital of approximately $2.2 billion (based on market values).
Harristons CFO, Margaret L. Hines, is concerned that its new investments be required to meet an appropriate cost of capital hurdle before capital is committed. Consequently, she initiated a cost of capital study by one of her senior financial analysts, Jack Frist. Shortly after receiving the assignment, Frist called the firms investment banker to get input on current capital costs.
Frist learned that, although the firms current debt capital required a 7.5% coupon rate of interest (with annual interest payments and no principal repayments until 2020), the current yield to maturity on similar debt had risen to 8.5% so that the current market value of the firms outstanding bonds had fallen to $624,385,826. Because the firms short-term notes were issued within the last thirty days, the 9% contract rate on the notes was the same as the current cost of credit for such notes.
- What are Harristons total invested capital and capital structure weights for debt and equity? (Hint: The firm has some short-term debt [notes payable] that, like long-term debt, is also interest-bearing debt.)
- Assuming a long-term US Treasury bond yield of 5.42% and an estimated market risk premium of 5%, what is Harristons cost of equity based on CAPM if the firms levered equity beta is 1.2?
- What is your estimate of Harristons WACC? The firms tax rate is 35%.
( THE QUESTION IS TO ONLY FILL THE BLUE BOXES ON THE EXCEL PICTURES)
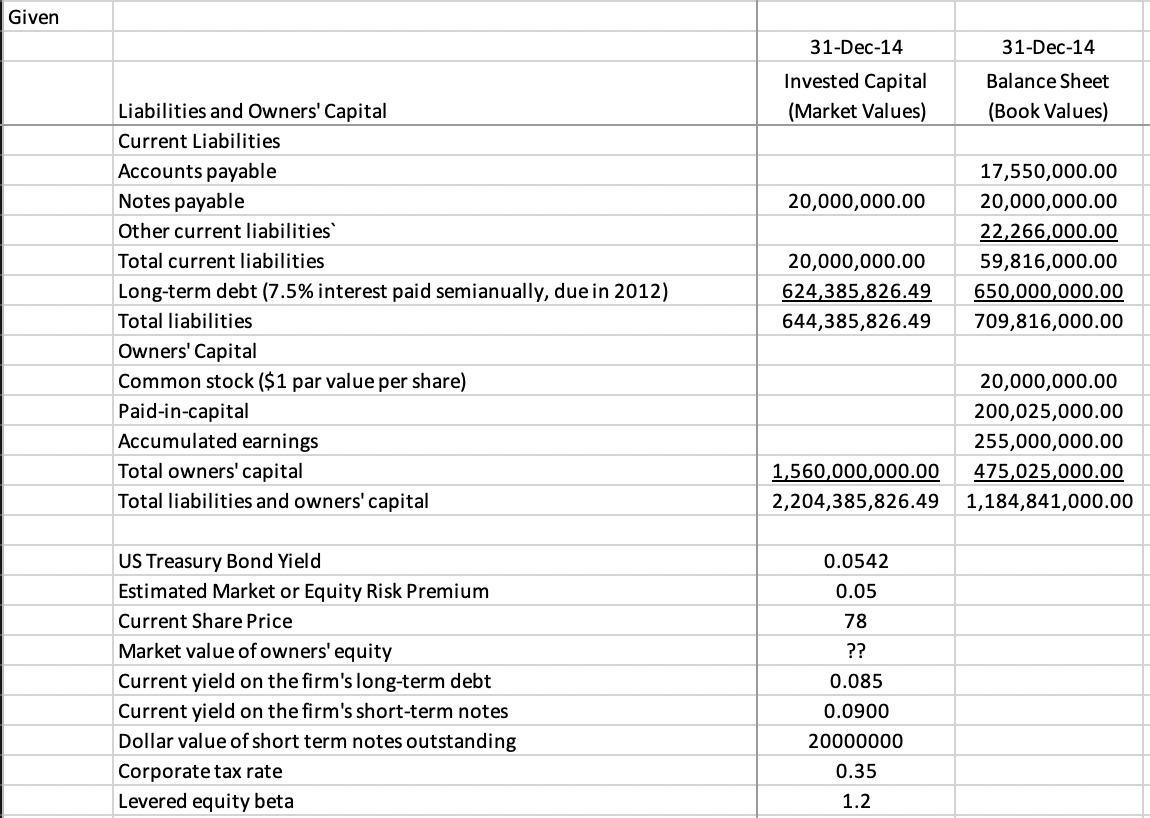
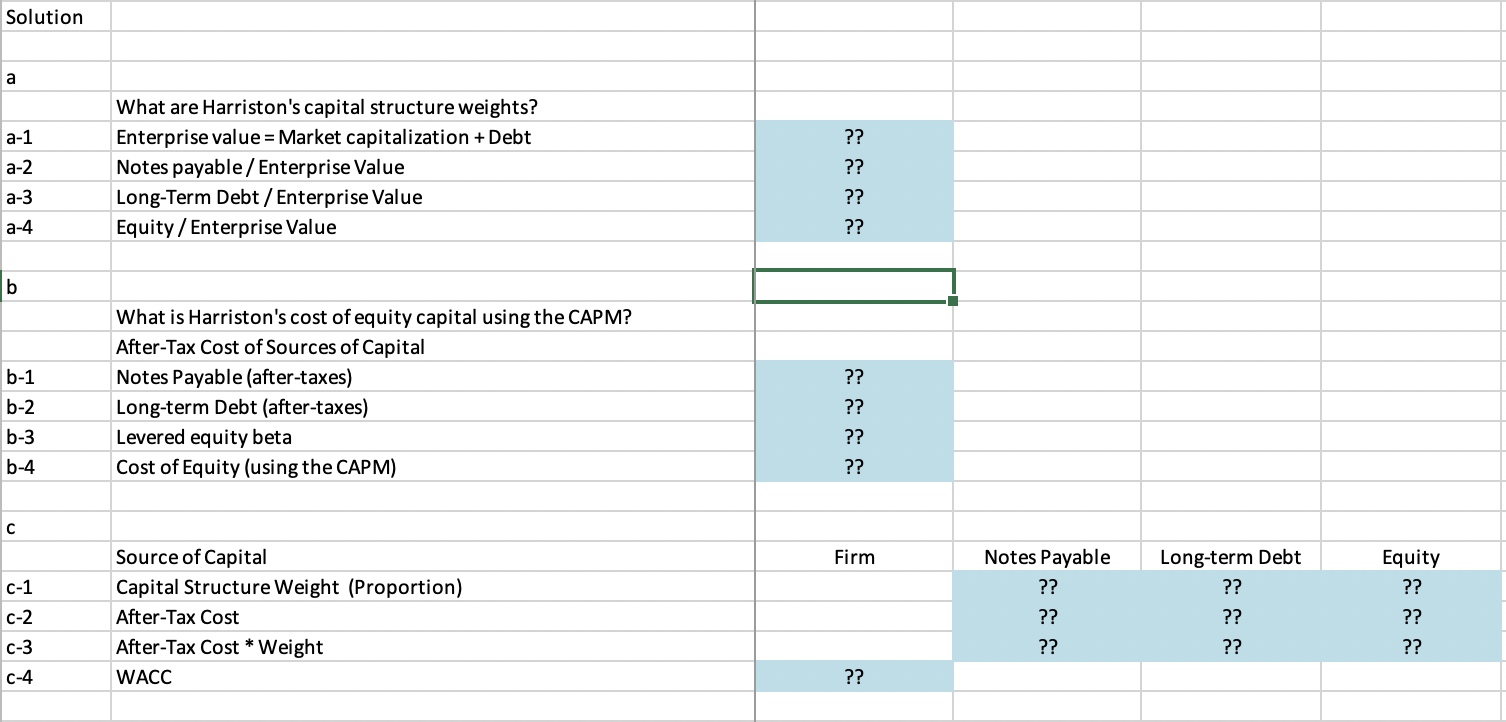
Given 31-Dec-14 31-Dec-14 Invested Capital (Market Values) Balance Sheet (Book Values) 20,000,000.00 Liabilities and Owners' Capital Current Liabilities Accounts payable Notes payable Other current liabilities Total current liabilities Long-term debt (7.5% interest paid semianually, due in 2012) Total liabilities Owners' Capital Common stock ($1 par value per share) Paid-in-capital Accumulated earnings Total owners' capital Total liabilities and owners' capital 17,550,000.00 20,000,000.00 22,266,000.00 59,816,000.00 650,000,000.00 709,816,000.00 20,000,000.00 624,385,826.49 644,385,826.49 20,000,000.00 200,025,000.00 255,000,000.00 475,025,000.00 1,184,841,000.00 1,560,000,000.00 2,204,385,826.49 US Treasury Bond Yield Estimated Market or Equity Risk Premium Current Share Price Market value of owners' equity Current yield on the firm's long-term debt Current yield on the firm's short-term notes Dollar value of short term notes outstanding Corporate tax rate Levered equity beta 0.0542 0.05 78 ?? 0.085 0.0900 20000000 0.35 1.2 Solution a a-1 a-2 What are Harriston's capital structure weights? Enterprise value = Market capitalization + Debt Notes payable / Enterprise Value Long-Term Debt / Enterprise Value Equity / Enterprise Value ?? ?? ?? ?? a-3 a-4 b b-1 b-2 What is Harriston's cost of equity capital using the CAPM? After-Tax Cost of sources of Capital Notes Payable (after-taxes) Long-term Debt (after-taxes) Levered equity beta Cost of Equity (using the CAPM) ?? ?? ?? ?? b-3 b-4 Firm C-1 C-2 Source of Capital Capital Structure Weight (Proportion) After-Tax Cost After-Tax Cost * Weight WACC Notes Payable ?? ?? ?? Long-term Debt ?? ?? ?? Equity ?? ?? ?? C-3 C-4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


